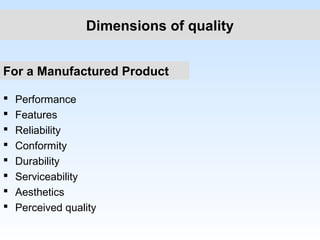
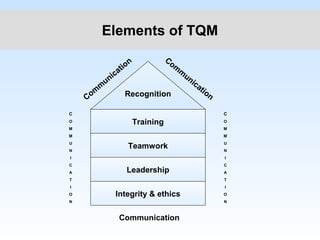
India lags behind other industrialized nations in quality and competitiveness due to its antiquated production systems and high rejection rates. Most Indian plants struggle to achieve rejection rates under 5%, whereas Motorola achieved a defect-free rate of 99.99997%. To remain competitive in global markets with demands for mass customization, Indian companies must improve quality practices like other major corporations. Total quality is no longer optional but essential to long-term business success through customer satisfaction at lower costs.