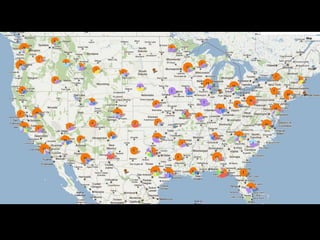
This document provides information about touring motor gliders (TMGs) presented by Richard Pearl and Michael Haisten. It discusses what a TMG is, legal issues, the types of TMGs throughout history from classic to modern models. It also covers mechanical components like engines, propellers, and additional systems required. The document concludes with discussing what's new with the Touring Motor Glider Association and their goals of gaining formal status within the Soaring Society of America and organizing fly-ins, contests, and international participation.