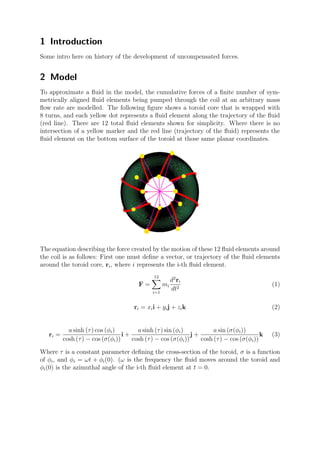
This document describes a model of a fluidic toroidal drive. The model develops parametric equations to define the wrapping of a toroidal core and uses Newtonian mechanics to calculate the forces induced on the core from the symmetrical flow of fluid elements around it. For certain numbers of turns in the wrapping, an uncompensated thrust is produced that could enable propulsion. Figures 1-3 show contours of the x, y, and z directional forces on the core over time for different numbers of turns in the wrapping using 500 fluid elements in the simulation.