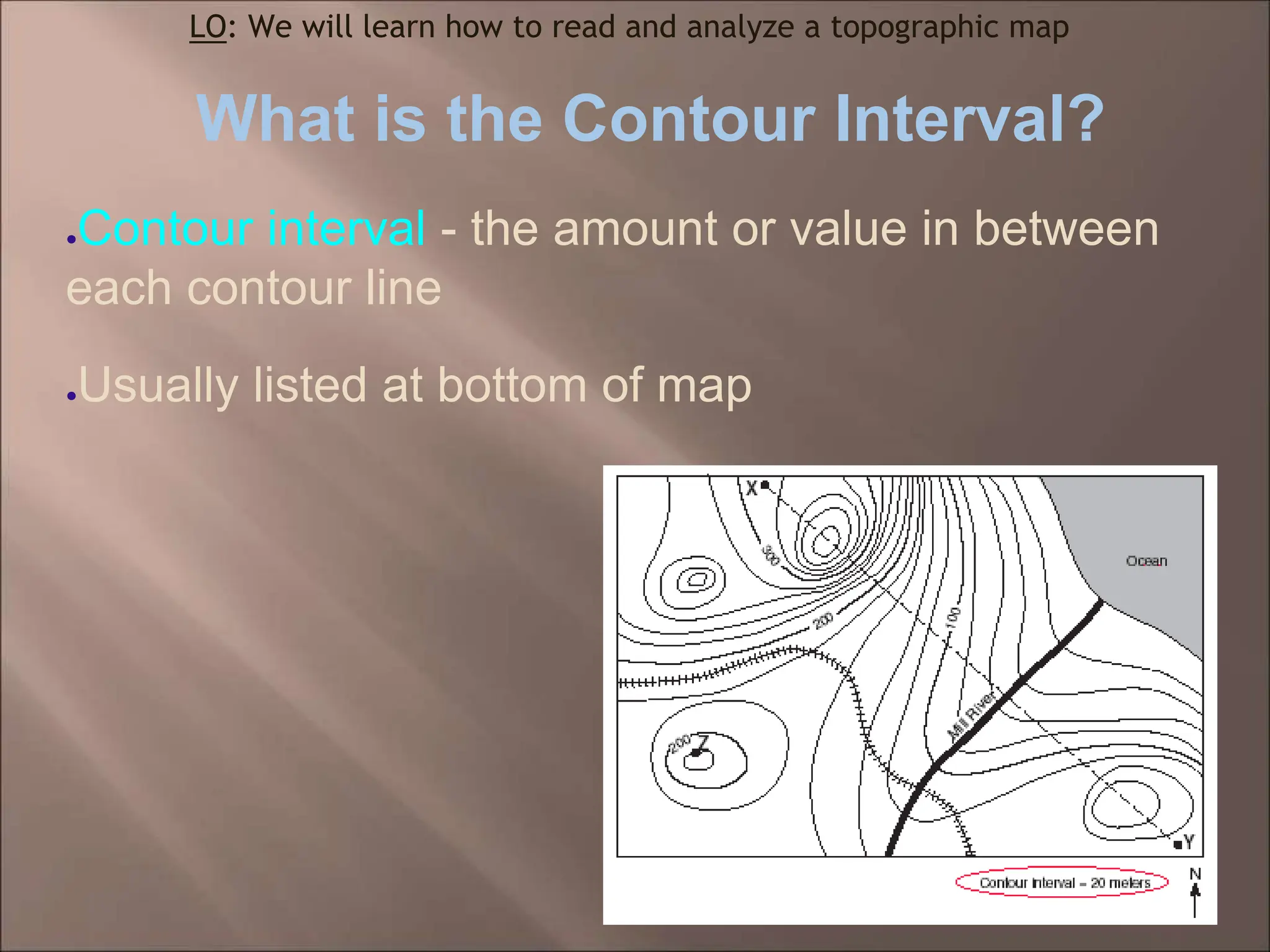
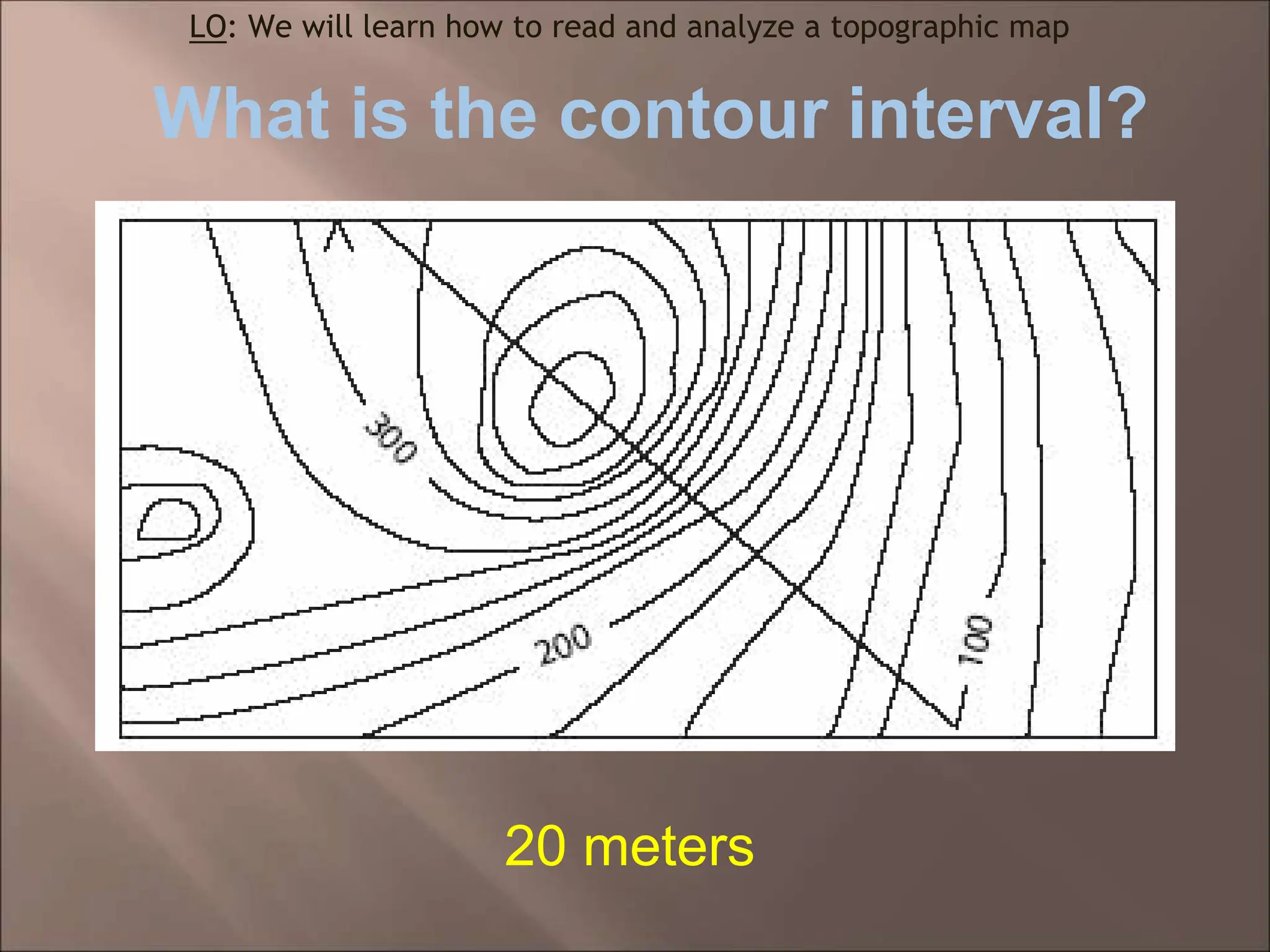
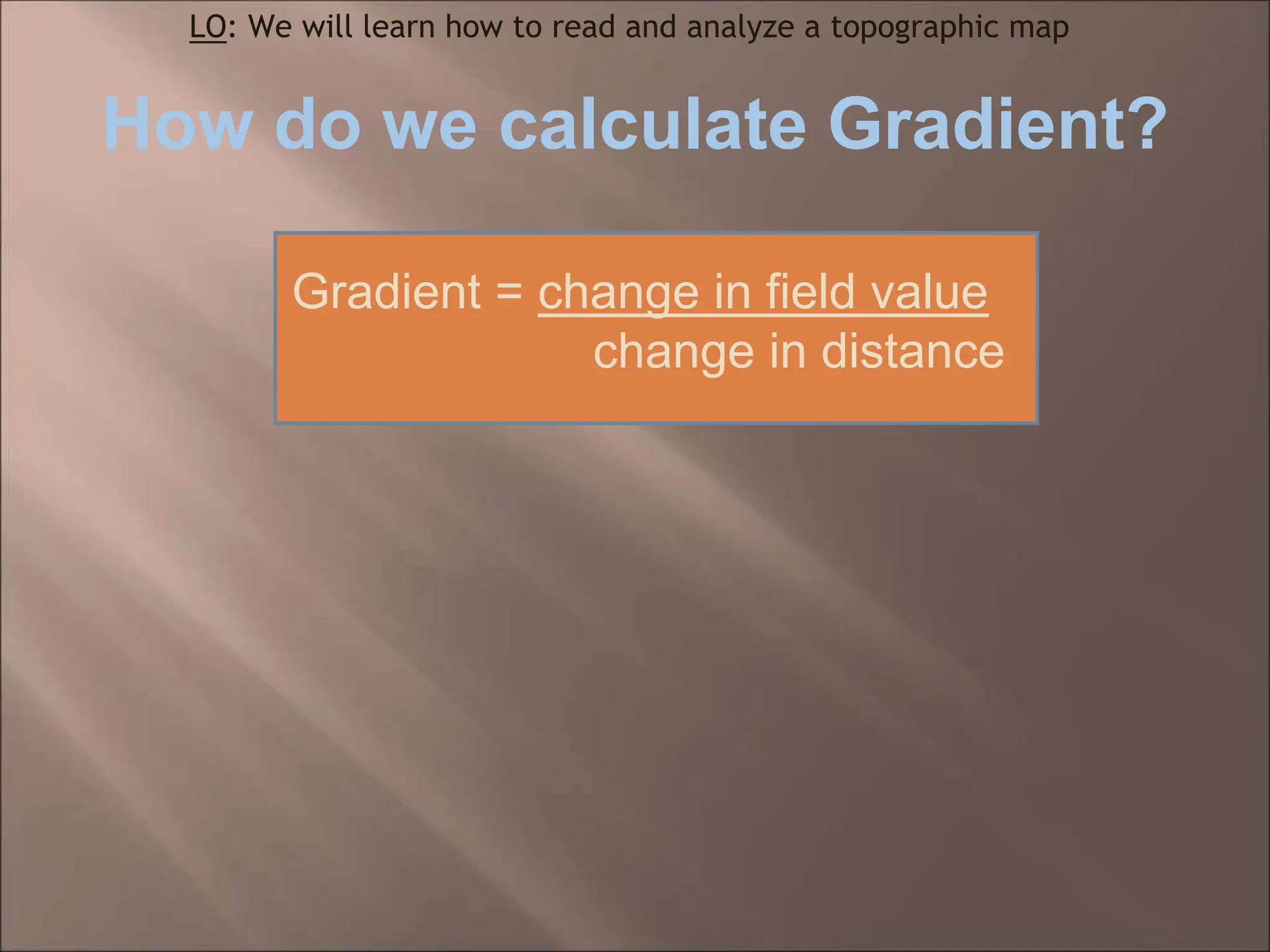
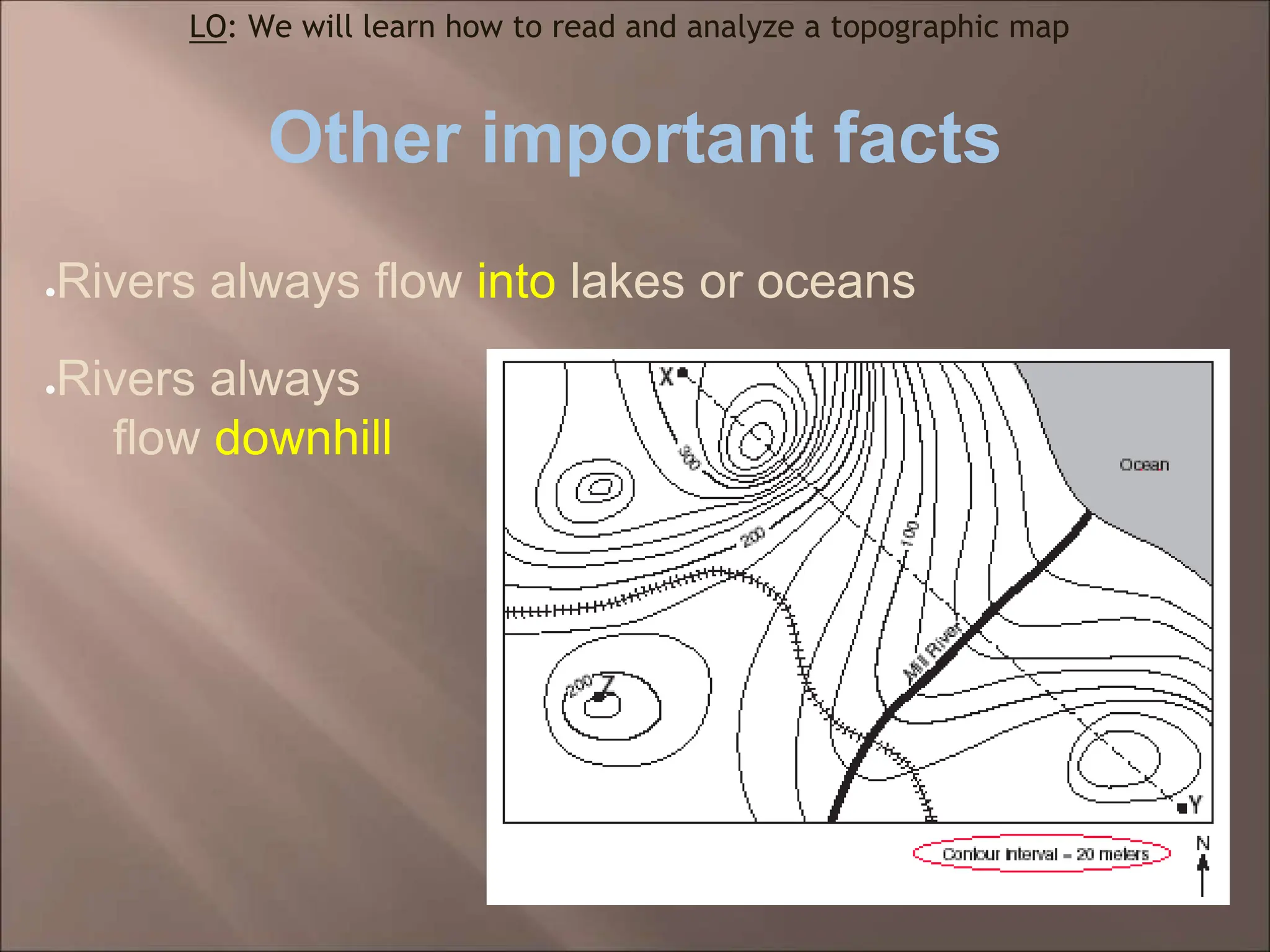
The document discusses topographic maps and how to read them. It defines a topographic map as a map that shows elevation, and explains that contour lines connect points of equal elevation. It describes how to calculate gradient by finding the change in elevation over the change in distance between two points. It also explains how to create a topographic map profile by tracing contour lines to show what the landscape would look like if viewed directly.