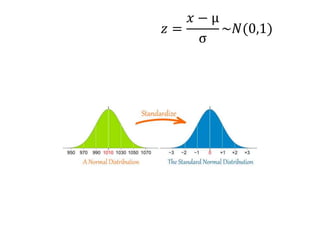
The document discusses the standard normal distribution and provides examples of calculating probabilities and number of occurrences given a normal distribution. It begins by defining the standard normal variate Z as representing the number of standard deviations a point is from the mean. It then provides 10 problems as examples, such as calculating the number of students over a certain height given the mean and standard deviation of student heights, or the probability of a value falling within an interval of a normal distribution.