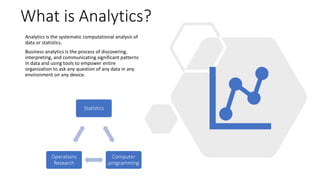
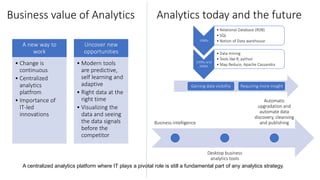
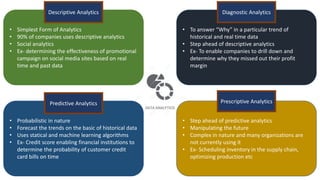
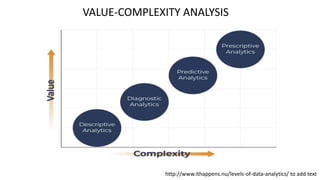
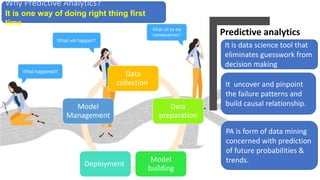
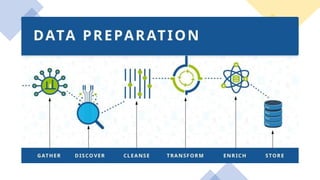
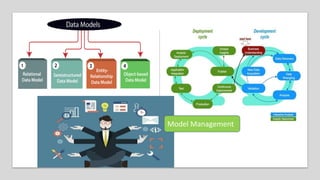
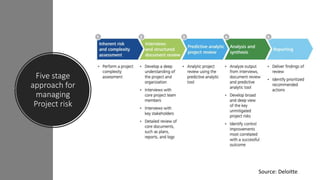
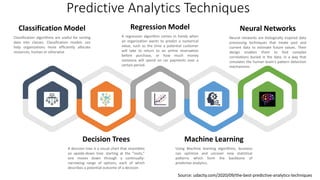
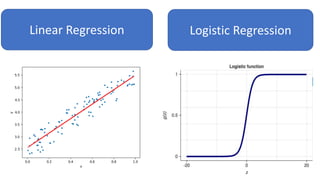
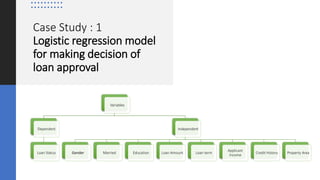
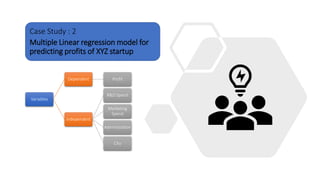
The document discusses tools and techniques for predictive analytics in project risk management, emphasizing the importance of data analytics as a systematic approach to understanding and utilizing data for better decision-making. It outlines various types of analytics, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive, along with examples and applications in project management. The text also highlights the benefits of predictive analytics, such as improved monitoring and increased project success rates, and presents case studies on using regression models for decision-making.