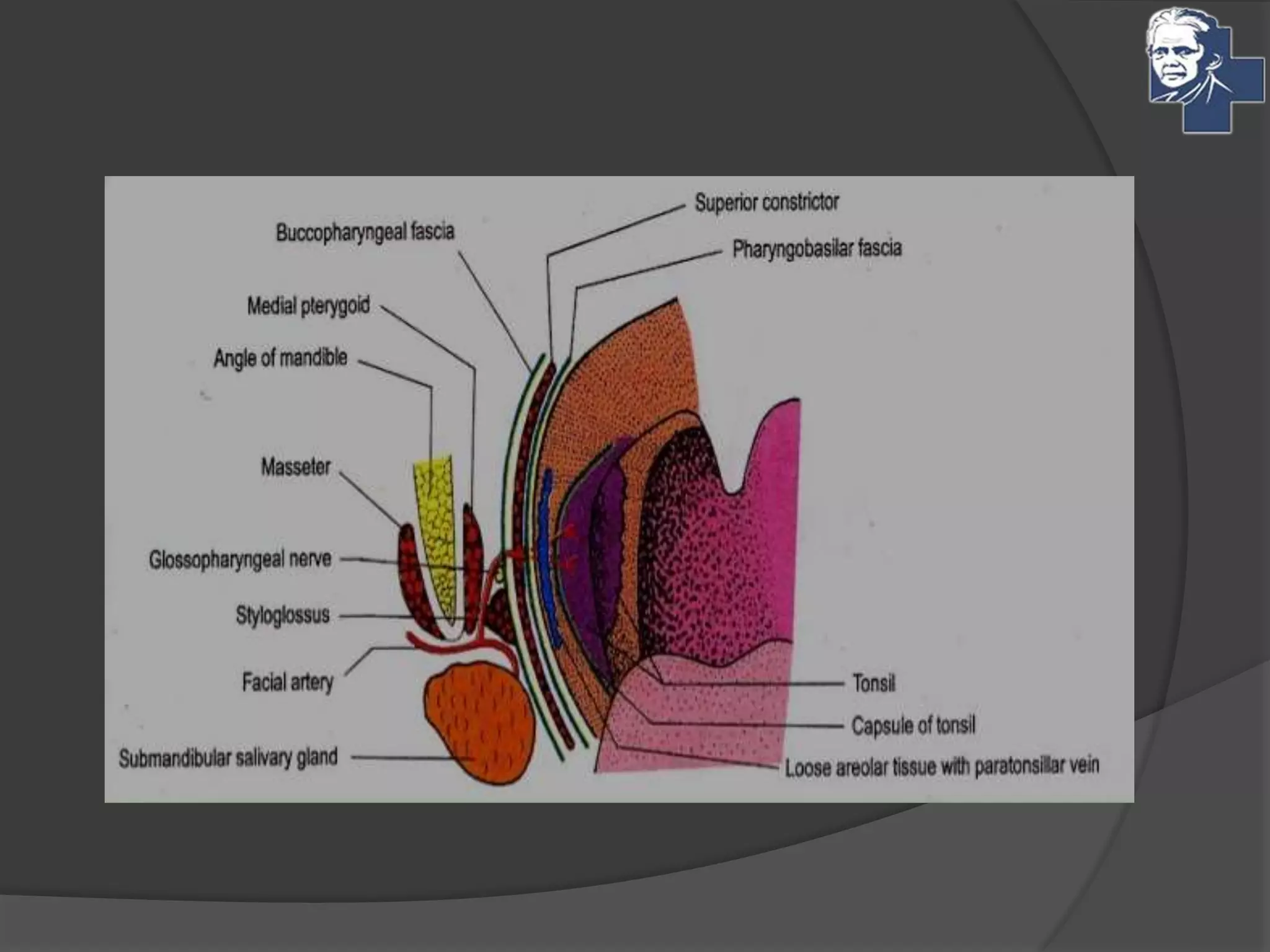
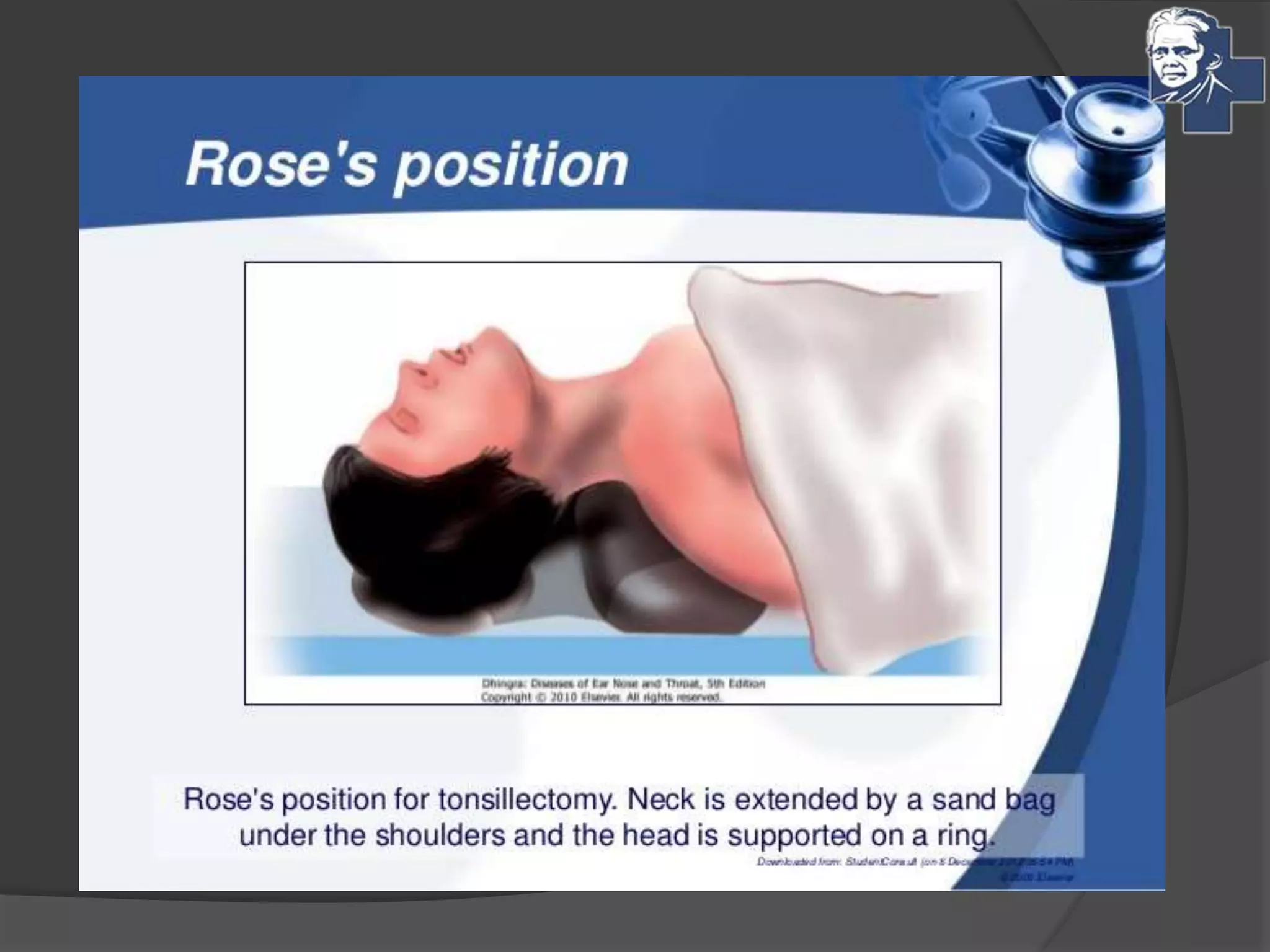
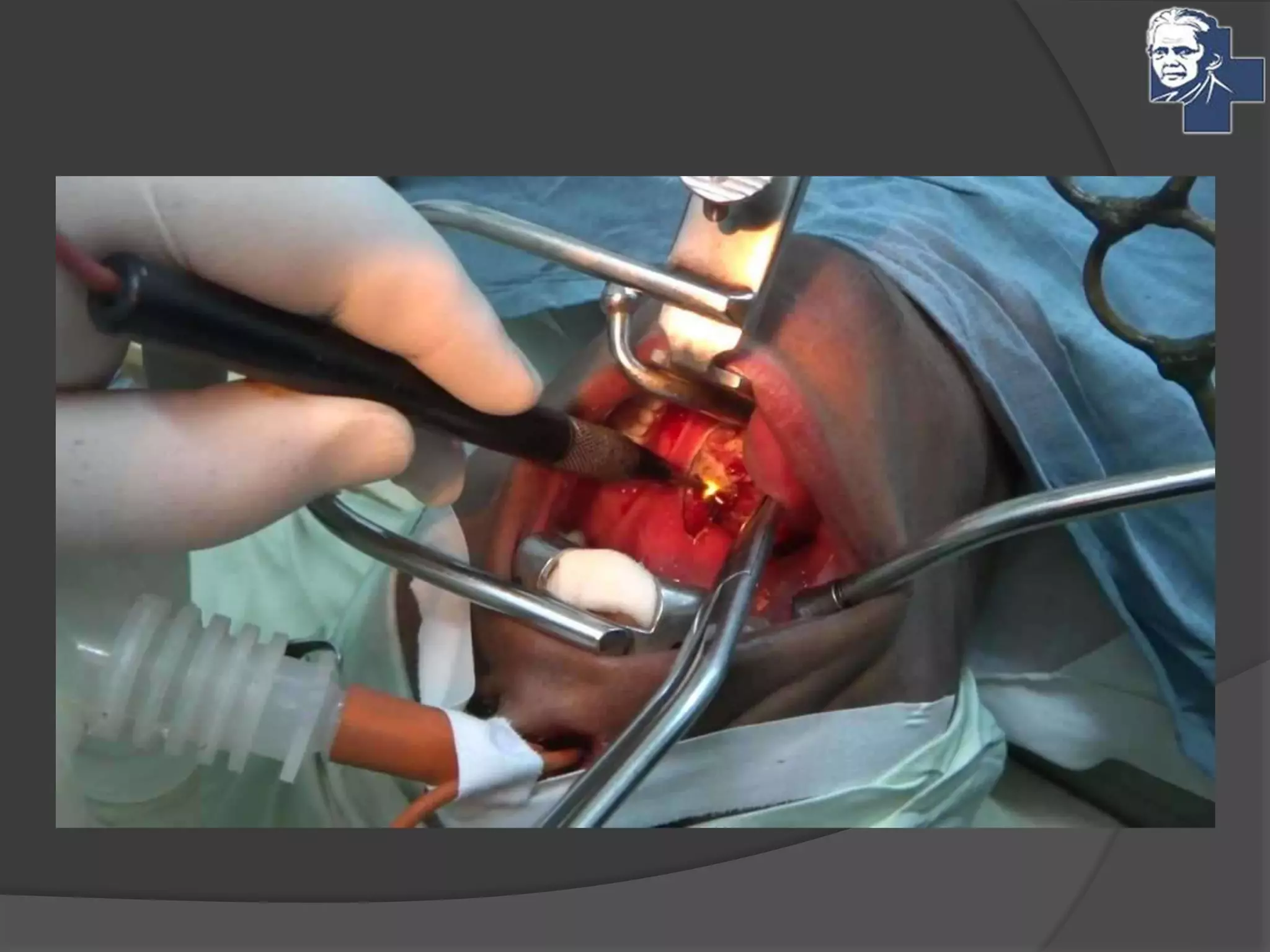
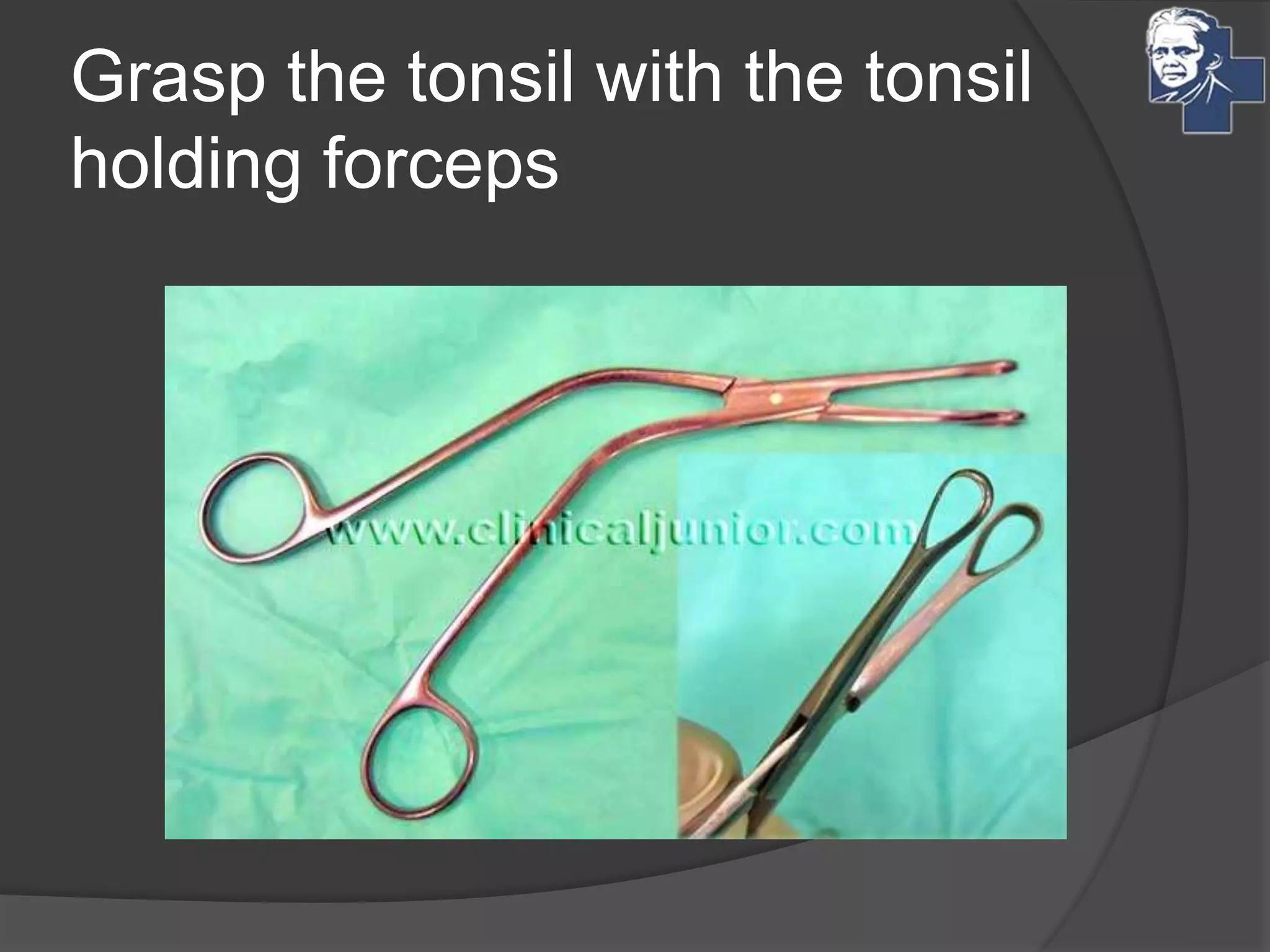
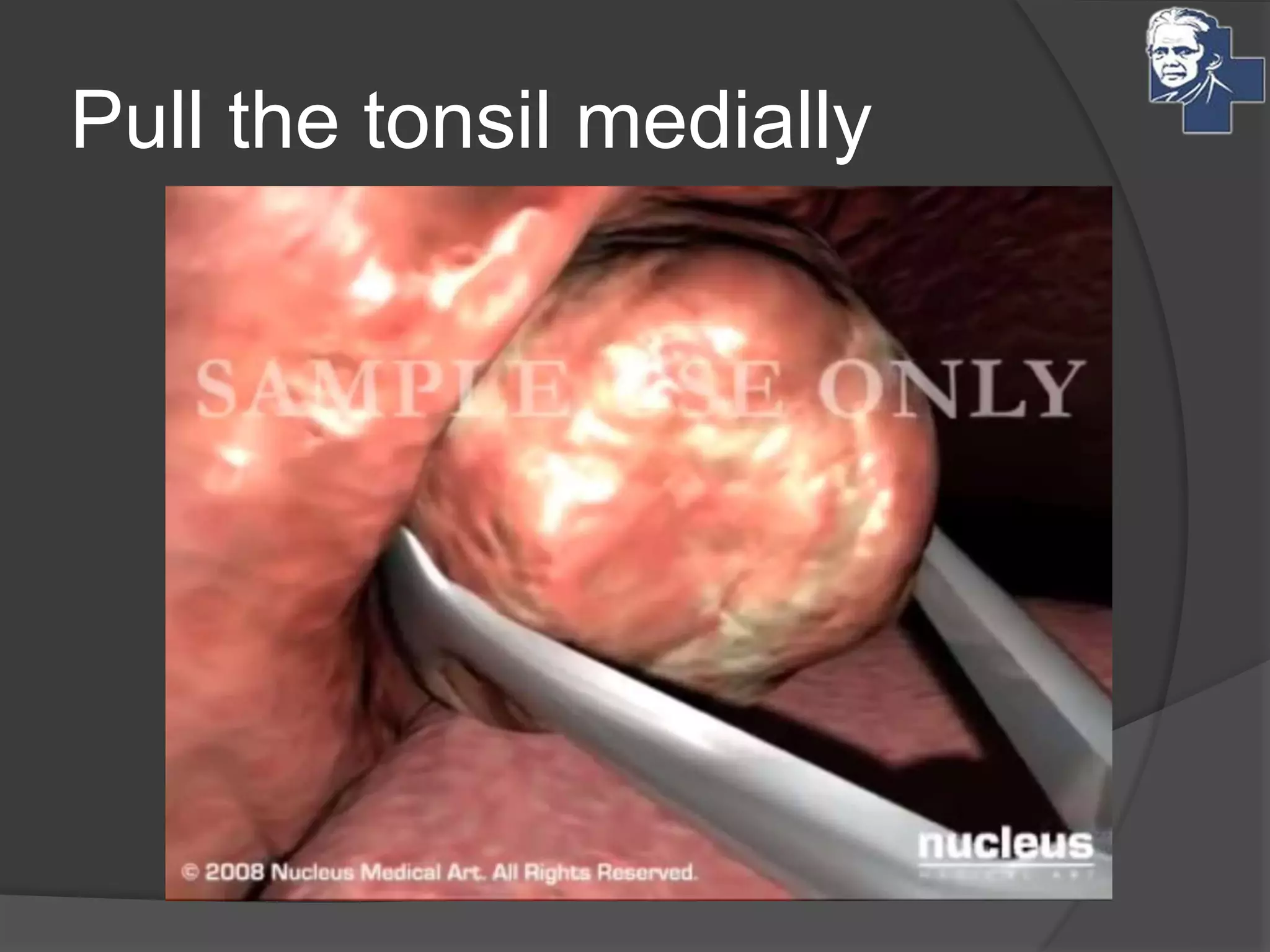
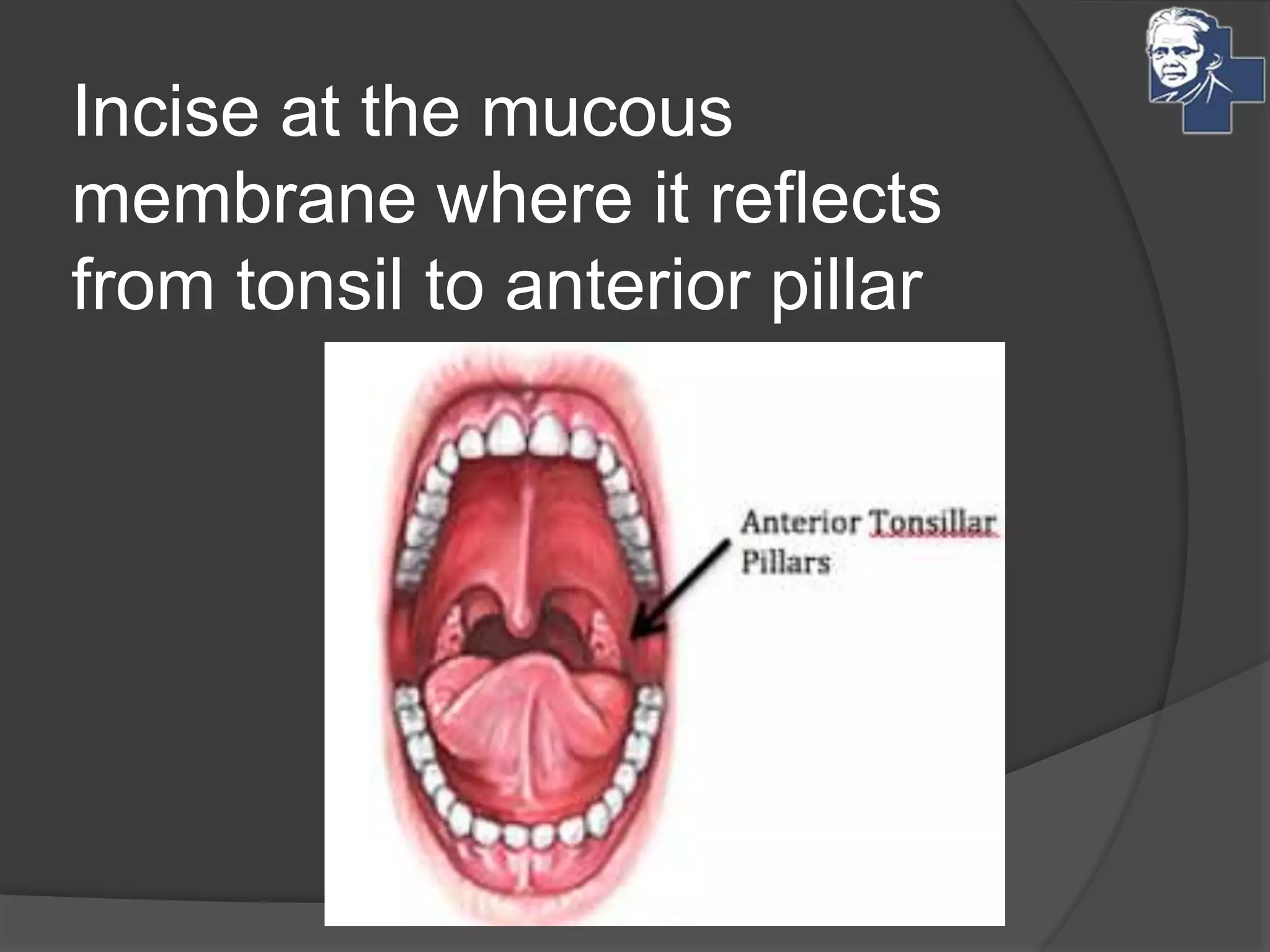
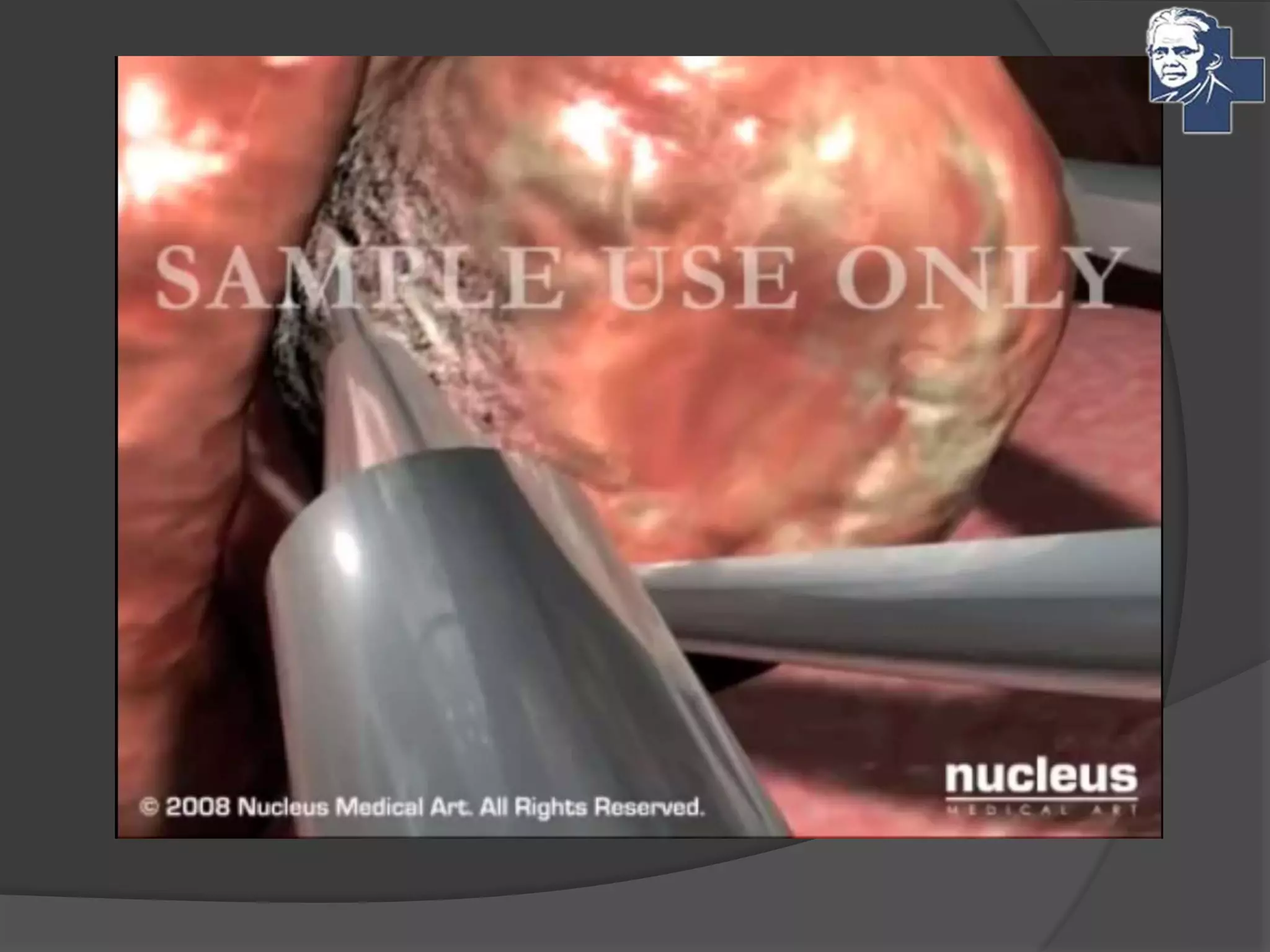
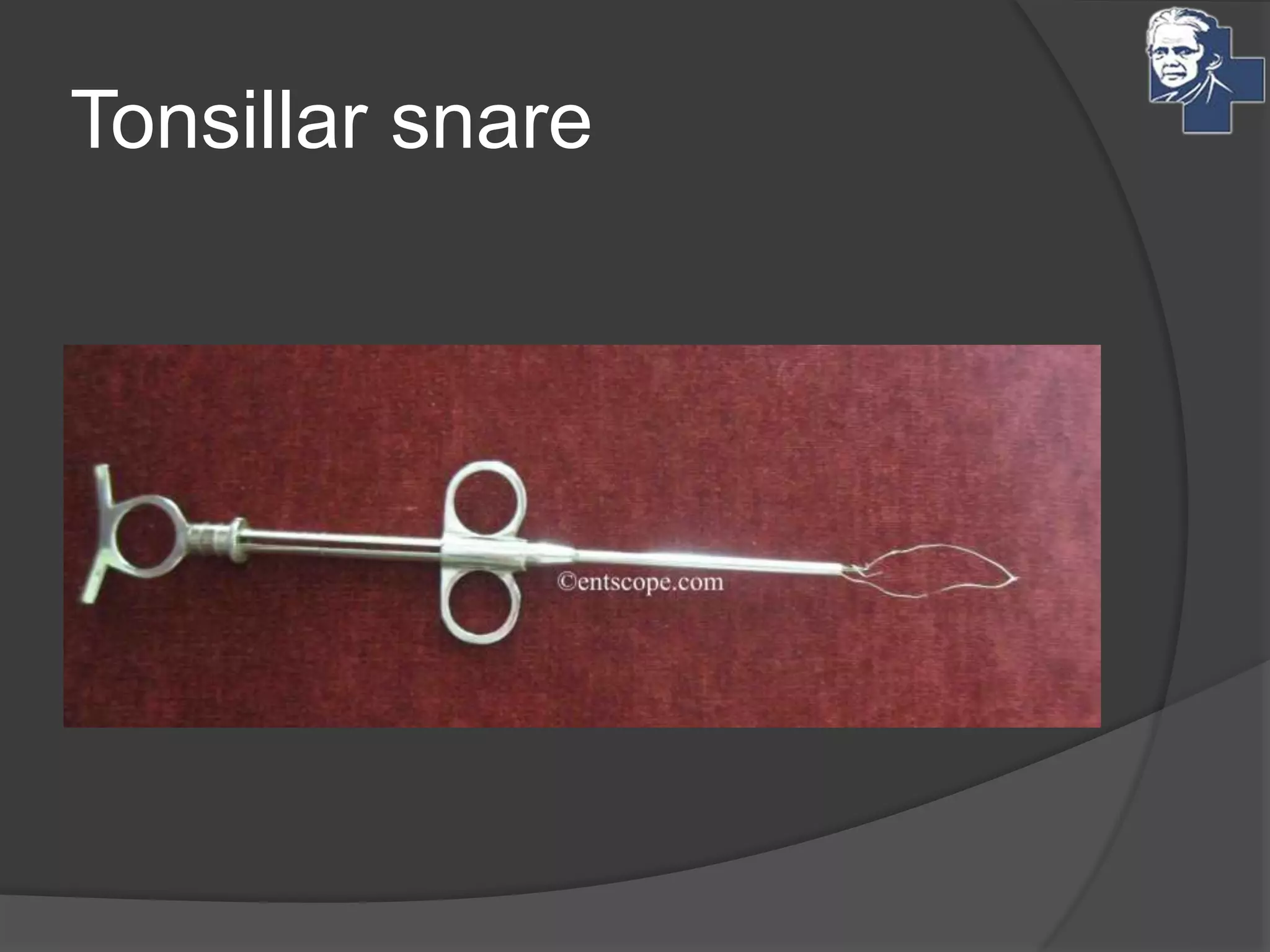
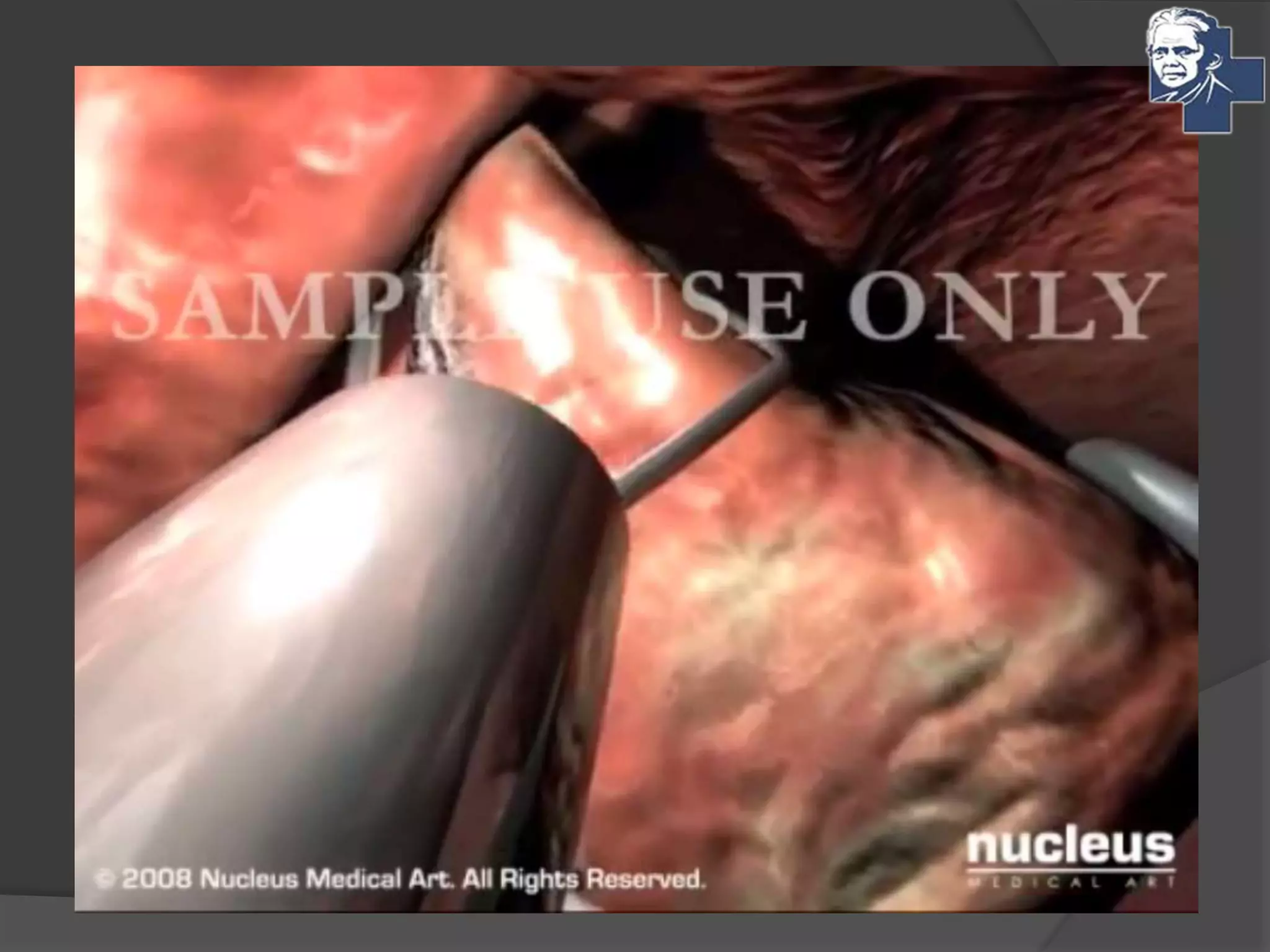
This document discusses the management of tonsillitis, including both medical and surgical options. Surgical management involves tonsillectomy, which has absolute indications like recurrent infections or peritonsillar abscess, and relative indications such as being a carrier. Contraindications include anemia or bleeding disorders. The dissection and snare method is described, involving using a mouth gag, grasping the tonsil and cutting it out with a snare. Post-operative care involves a liquid diet, salt water gargles and analgesics. Other techniques like cold methods using guillotines or lasers and hot methods using electrocautery or radiofrequency are also mentioned.