1. The experiment aims to determine the frequency of alternating current (AC) mains using an electric vibrator. An electric vibrator, thread, pan, weight box, frictionless pulley and meter scale are used.
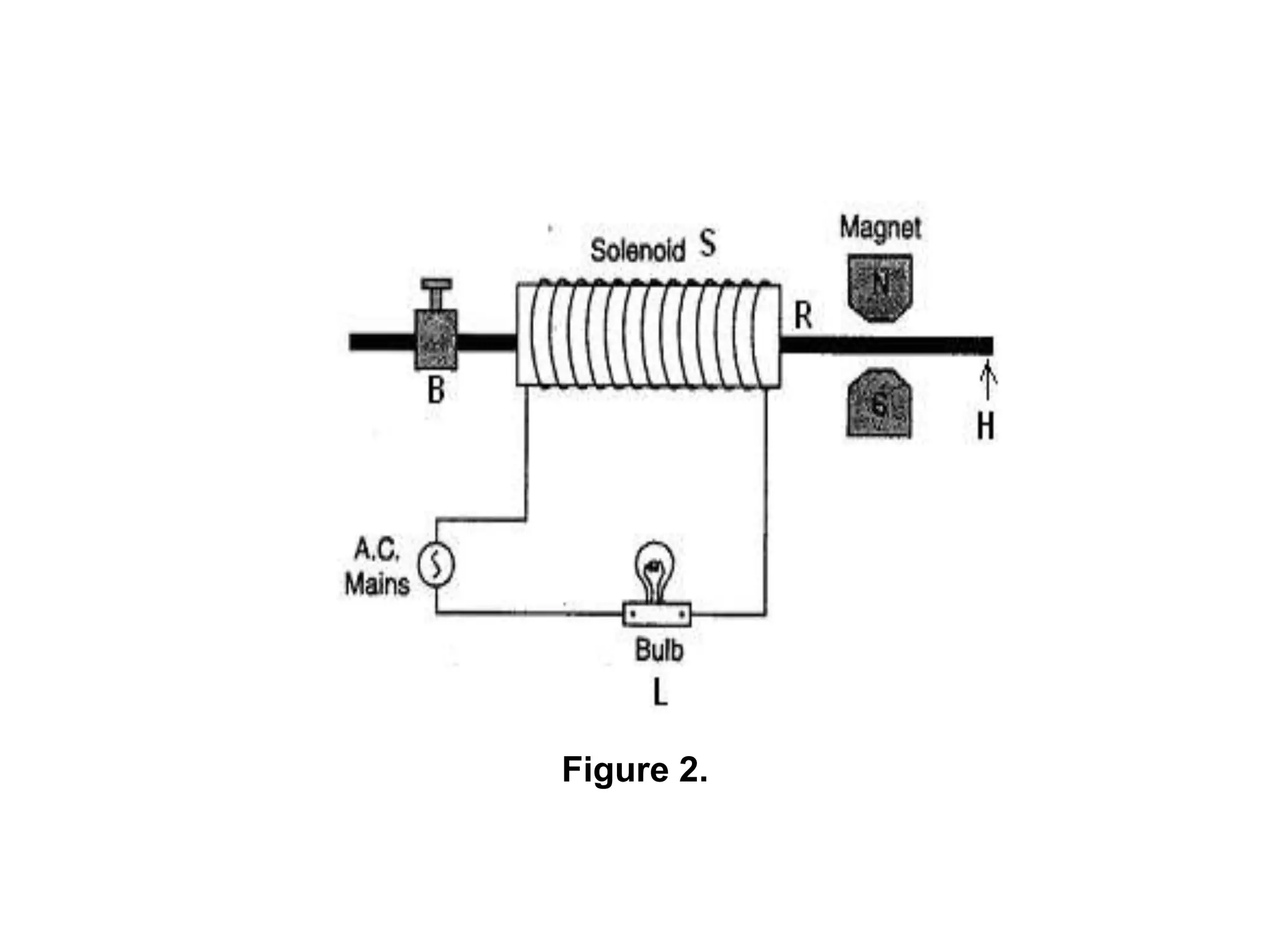
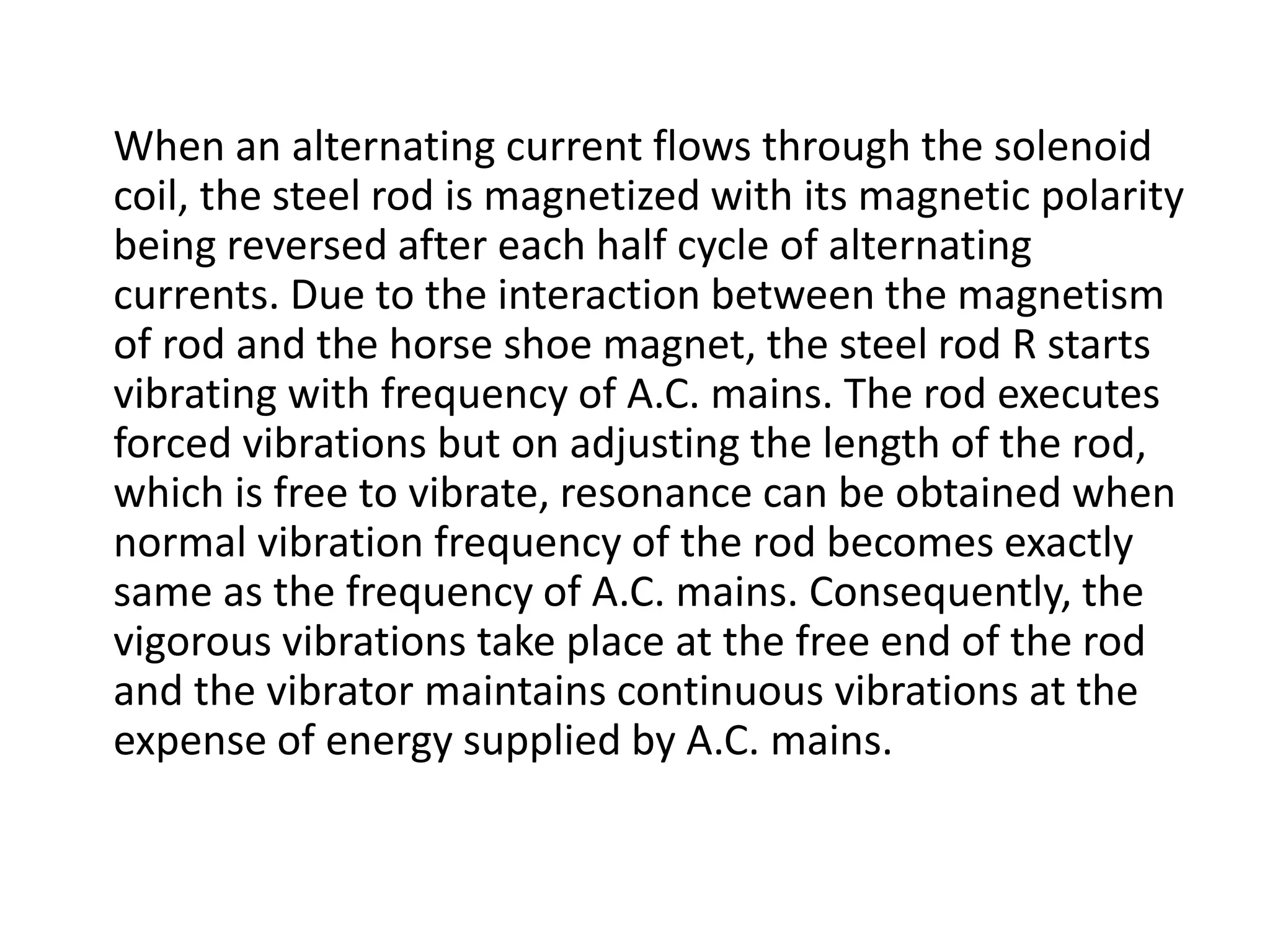
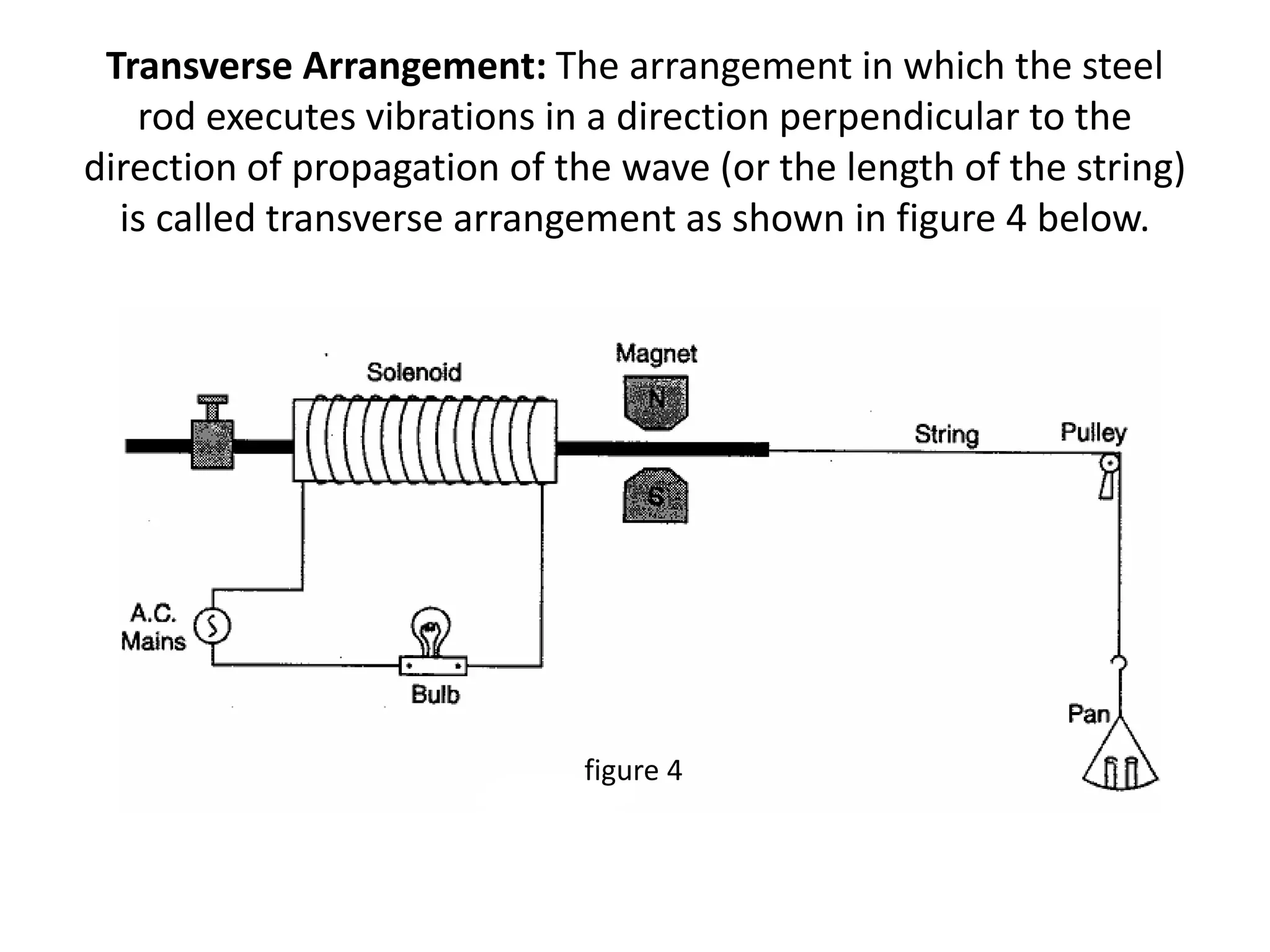
2. When alternating current passes through the solenoid coil of the electric vibrator, the steel rod inside vibrates at the same frequency as the AC mains due to the interaction between the rod's magnetism and a permanent horseshoe magnet.
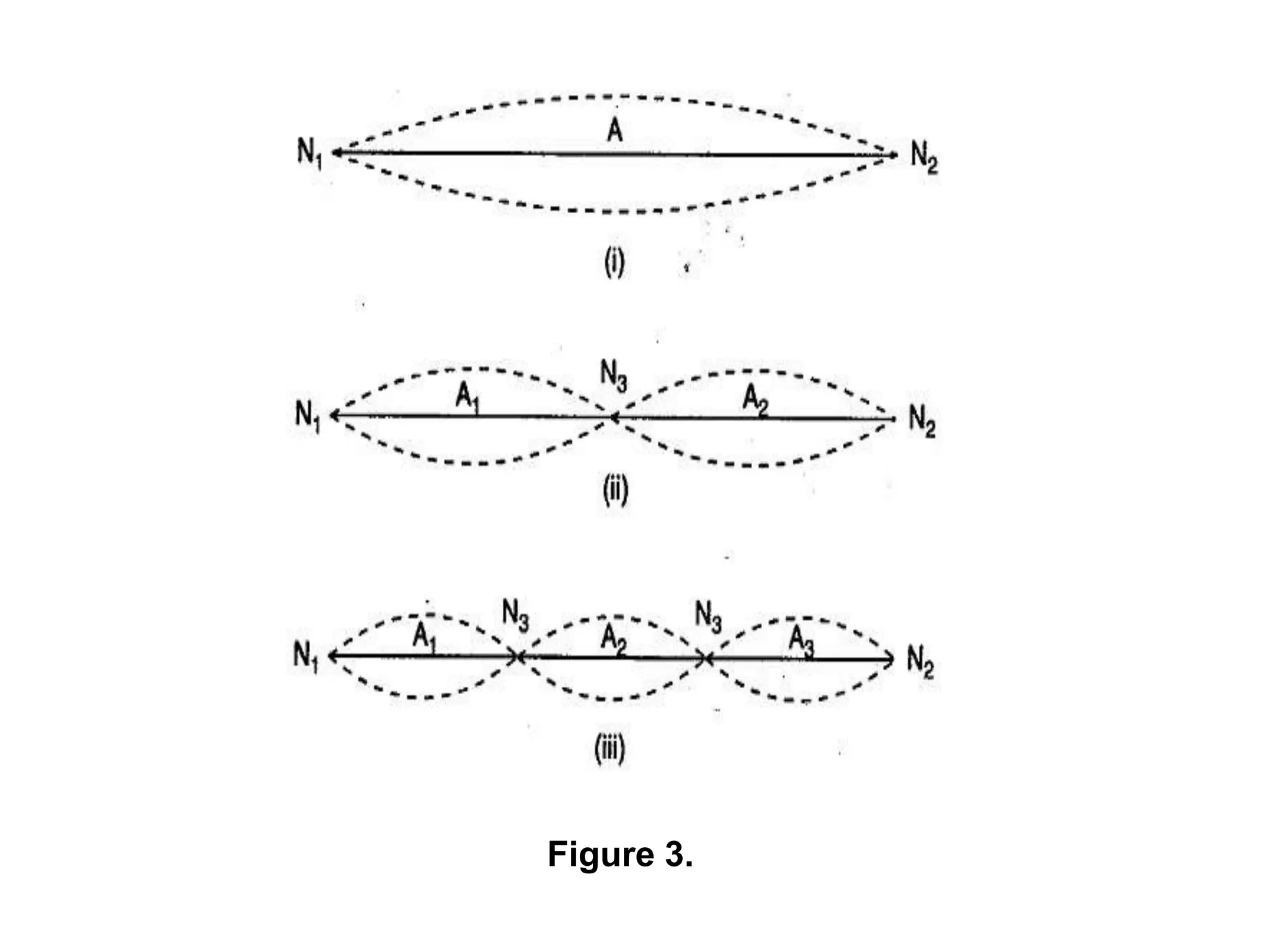
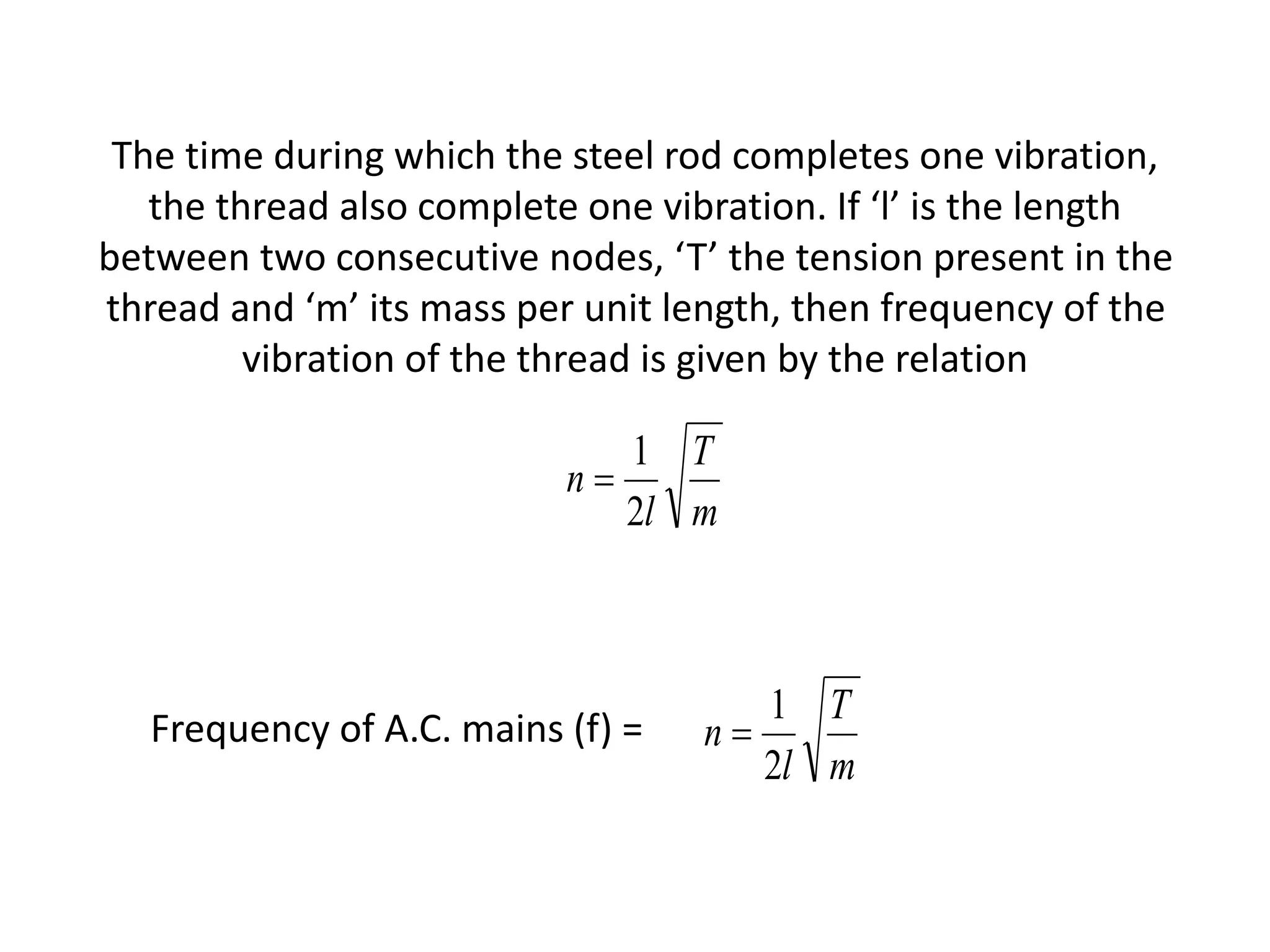
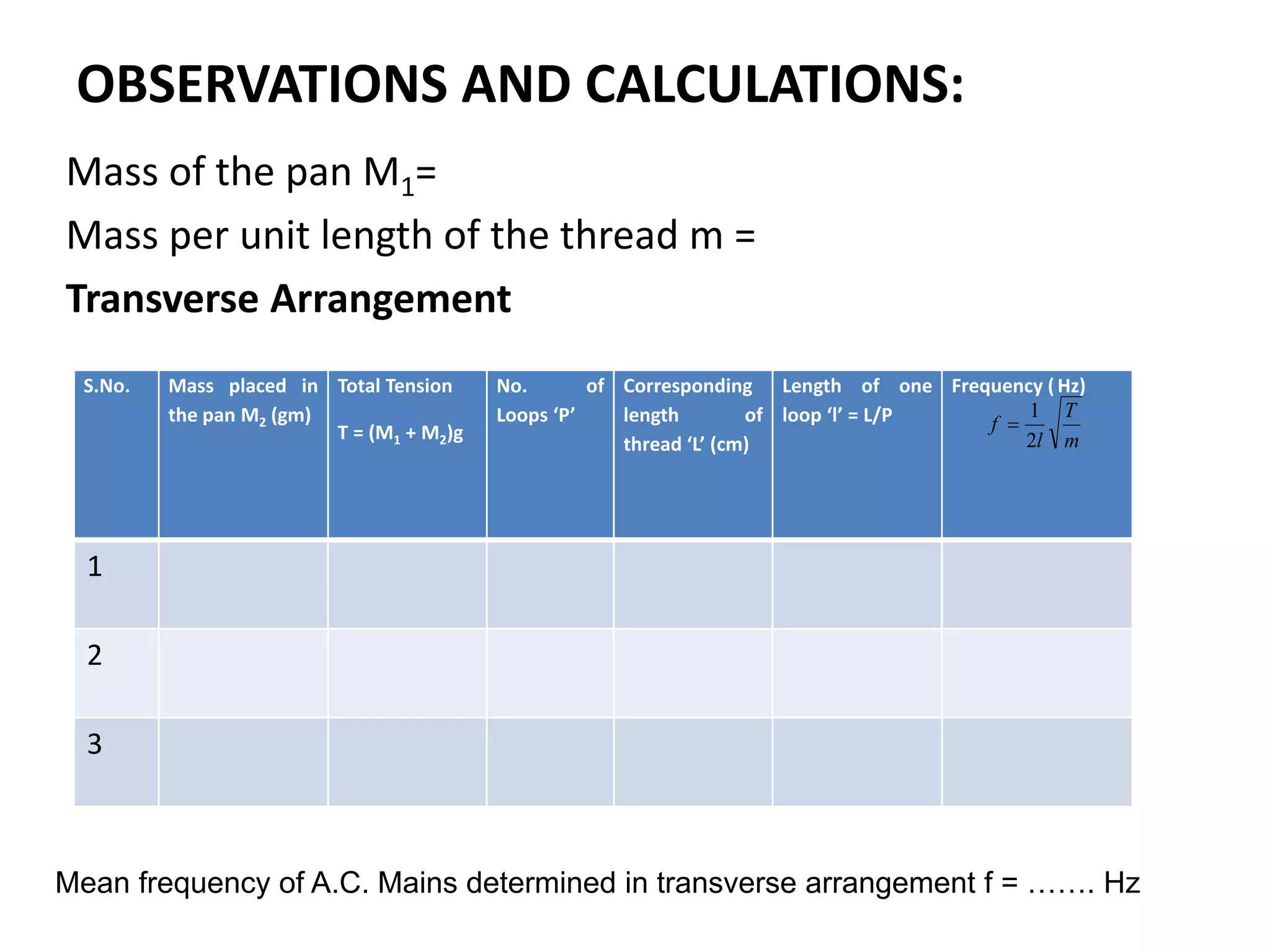
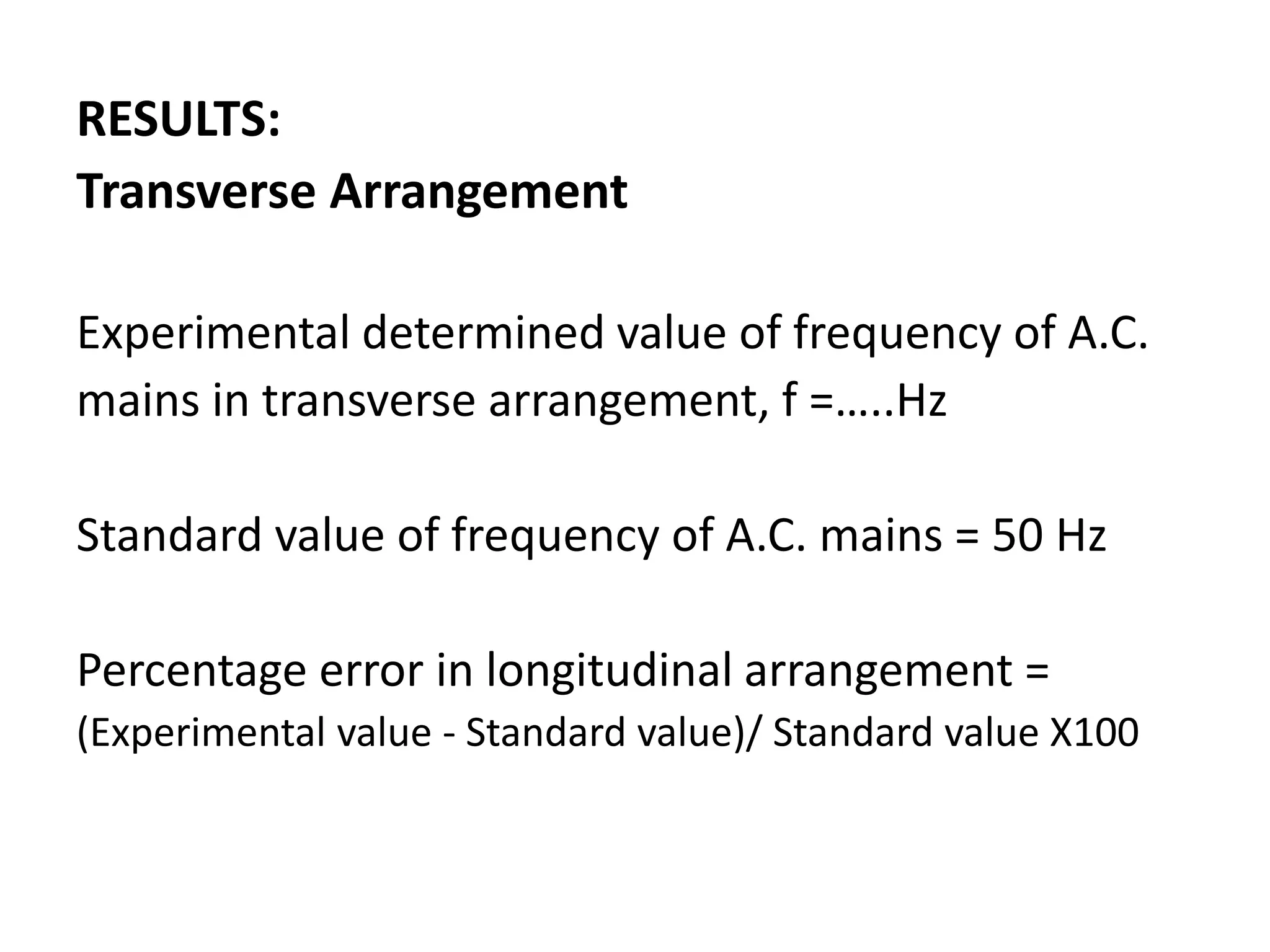
3. By adjusting the mass in the pan, the thread length is varied until resonance occurs, where the thread vibrates with a maximum amplitude at points called antinodes. Counting the number of antinodes between two nodes and