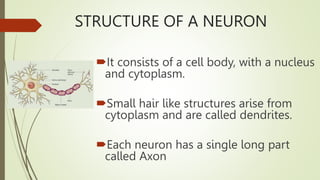
The document discusses the four main types of tissues in animals: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. It provides examples of each type of tissue and their functions. Epithelial tissue covers and protects organs, connective tissue supports and connects, muscular tissue enables movement, and nervous tissue transmits signals in the brain and body. The document also describes some subtypes of tissues and their distinctive characteristics.