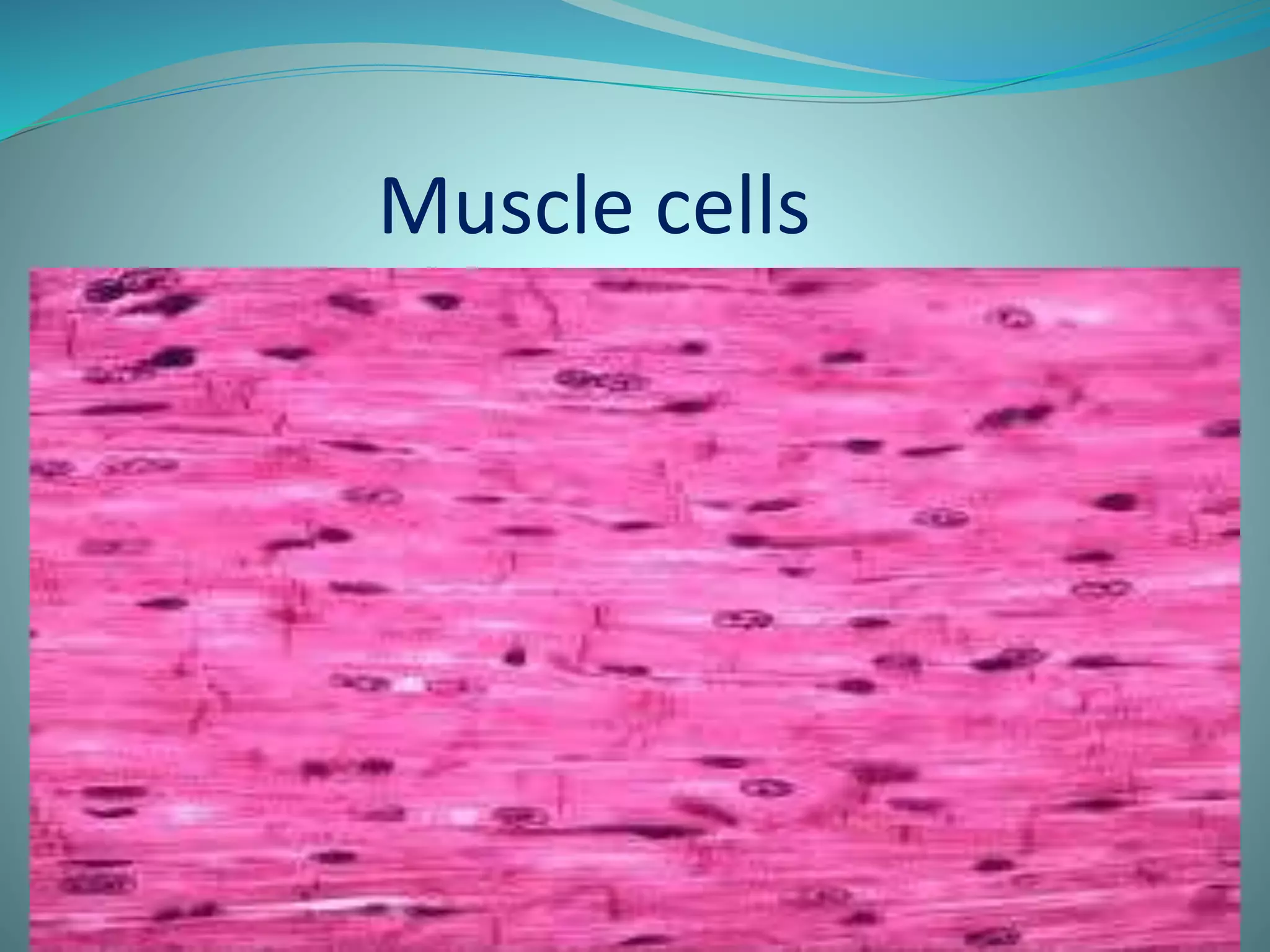
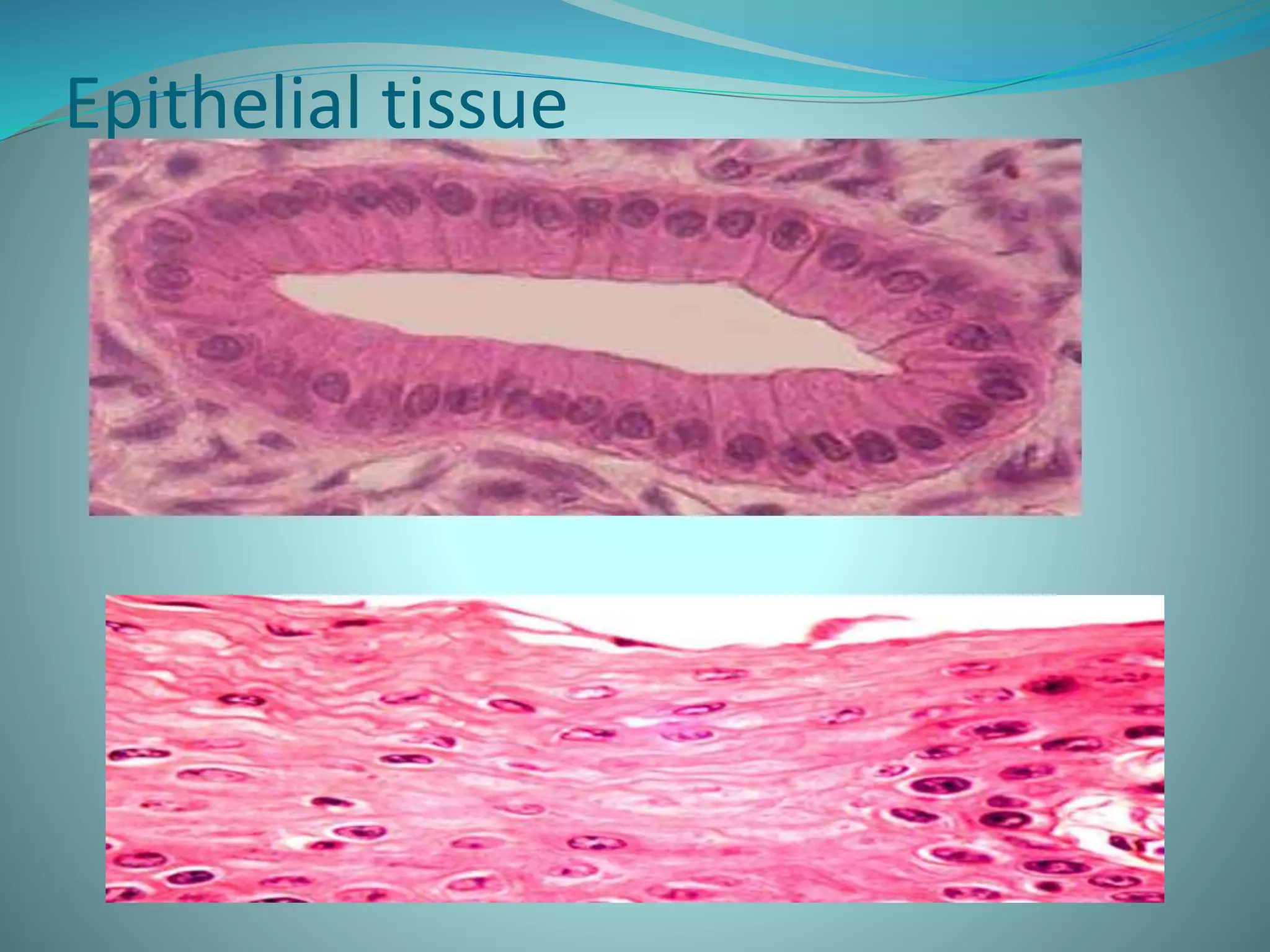
This document discusses the four main types of animal tissues: connective tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue, and epithelial tissue. Connective tissue includes cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix and provides structure and support. Muscle tissue contains three categories of muscle cells that produce movement. Nervous tissue forms the central and peripheral nervous systems. Epithelial tissue covers organ surfaces and forms protective barriers.