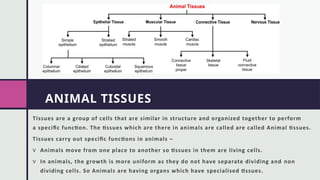
The document provides an overview of animal tissues, categorizing them into epithelial, muscular, connective, and nervous tissues, each with unique functions and structures. Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces and is involved in secretion and absorption, muscular tissue facilitates movement, connective tissue supports and protects the body, and nervous tissue is responsible for impulse transmission and coordination. Each type of tissue has specific characteristics and roles in overall bodily functions.