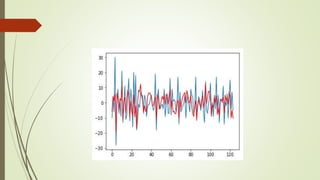
This document discusses time series forecasting. It defines a time series as observations of a variable over time and notes they are used in fields like statistics, finance, and weather forecasting. It describes the main components that influence time series as secular trends, seasonal variation, cyclical variation, and irregular variation. It provides examples of each component and how they can impact a time series. It also includes an example Python code for performing time series forecasting using an autoregressive model.






![Example
from pandas import Series
from matplotlib import pyplot
from statsmodels.tsa.ar_model import AR
from sklearn.metrics import
mean_squared_error
import numpy
# create a difference transform of the dataset
def difference(dataset):
diff = list()
for i in range(1, len(dataset)):
value = dataset[i] - dataset[i - 1]
diff.append(value)
return numpy.array(diff)
def predict(coef, history):
# Make a prediction give regre
yhat = coef[0]
for i in range(1, len(coef)):
yhat += coef[i] * history[-i]
return yhat
series = Series.from_csv('daily-total-female-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timeserialforcasting-190430123430/85/Time-serial-forcasting-7-320.jpg)