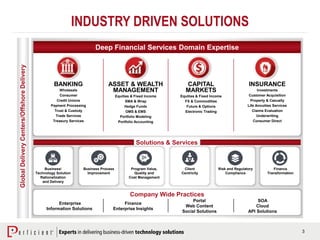
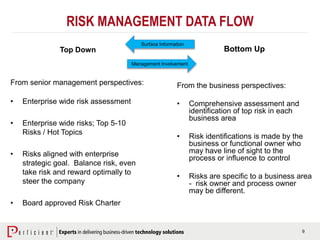
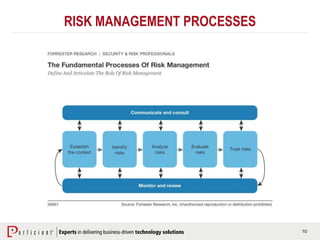
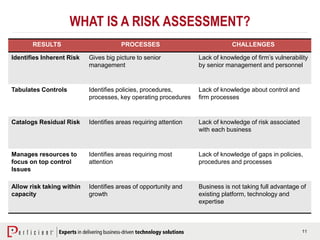
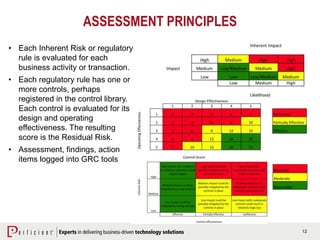
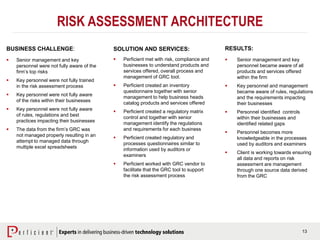
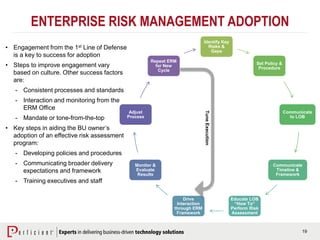
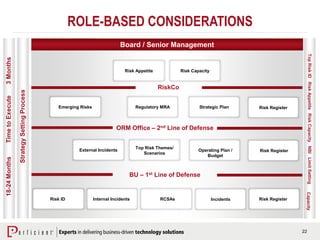
The document discusses the importance of operational risk management in financial services, emphasizing the need for effective risk identification, data aggregation, and leveraging risk intelligence for strategic decision-making. It outlines the role of senior management in ensuring compliance with regulations, fostering a strong risk culture, and optimizing organizational processes to enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, it details the steps taken by Perficient to assist clients in improving their operational risk frameworks and achieving better risk management outcomes.