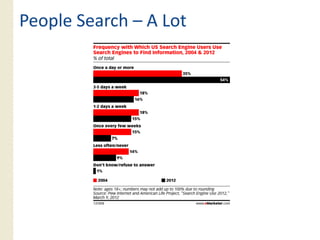
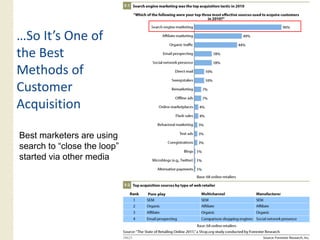
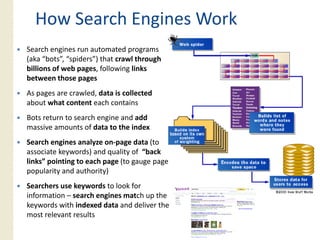
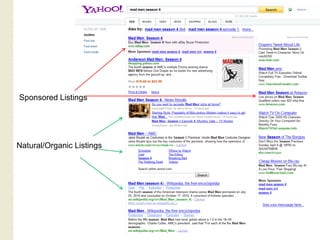
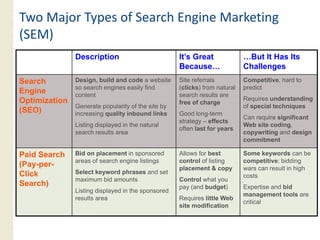
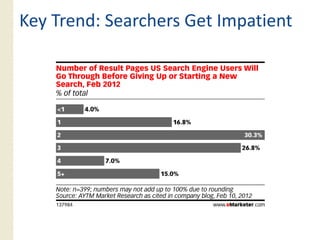
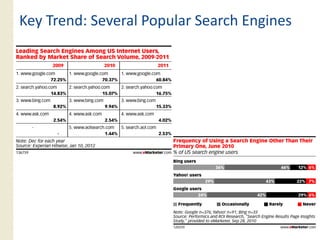
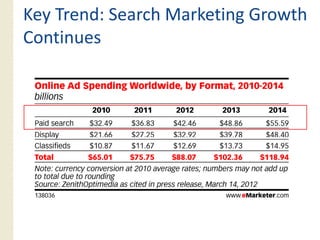
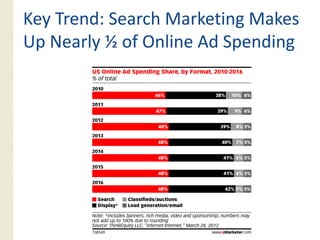
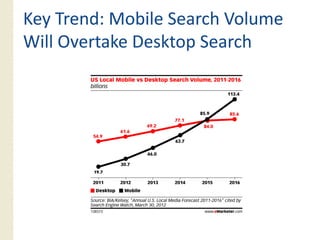
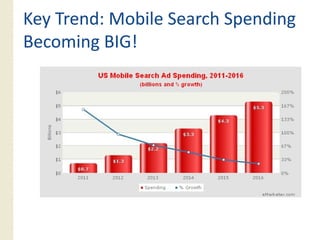
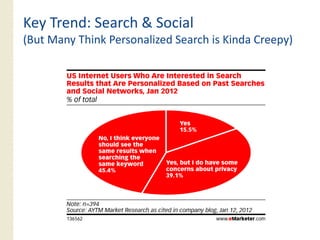
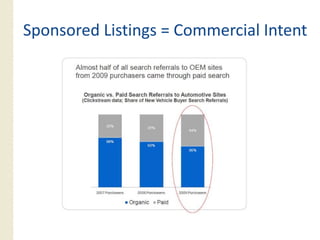
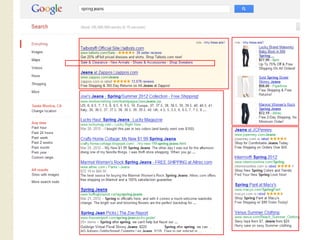
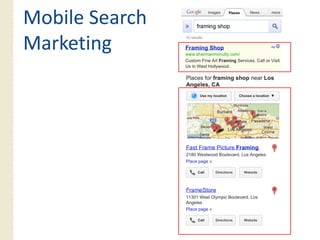
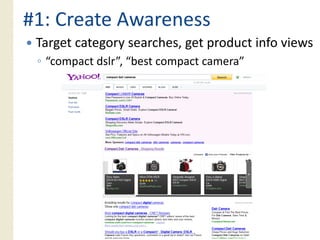
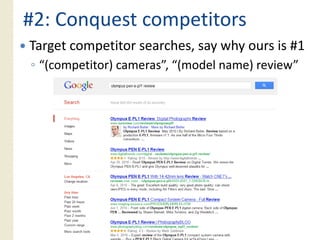
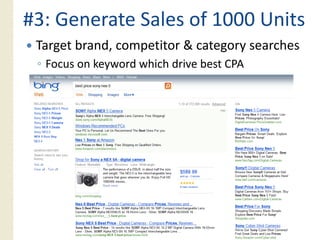
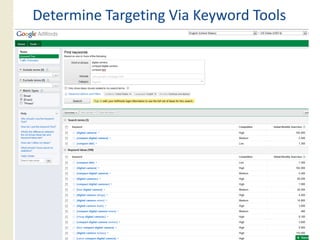
This document provides an overview of search marketing and search engine optimization (SEO). It discusses how search engines work by crawling the web and indexing pages. It also covers the two main types of search engine marketing: SEO, which involves optimizing websites for organic search results, and paid search advertising. Key trends in search such as the growth of mobile search and the relationship between search and social media are also summarized.