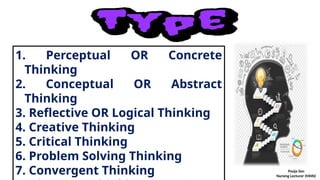
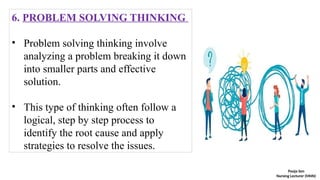
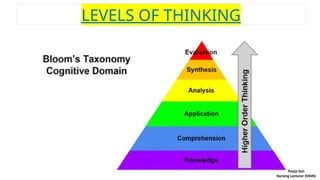
The document discusses the concept of thinking, or cognition, which includes processes such as problem-solving, memory retrieval, and response selection. It outlines different types of thinking, including perceptual, conceptual, reflective, creative, critical, problem-solving, convergent, and divergent thinking, each characterized by unique approaches and examples. Additionally, it highlights the nature and levels of thinking, emphasizing its importance in cognitive activity and problem-solving behaviors.