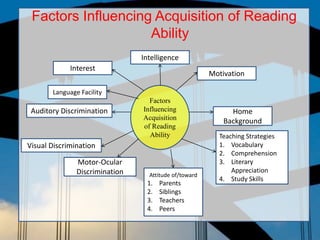
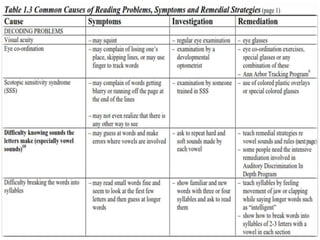
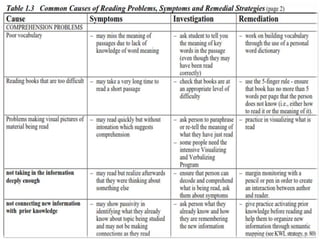
The document discusses reading skills and strategies for improving reading ability. It covers the three main components of reading: decoding, comprehension, and retention. Decoding involves translating print to sound while comprehension relies on understanding the meaning. The document also outlines stages of reading development from pre-reading to advanced reading. It discusses factors that influence reading acquisition and common reading difficulties such as dyslexia and attention issues. Finally, it provides strategies for teachers to help students improve reading comprehension through various techniques such as visualizing, discussing texts, and mapping concepts.