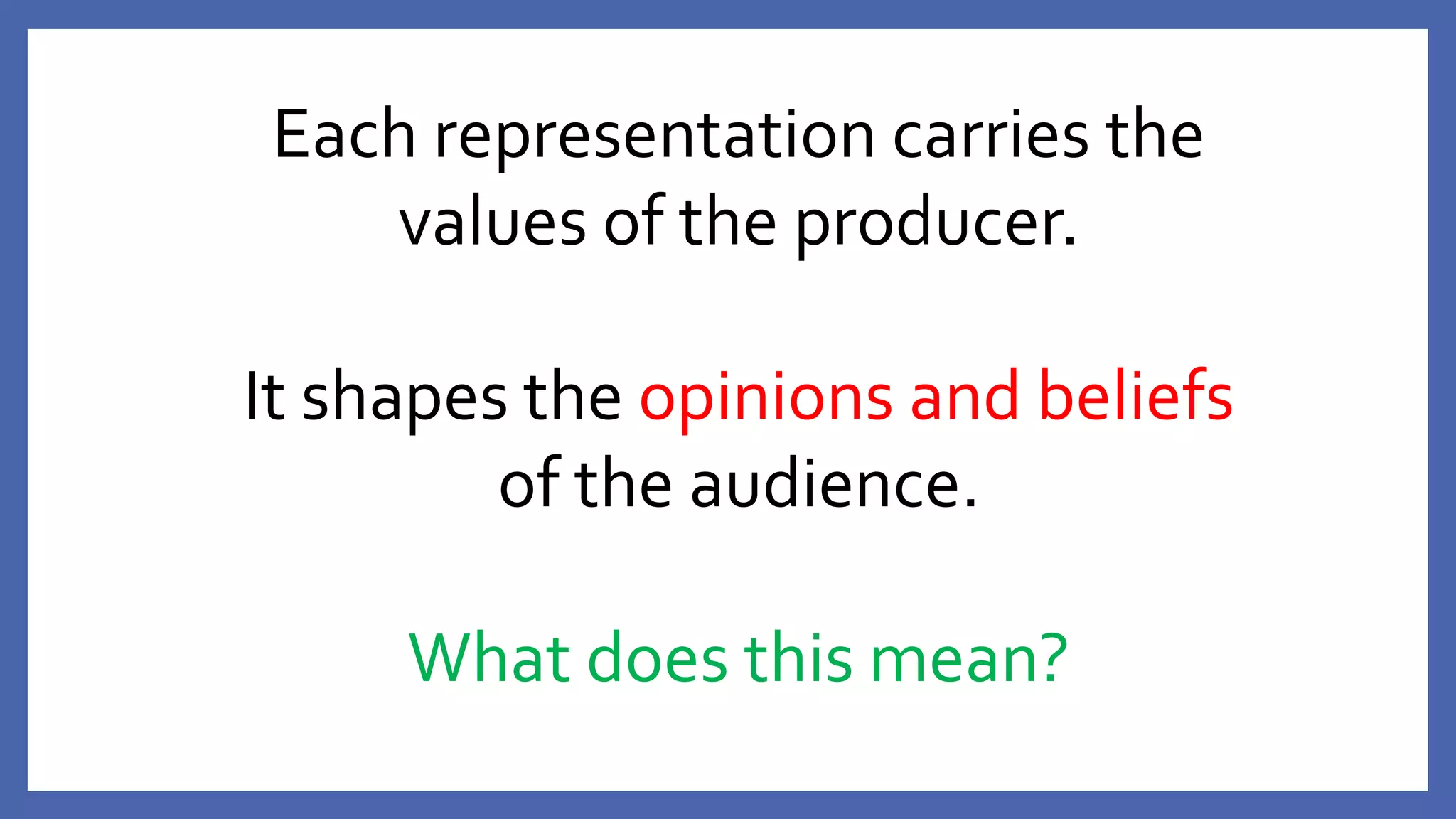
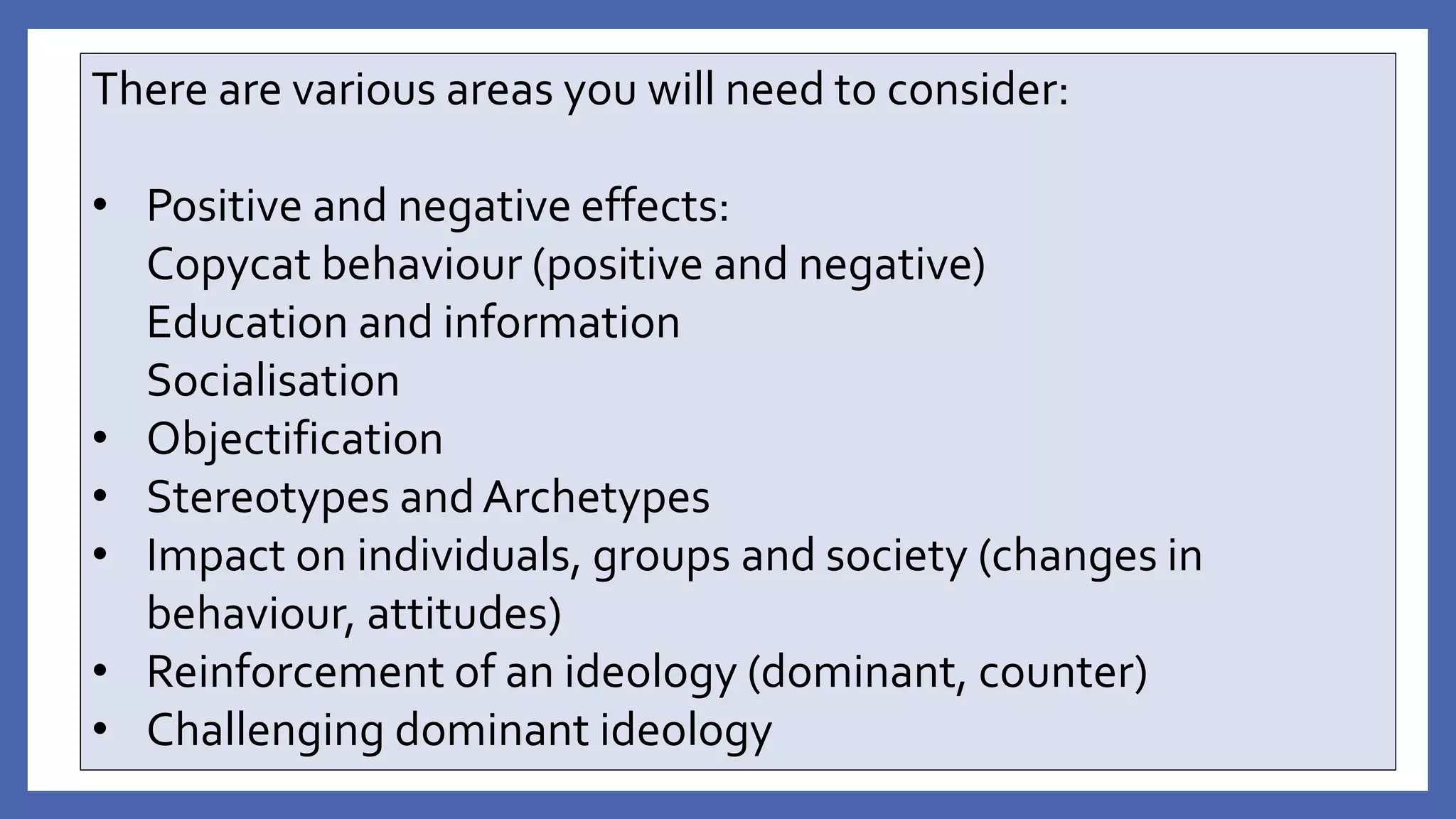
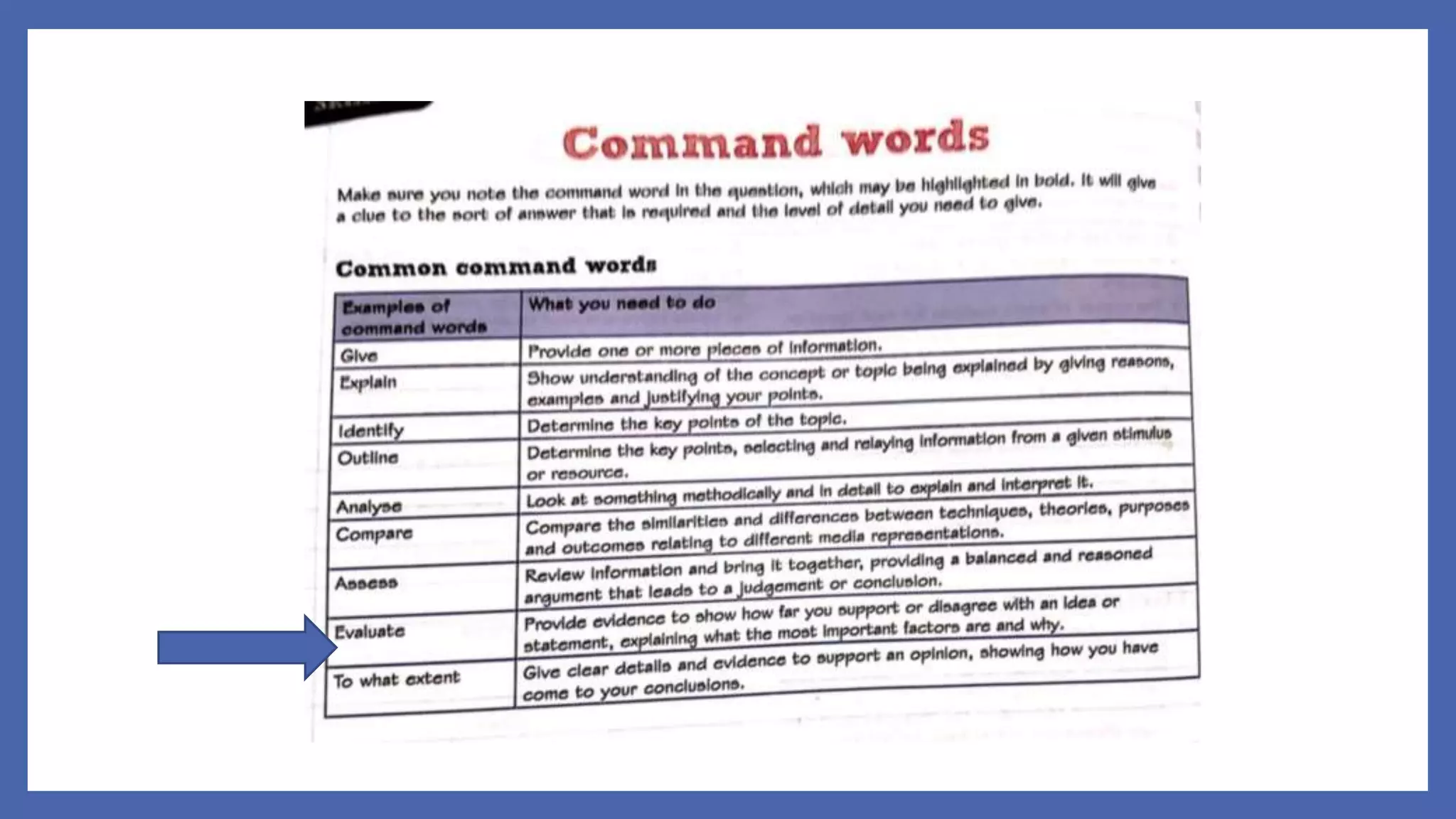
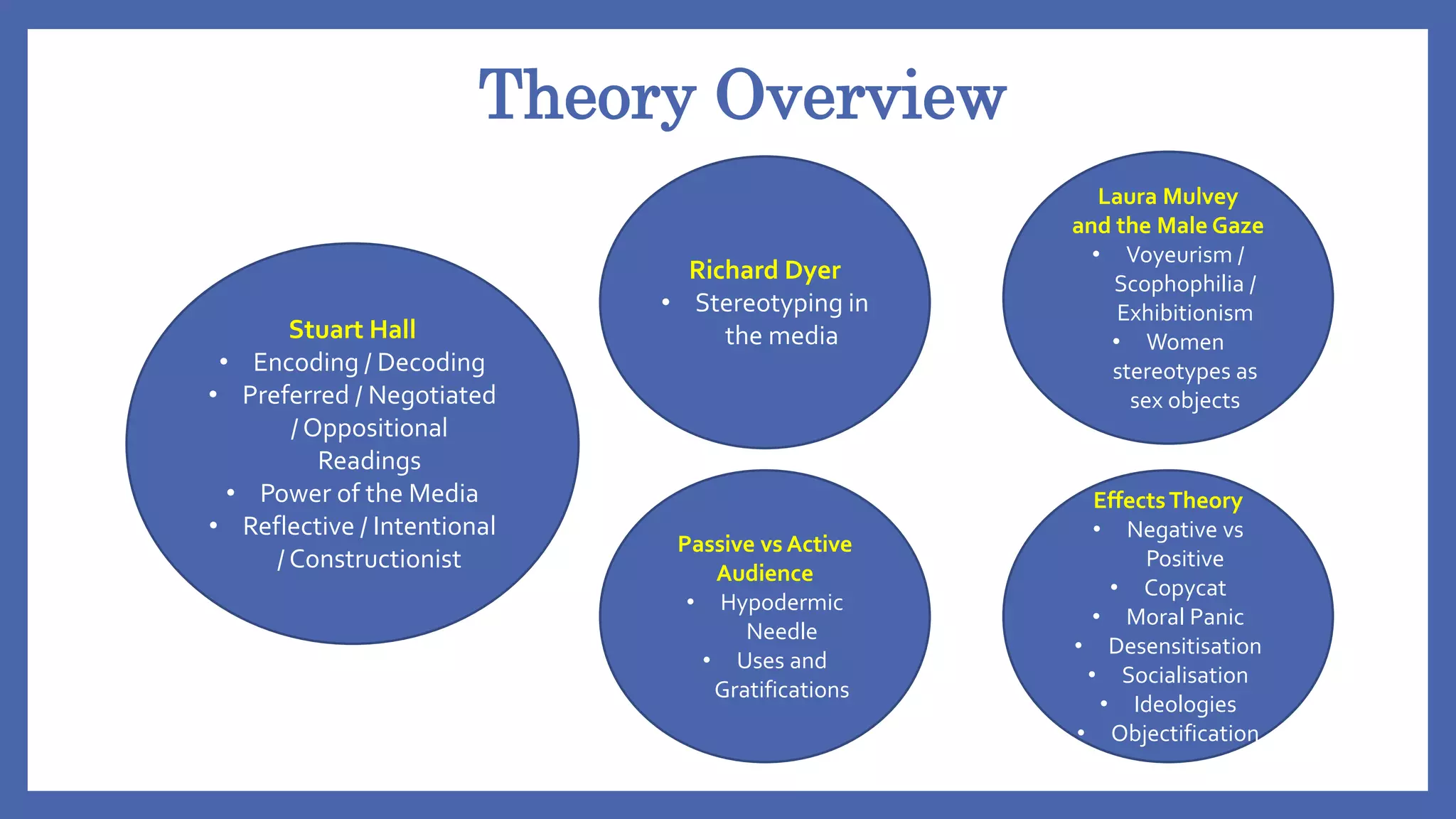
This document provides an overview of media representation theory and concepts for exam practice. It discusses key theories such as how media representations reflect the ideology and values of the producer. It also addresses how audiences can interpret representations in both passive and active ways and may be impacted both positively and negatively by media effects. Examples of potential impacts include copycat behavior, education, socialization, objectification, and reinforcement or challenging of dominant ideologies.