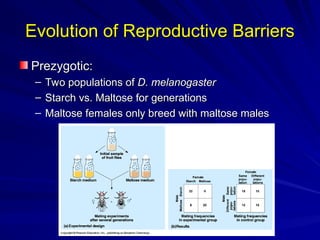
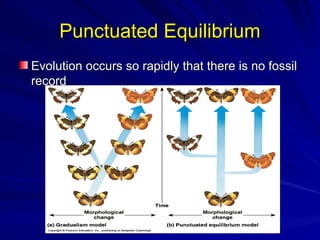
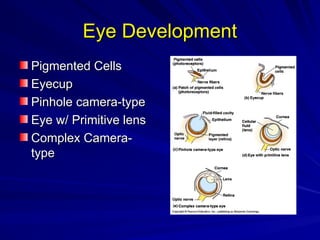
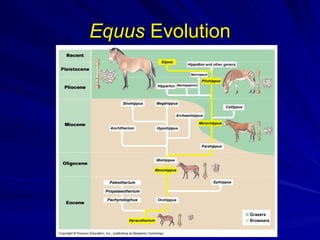
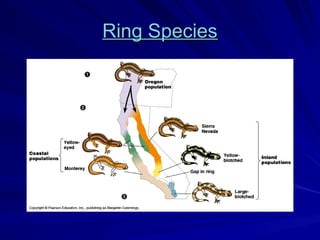
The document discusses concepts related to reproductive isolation and speciation, highlighting mechanisms such as prezygotic barriers (e.g., habitat, behavioral, temporal) and postzygotic barriers (e.g., reduced hybrid viability, fertility). It also explores various species classification methods and the processes of allopatric and sympatric speciation, including the role of polyploidy in plants. The document concludes with evolutionary principles and trends such as punctuated equilibrium, exaptations, and the non-goal-oriented nature of evolution.