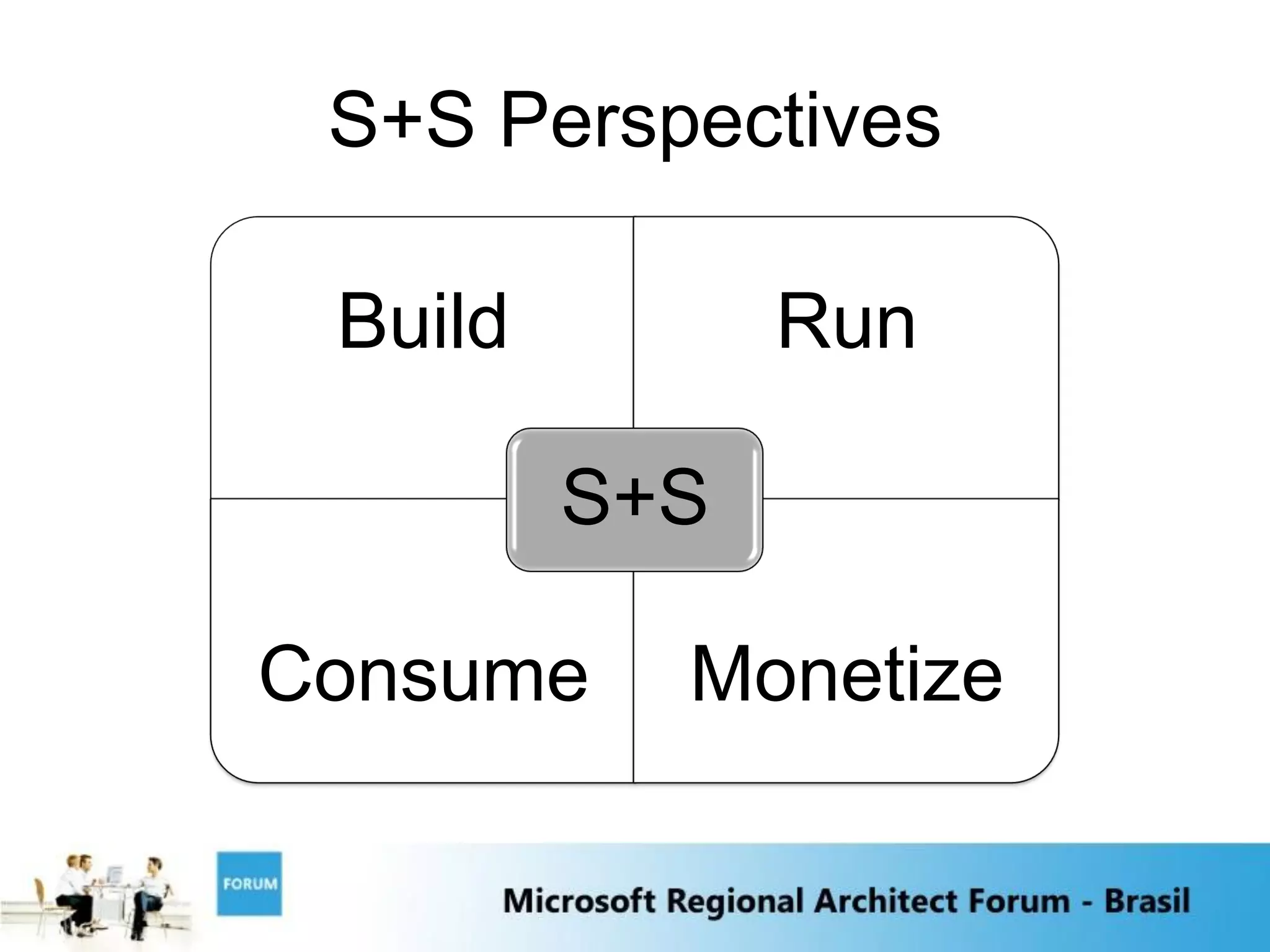
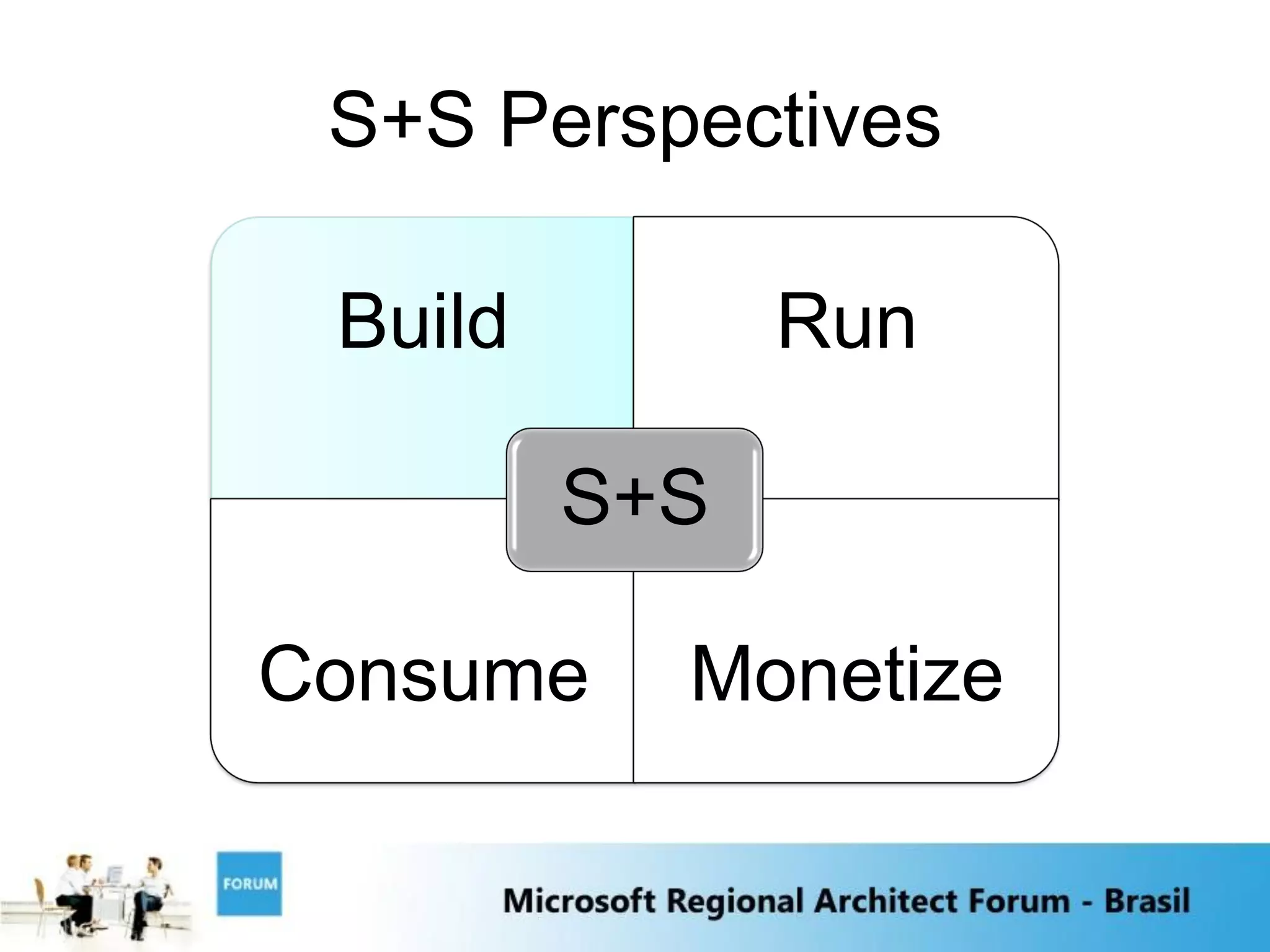
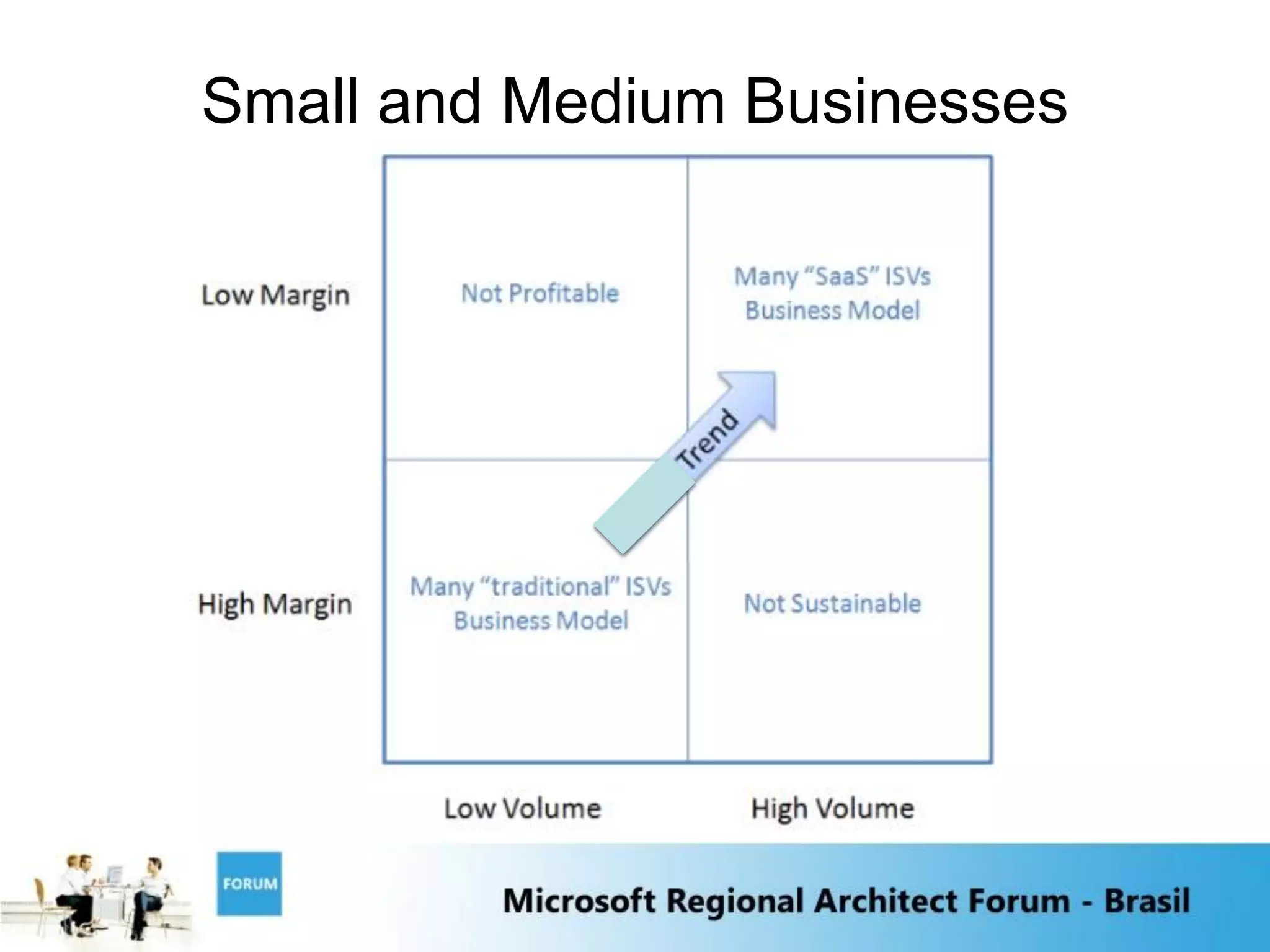
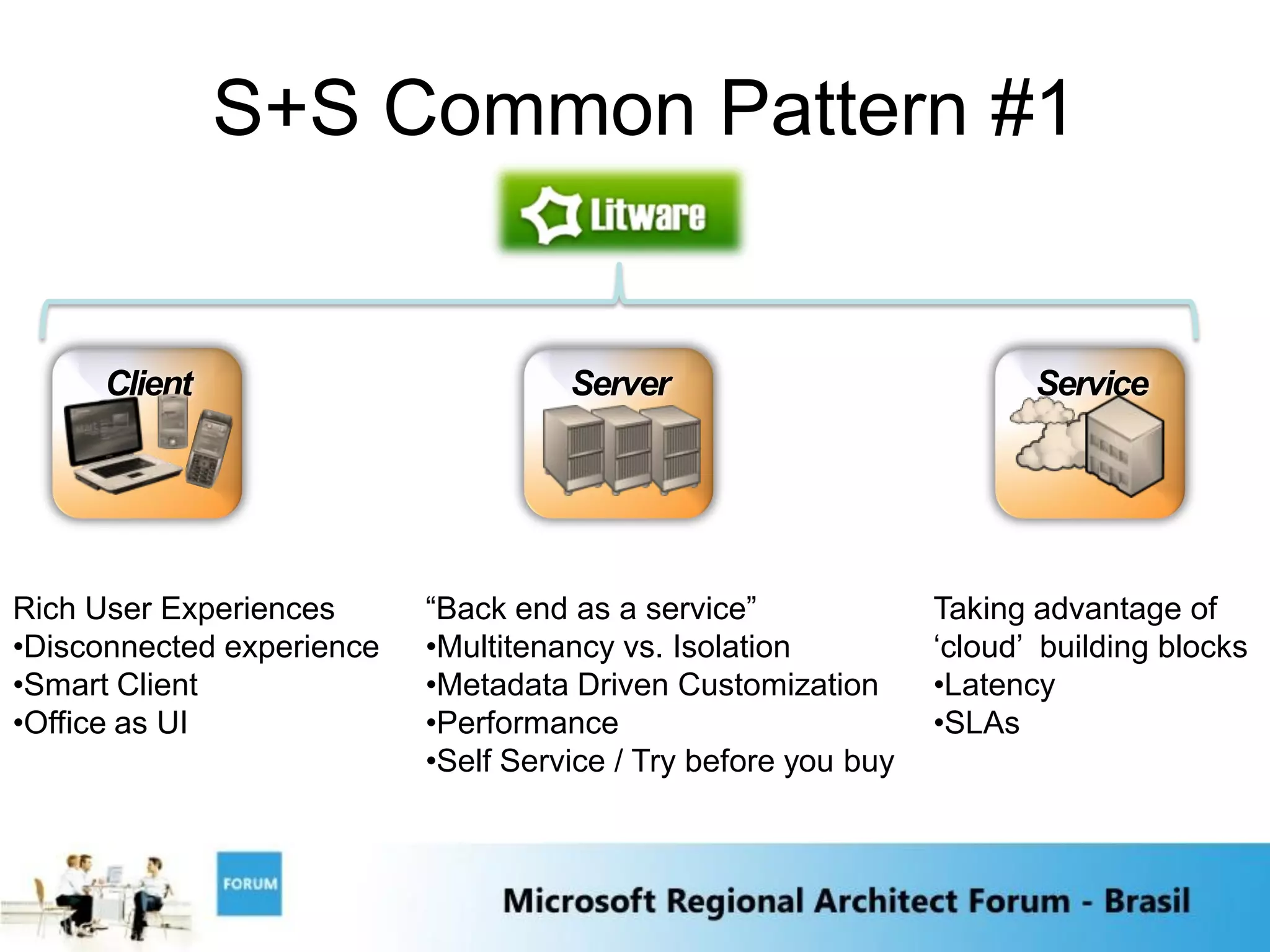
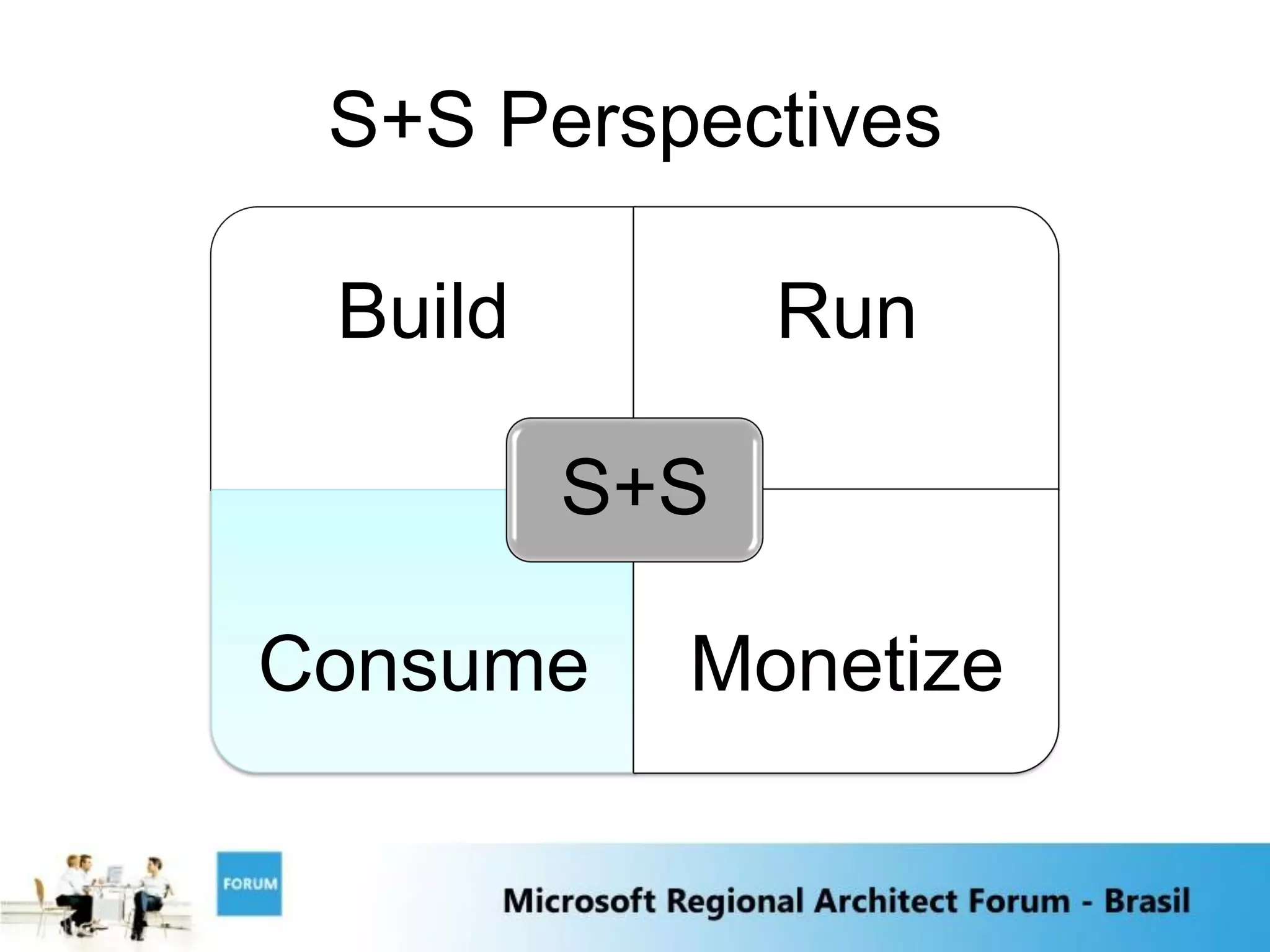
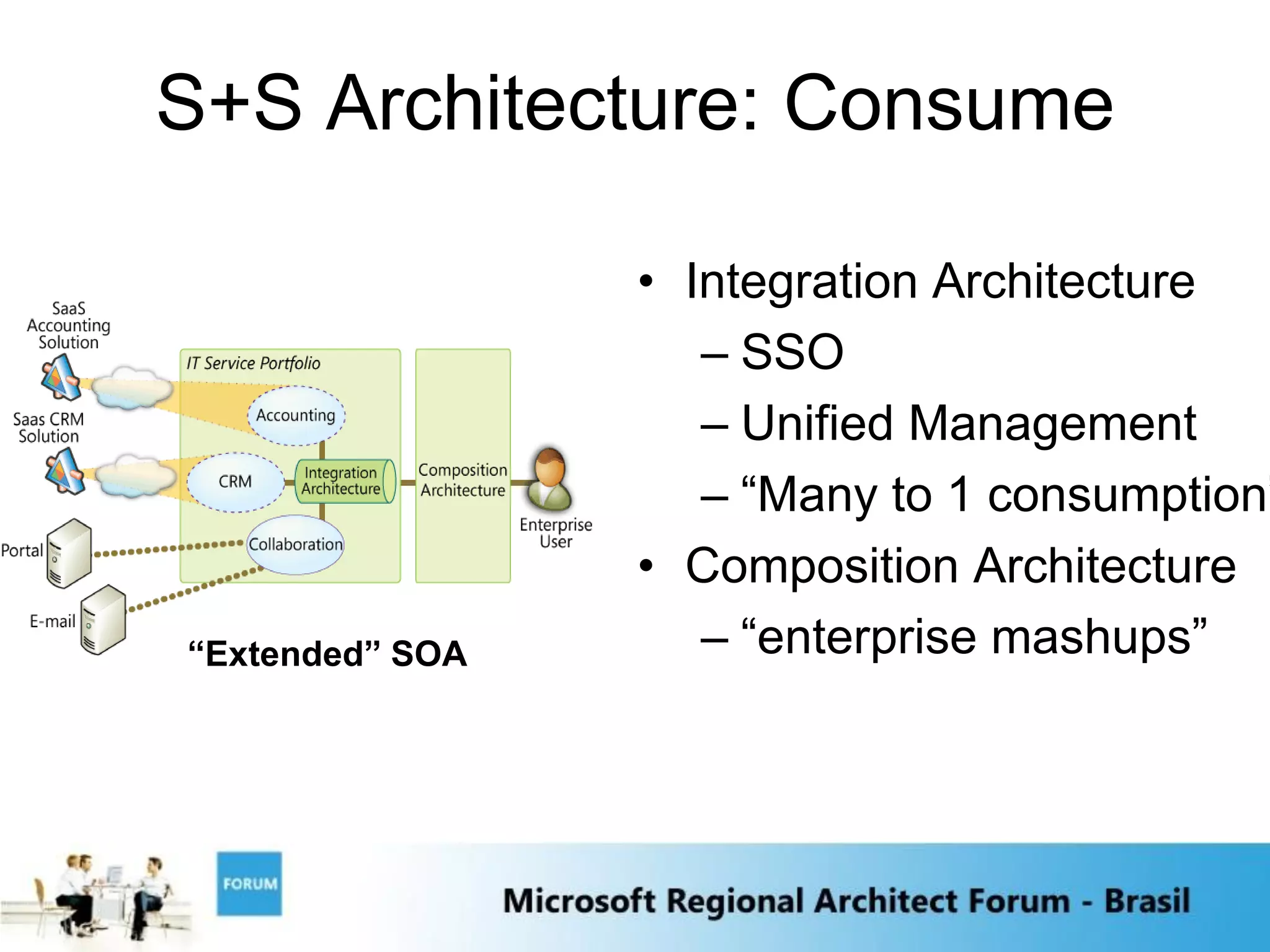
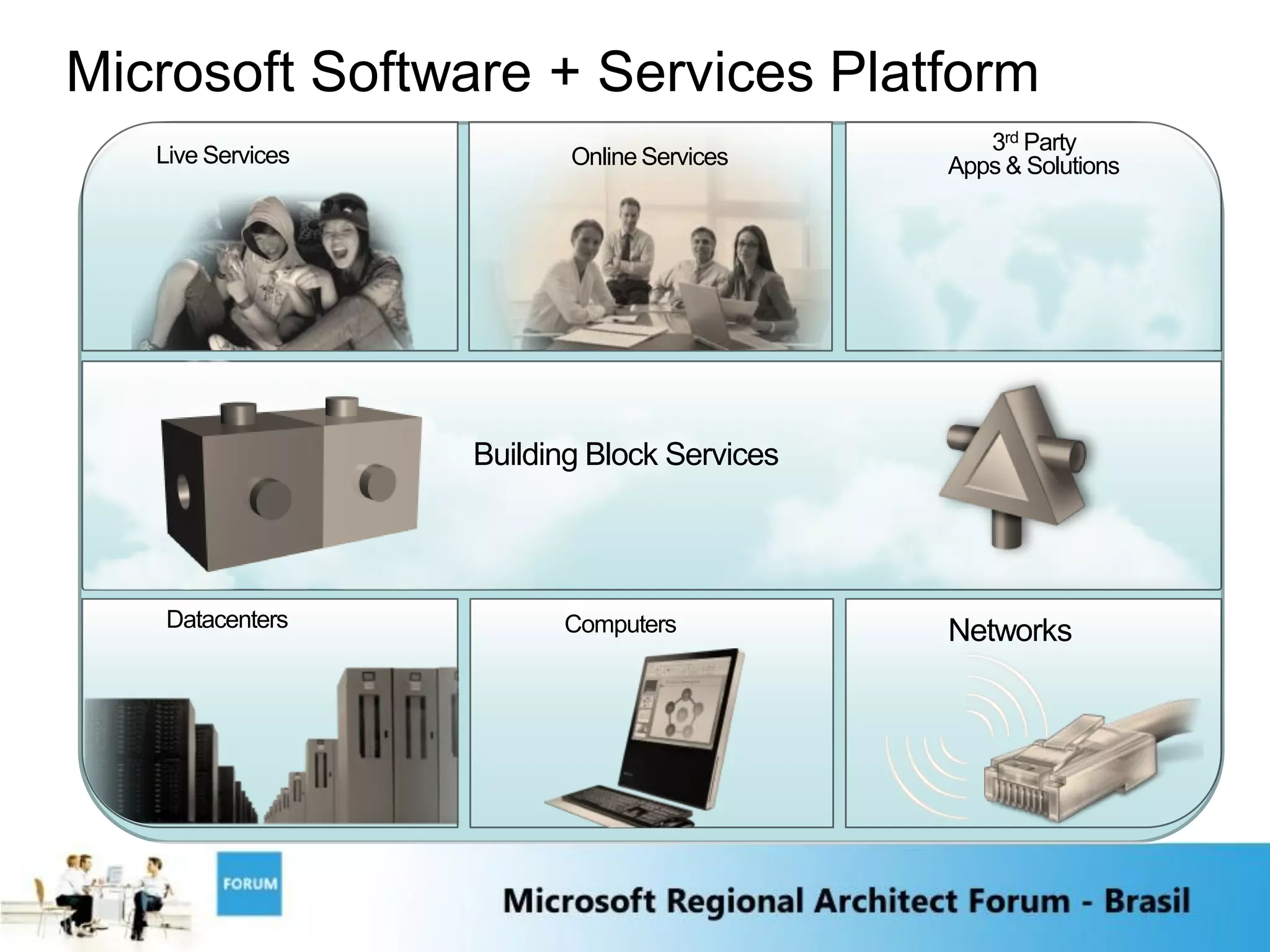
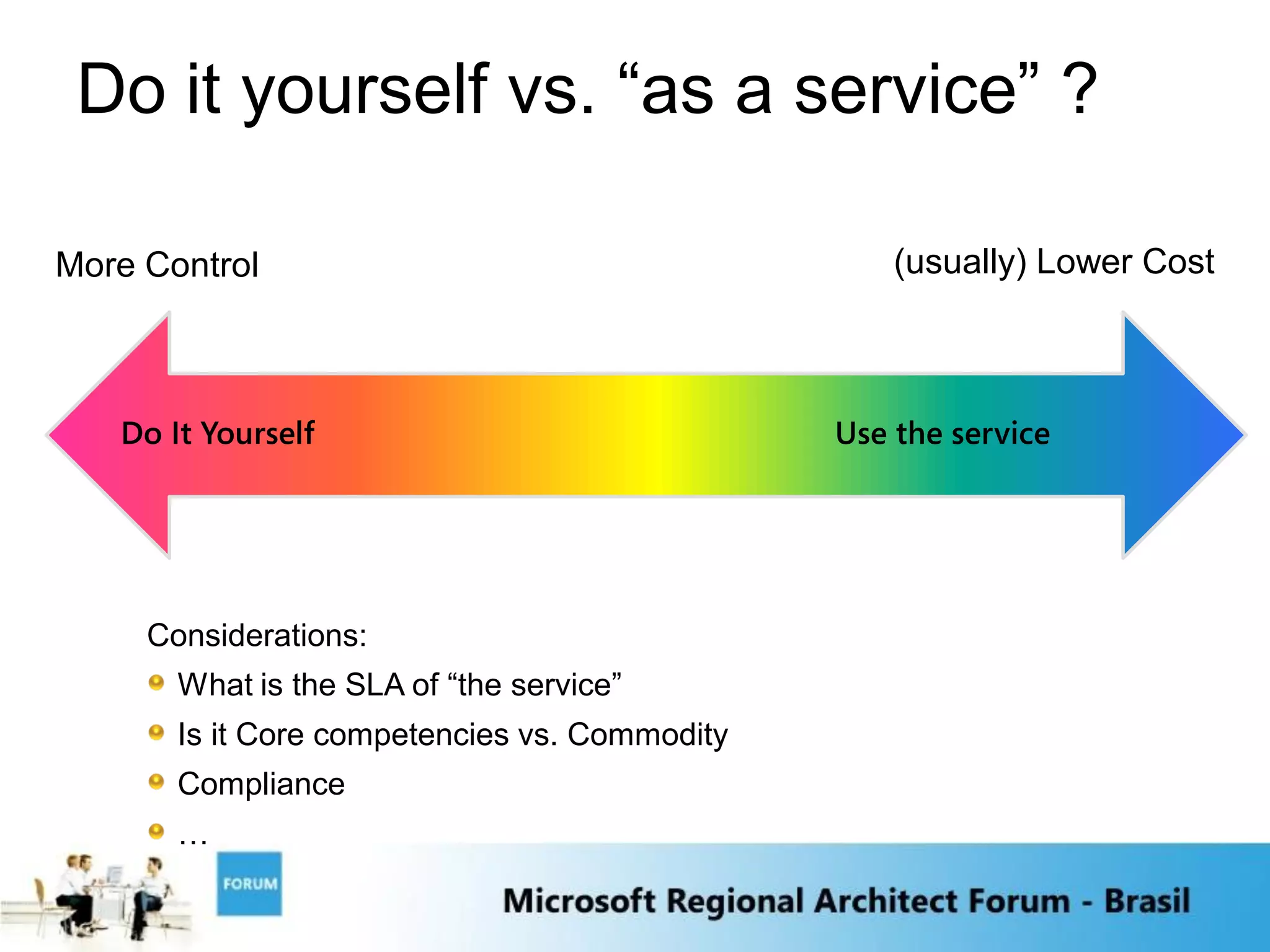
The document discusses emerging trends in software and services including:
1) Software as a Service and cloud computing which allows software to be delivered and consumed "as a service" with service level agreements.
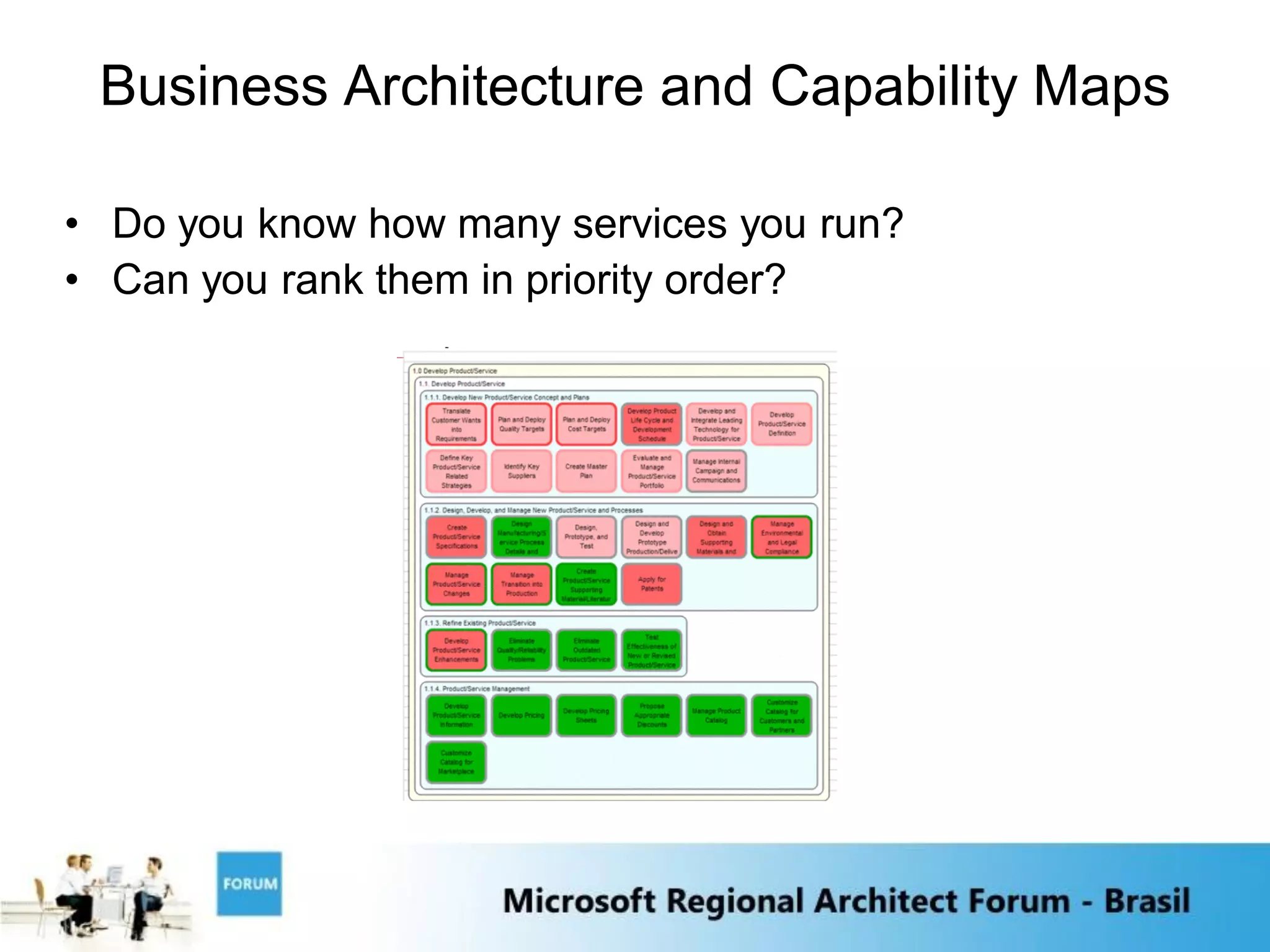
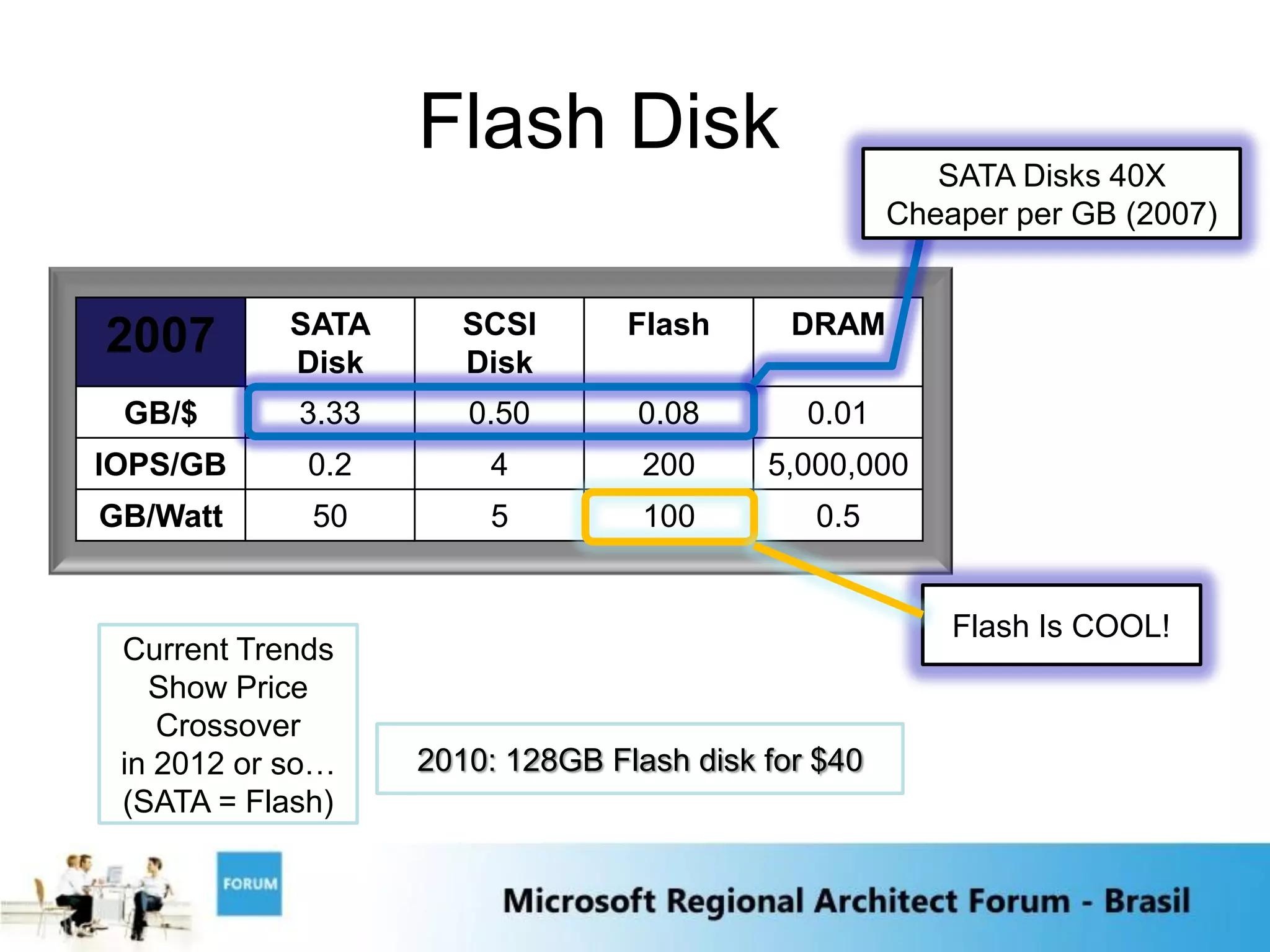
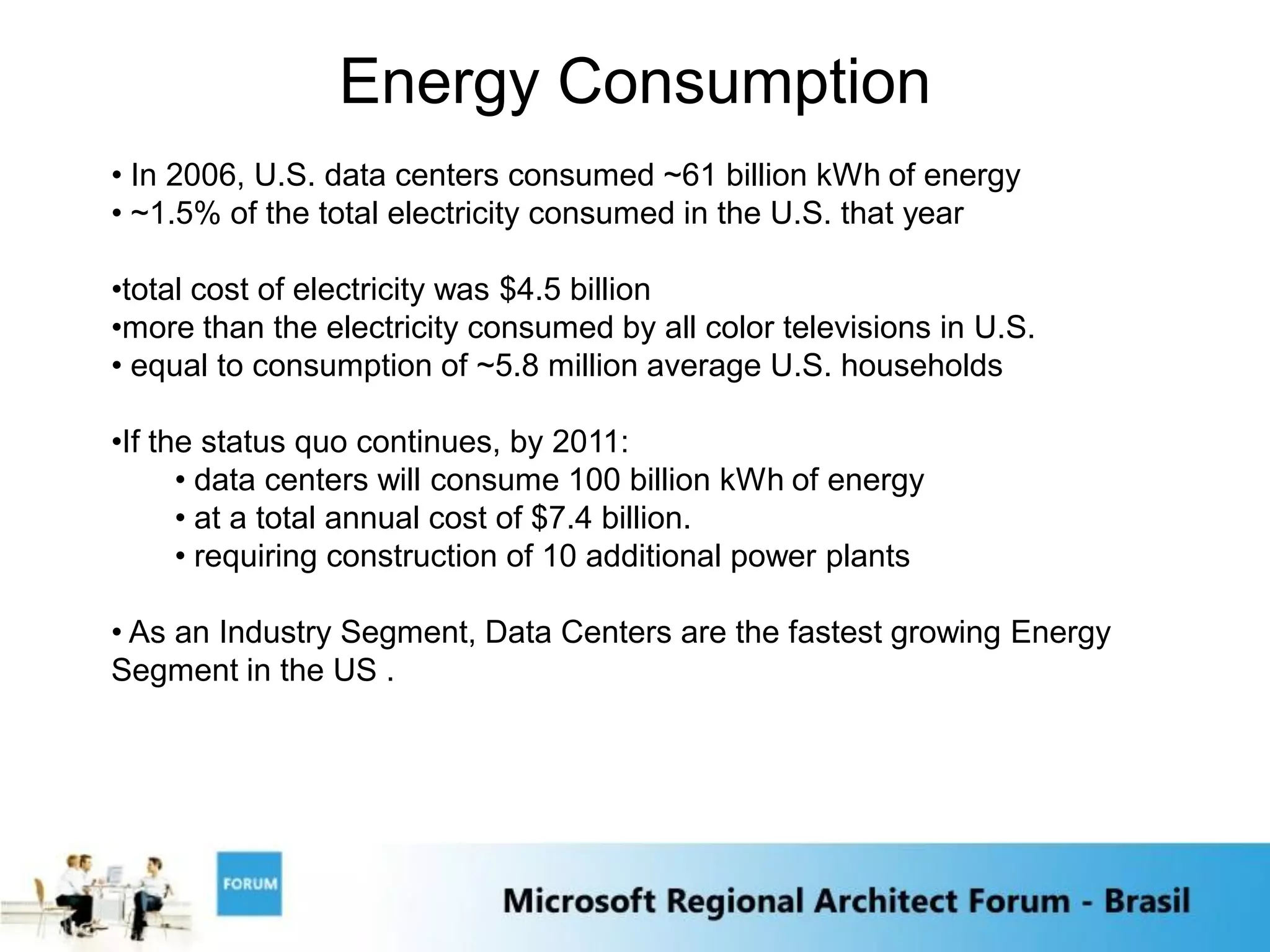
2) The growth of massive data centers which are becoming large physical assets requiring significant capital expenditures.
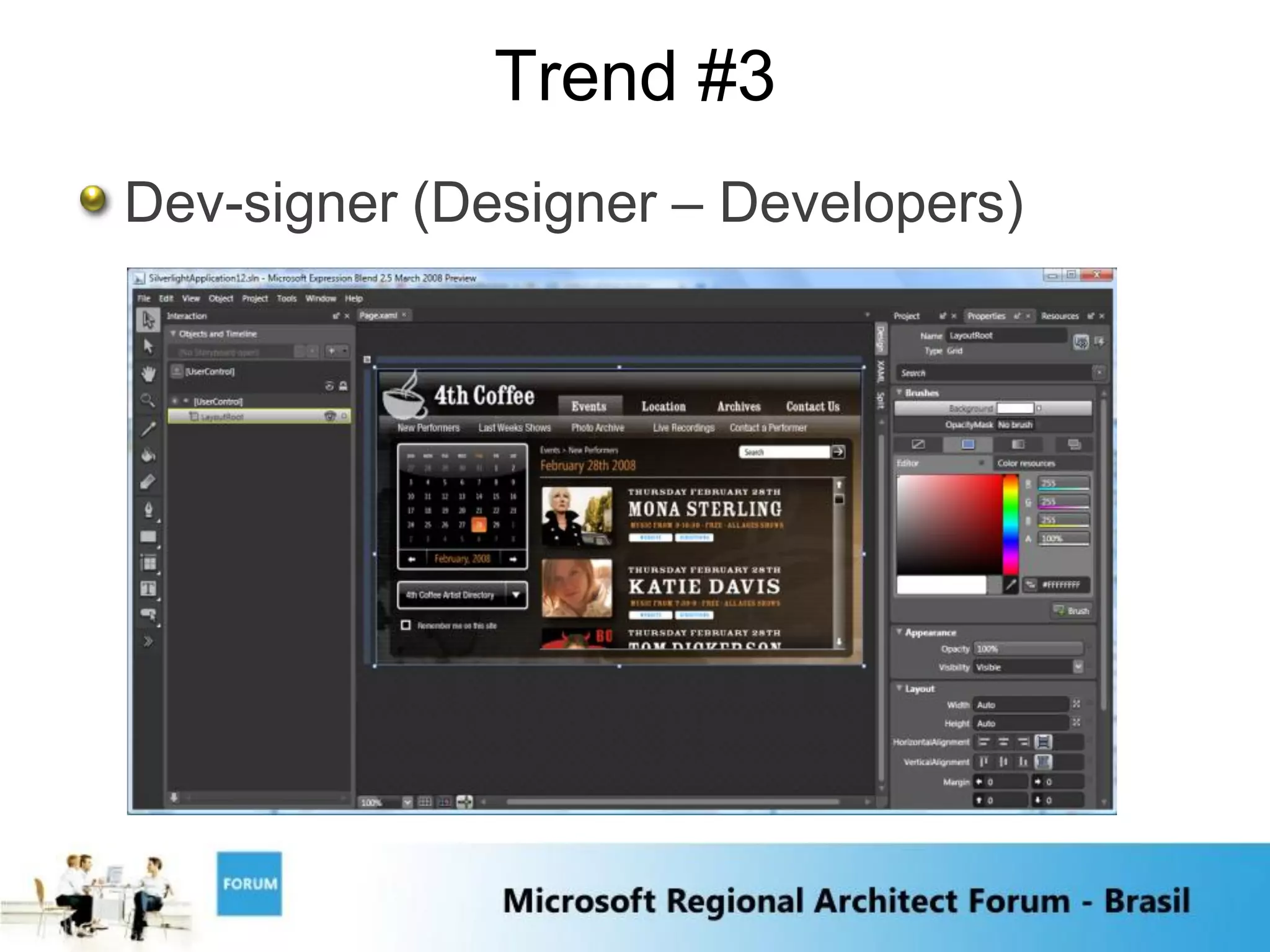
3) The rise of "Dev-signers" or designer-developers who are combining development and design skills.
4) The integration of software and services will be key as local software interacts with internet services to provide combined capabilities.






























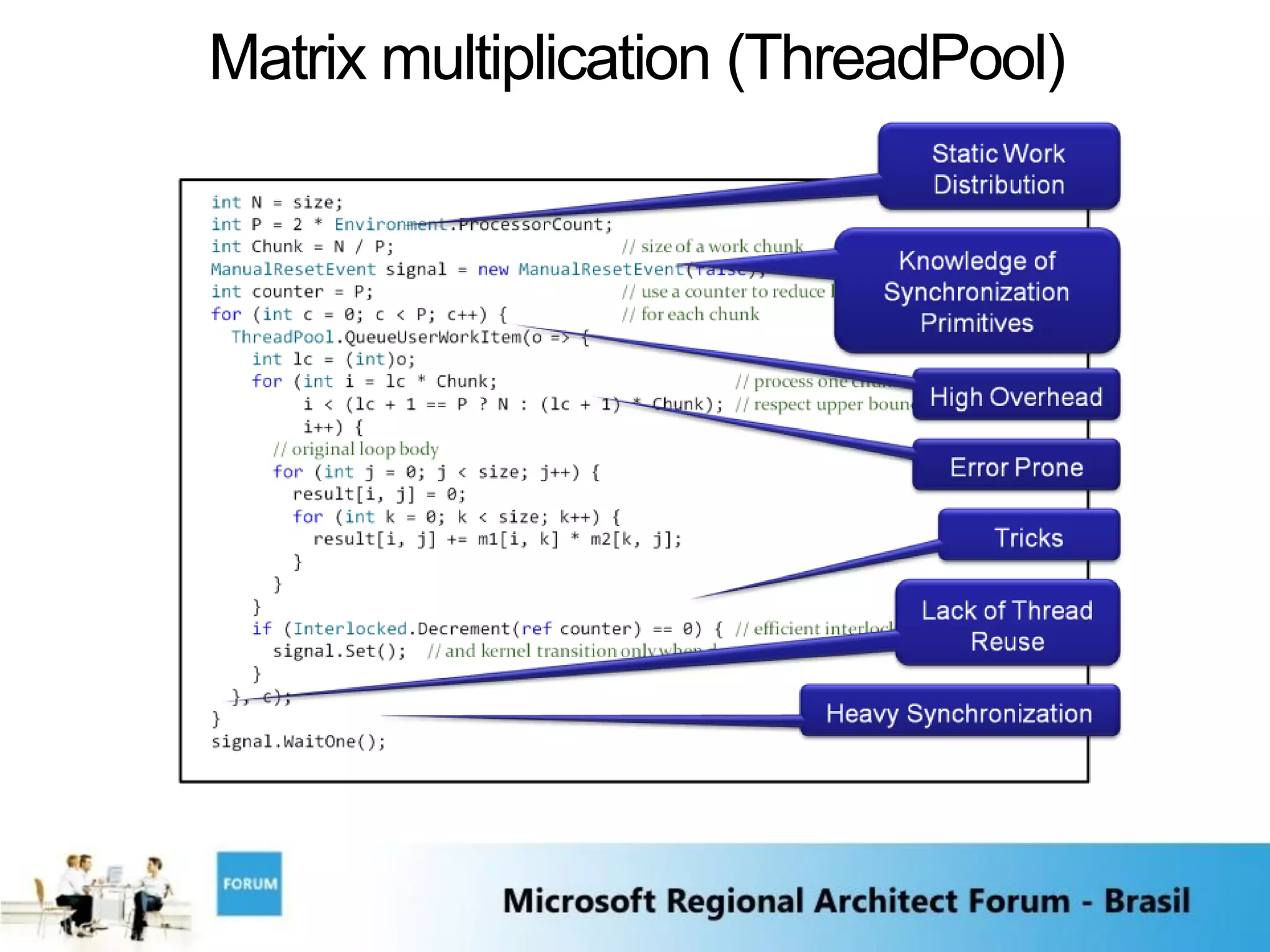
![Matrix multiplication (sequential)
void MultiplyMatrices(int size,
double[,] m1, double[,] m2, double[,] result)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
result[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) {
result[i, j] += m1[i, k] * m2[k, j];
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brazilraf2008gianpc-090801073758-phpapp02/75/The-Yin-and-Yang-of-Software-43-2048.jpg)
![Matrix multiplication (Parallel Extensions)
void MultiplyMatrices(int size,
double[,] m1, double[,] m2, double[,] result)
{
Parallel.For(0, size, i => {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
result[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) {
result[i, j] += m1[i, k] * m2[k, j];
}
}
});
}
Parallel Extensions to the .NET Framework http://msdn.com/concurrency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brazilraf2008gianpc-090801073758-phpapp02/75/The-Yin-and-Yang-of-Software-45-2048.jpg)