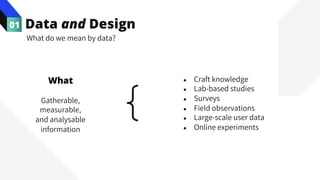
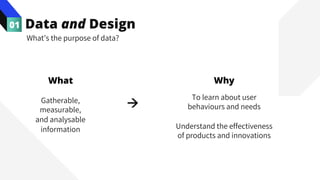
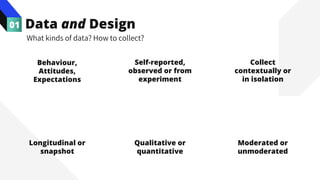
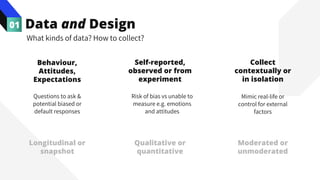
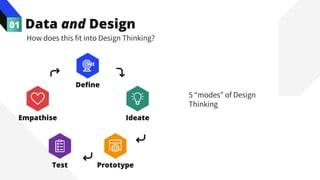
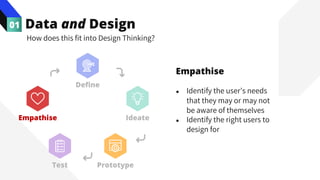
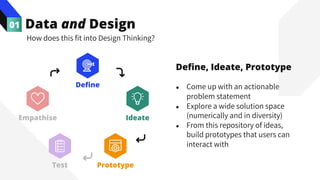
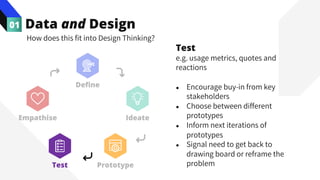
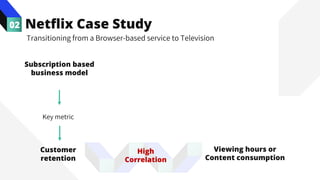
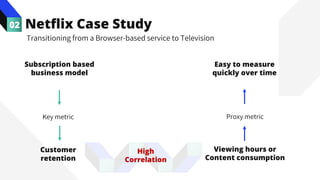
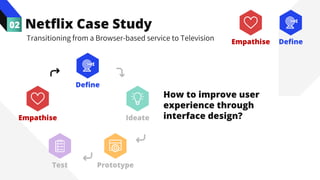
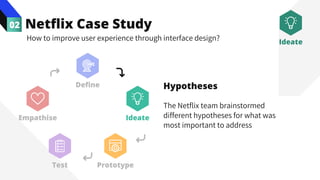
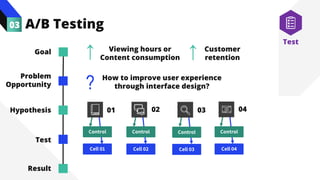
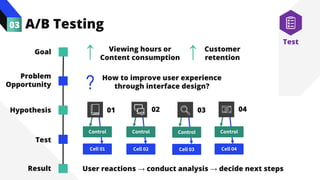
The document discusses the value of data in design. It presents the Netflix case study where they used A/B testing to improve their interface for streaming content. Netflix hypothesized different interface designs and tested them on users to see which improved key metrics like viewing time and retention. Their initial bias was wrong - data from A/B testing showed users preferred an interface that mimicked the website over other options. This demonstrated how data can help evaluate designs objectively and guide improvements.