Embed presentation
Download to read offline

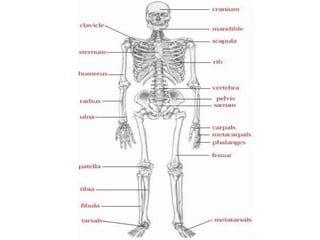








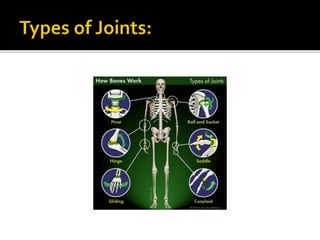


The document discusses the human skeletal system. It notes that the skeletal system protects organs, manufactures blood cells, supports the body, and facilitates movement. It then lists the number of bones in the skull, spine, ribs, arms, and legs. It categorizes bones as long, short, flat, or irregular shaped and lists examples of each type. Finally, it describes how bones and connective tissues are strengthened through exercise.












