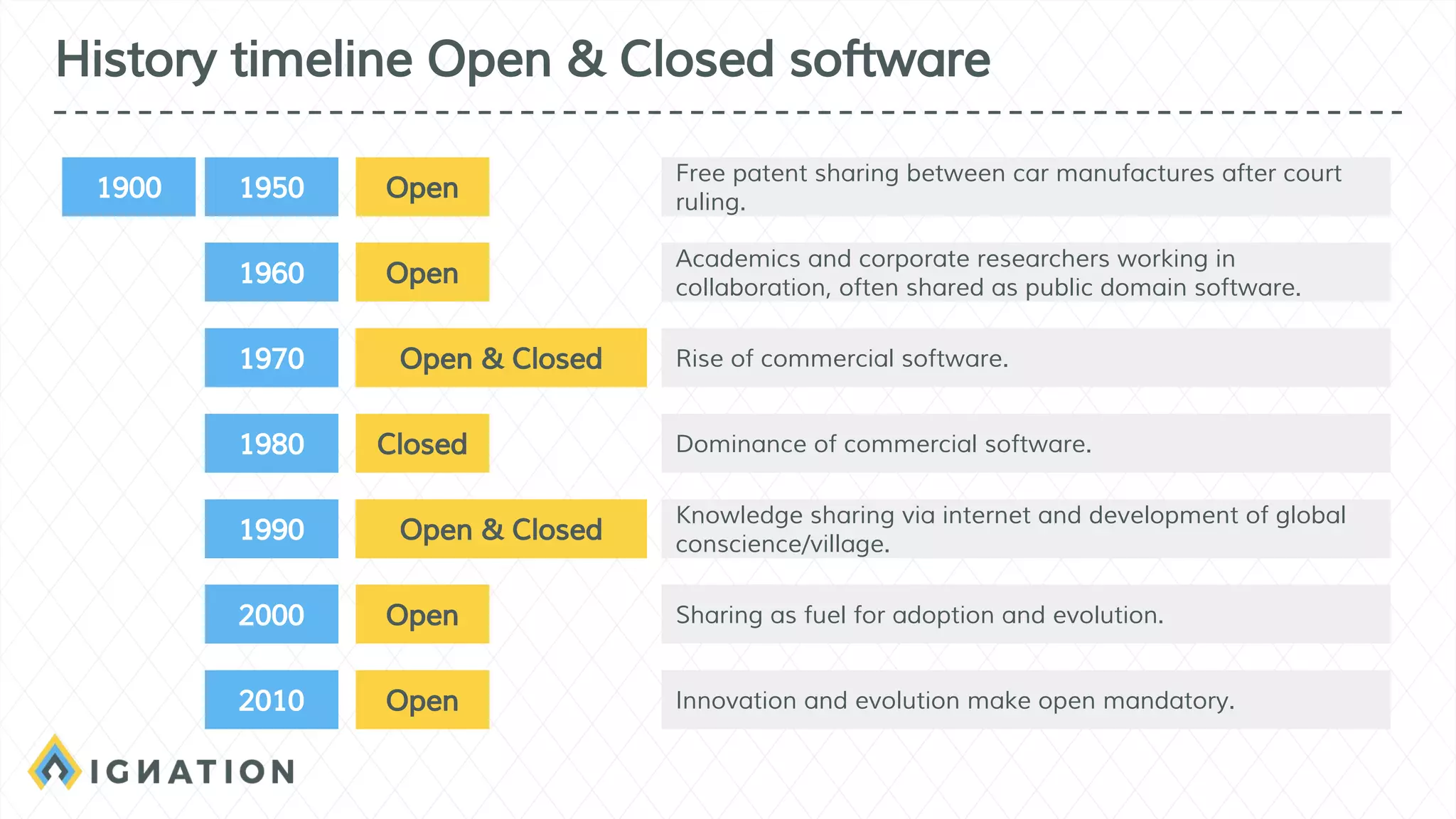
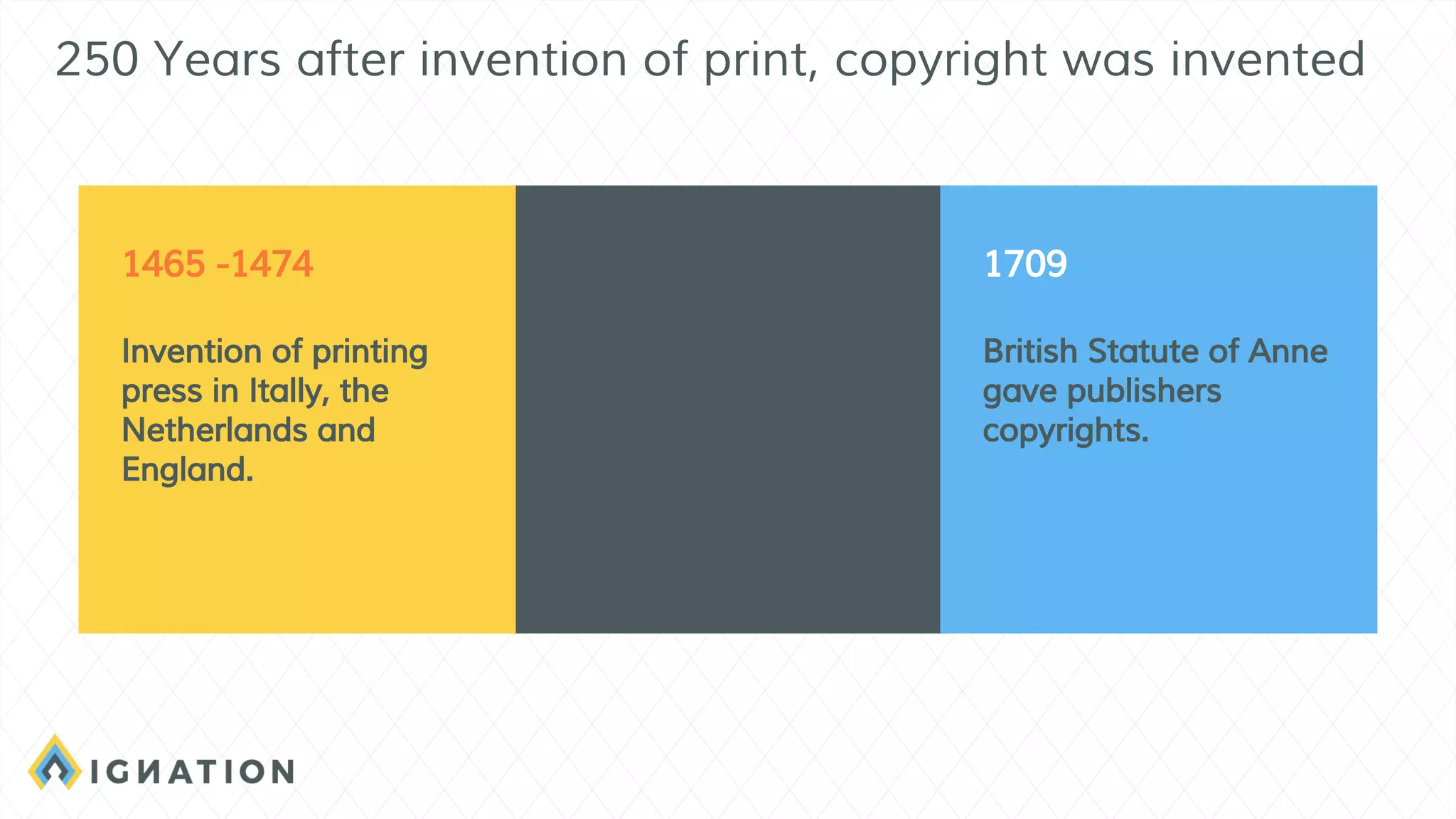
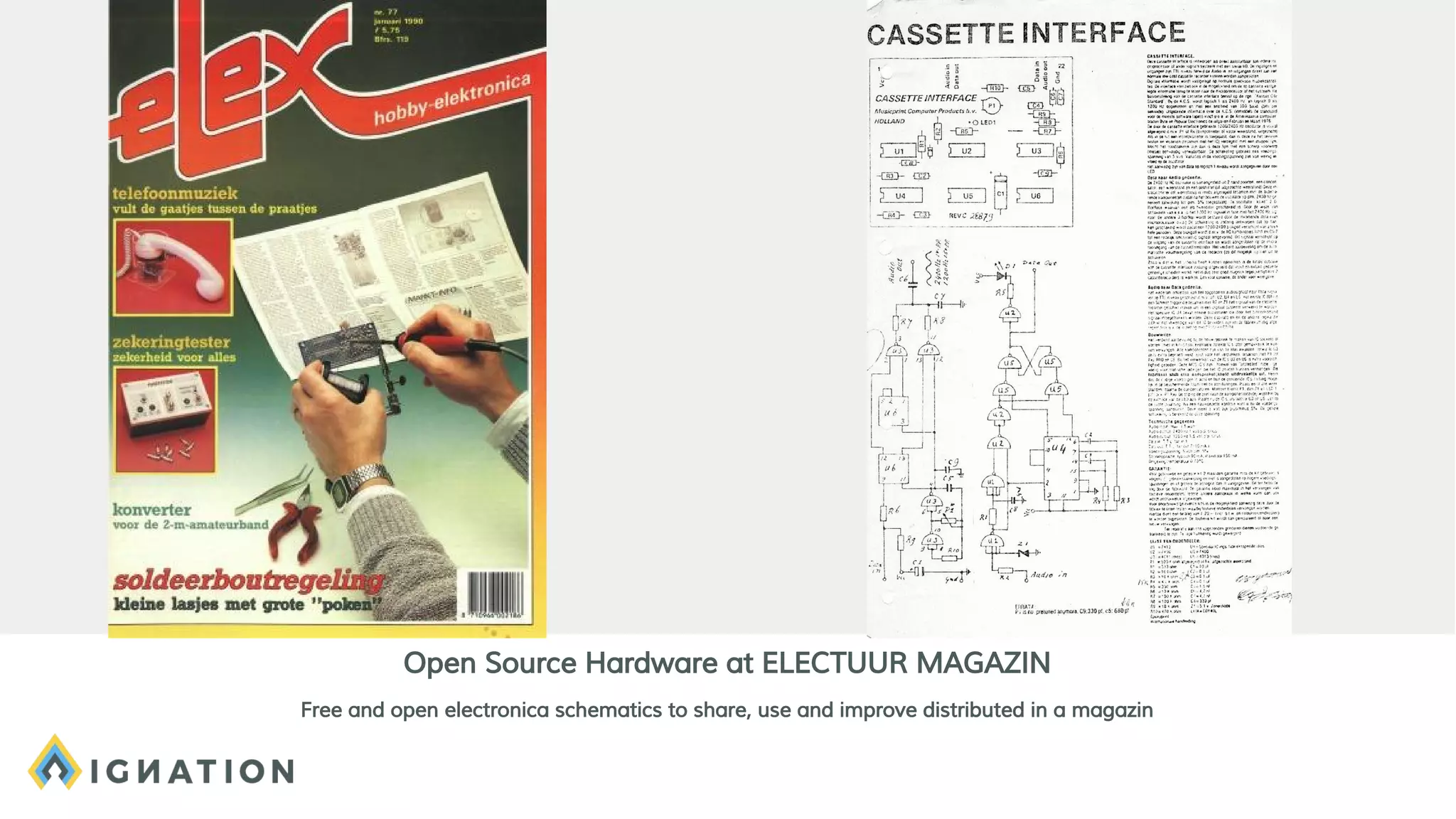
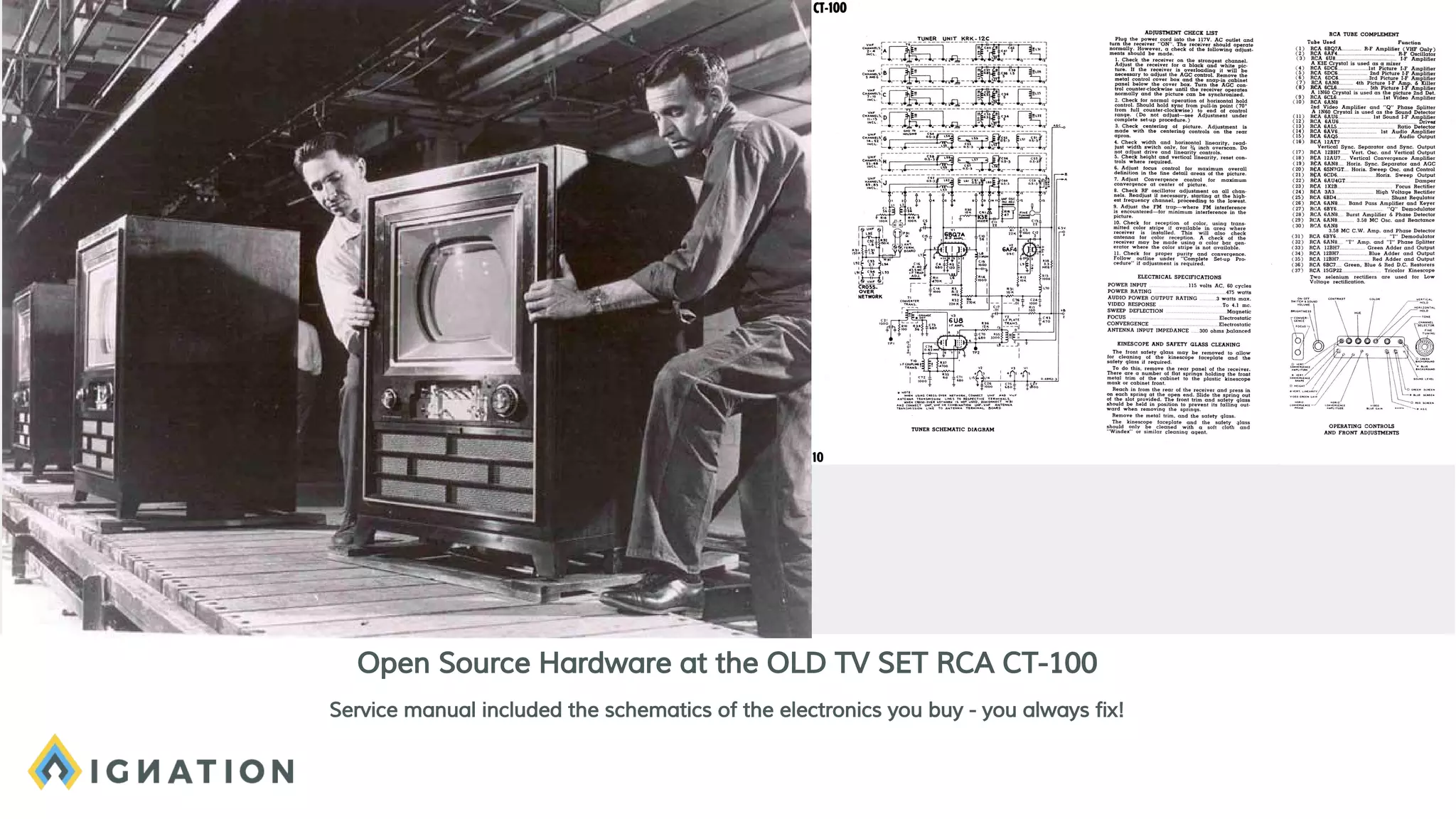
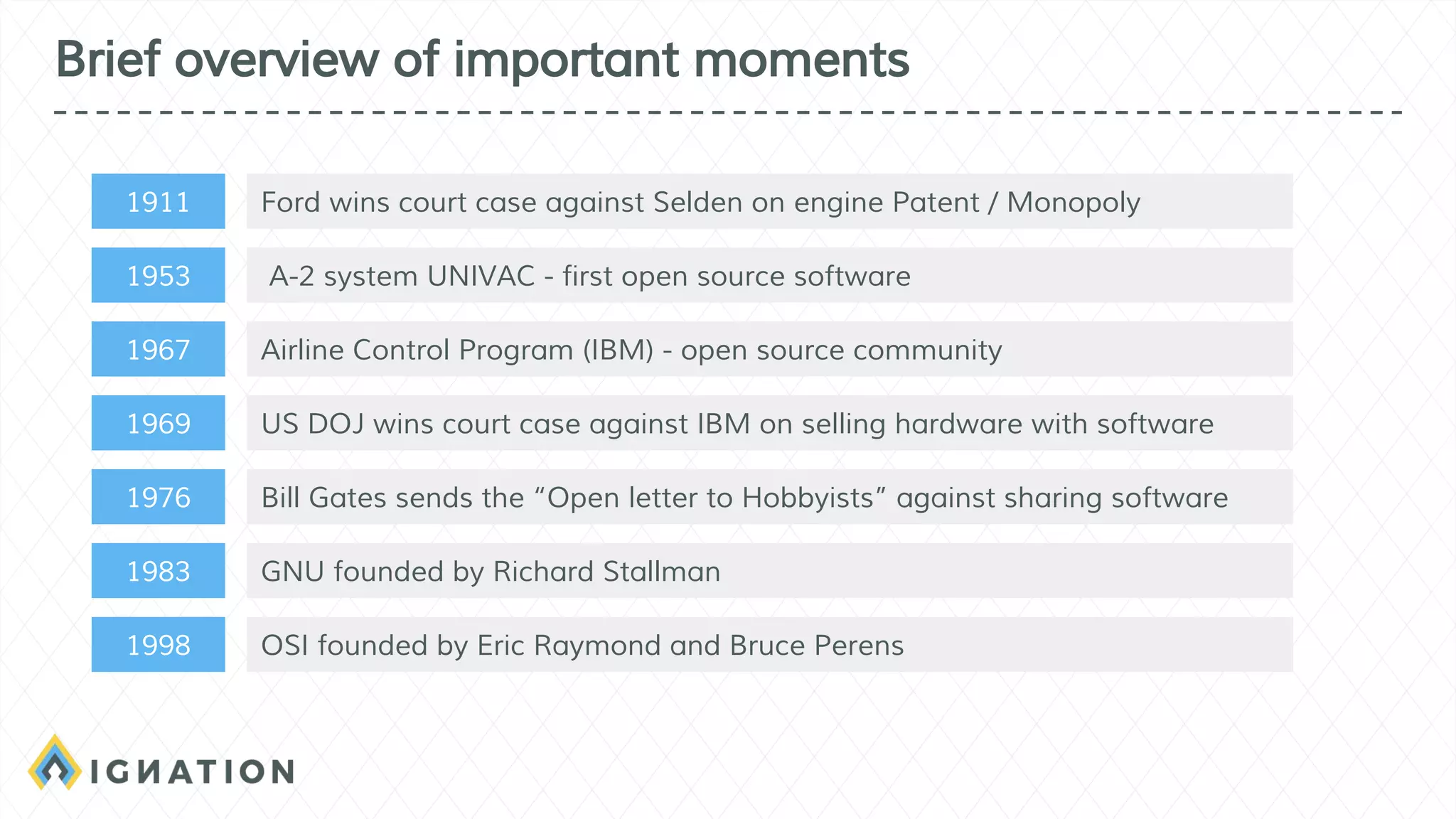
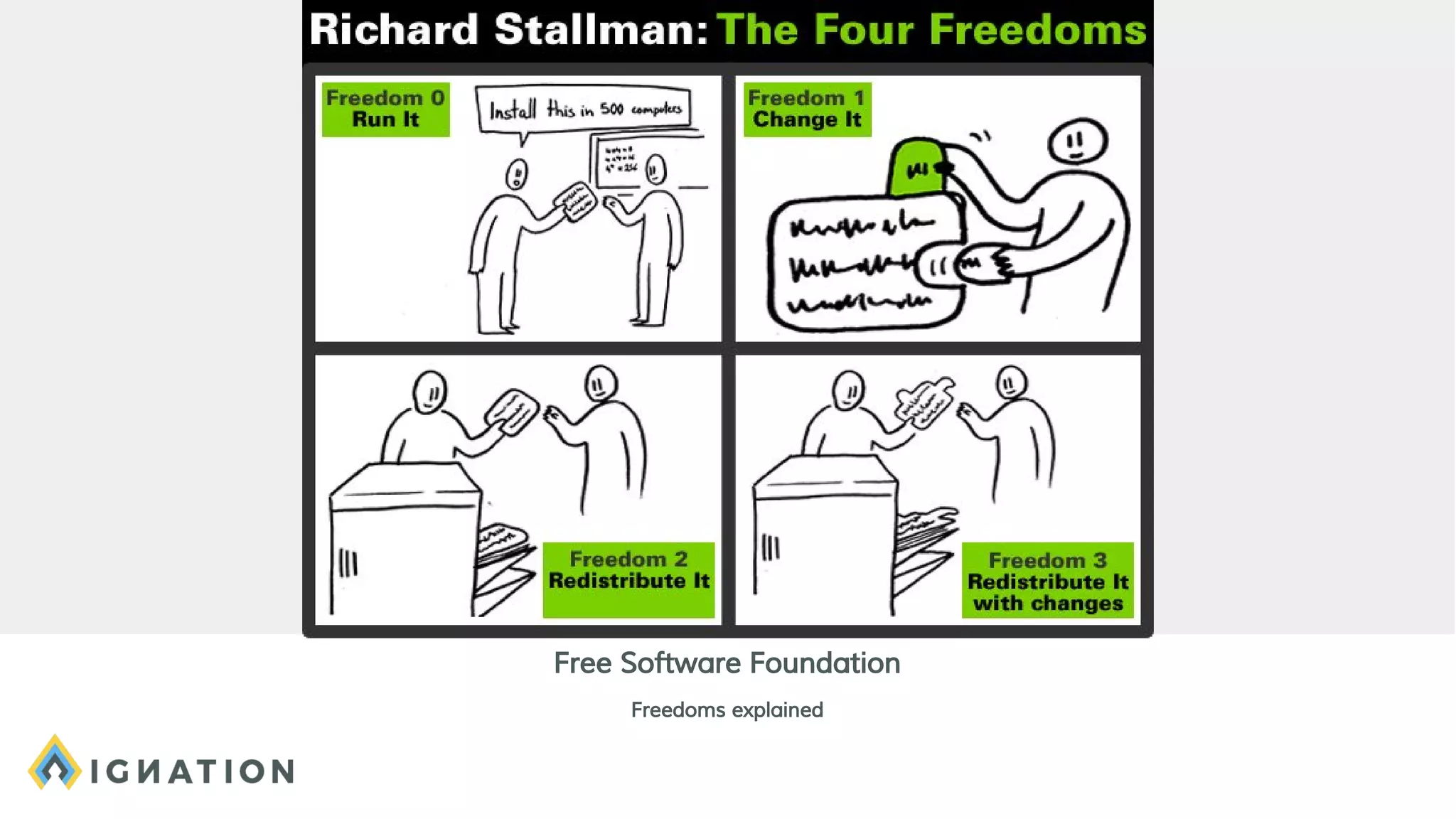
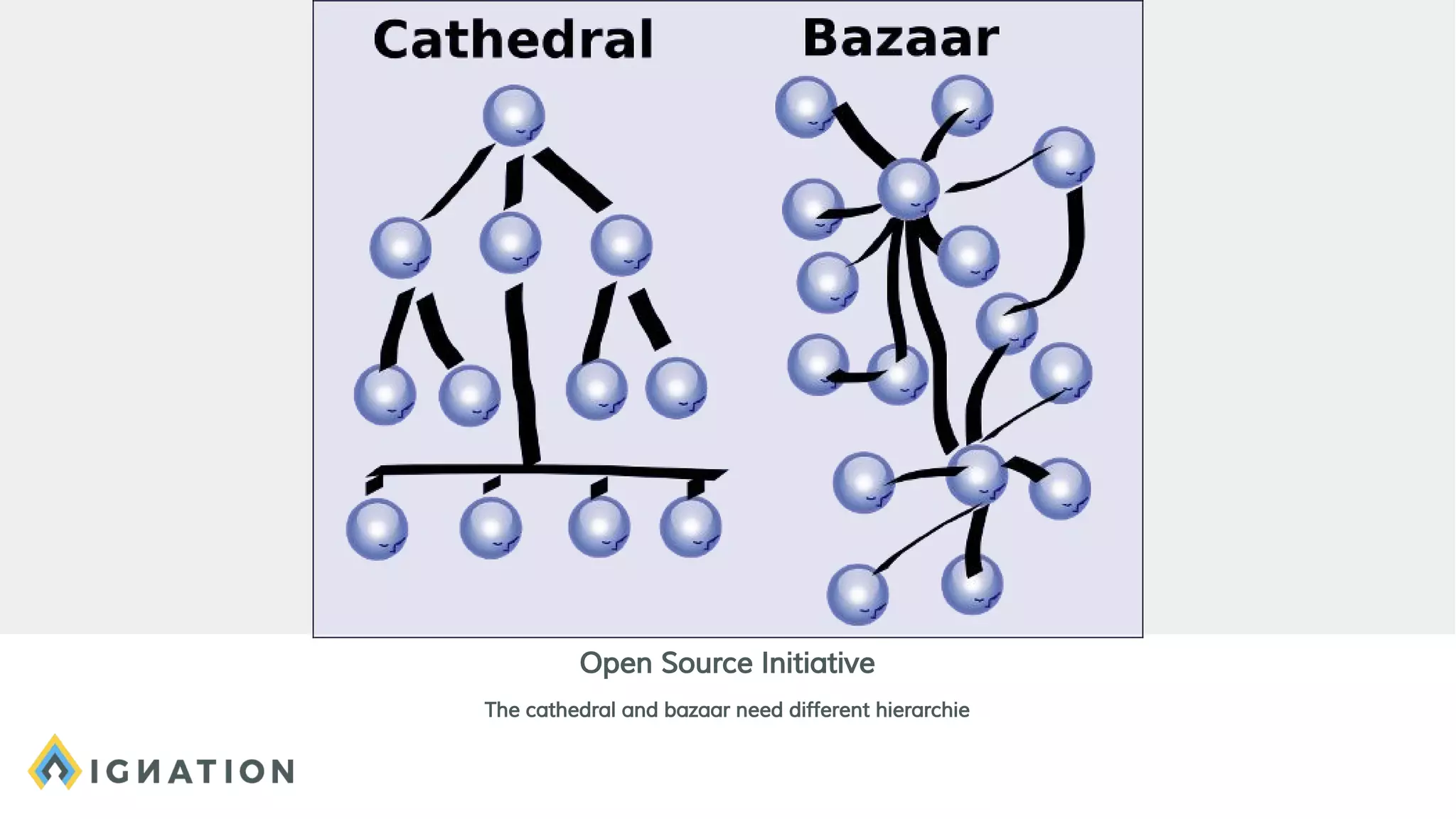
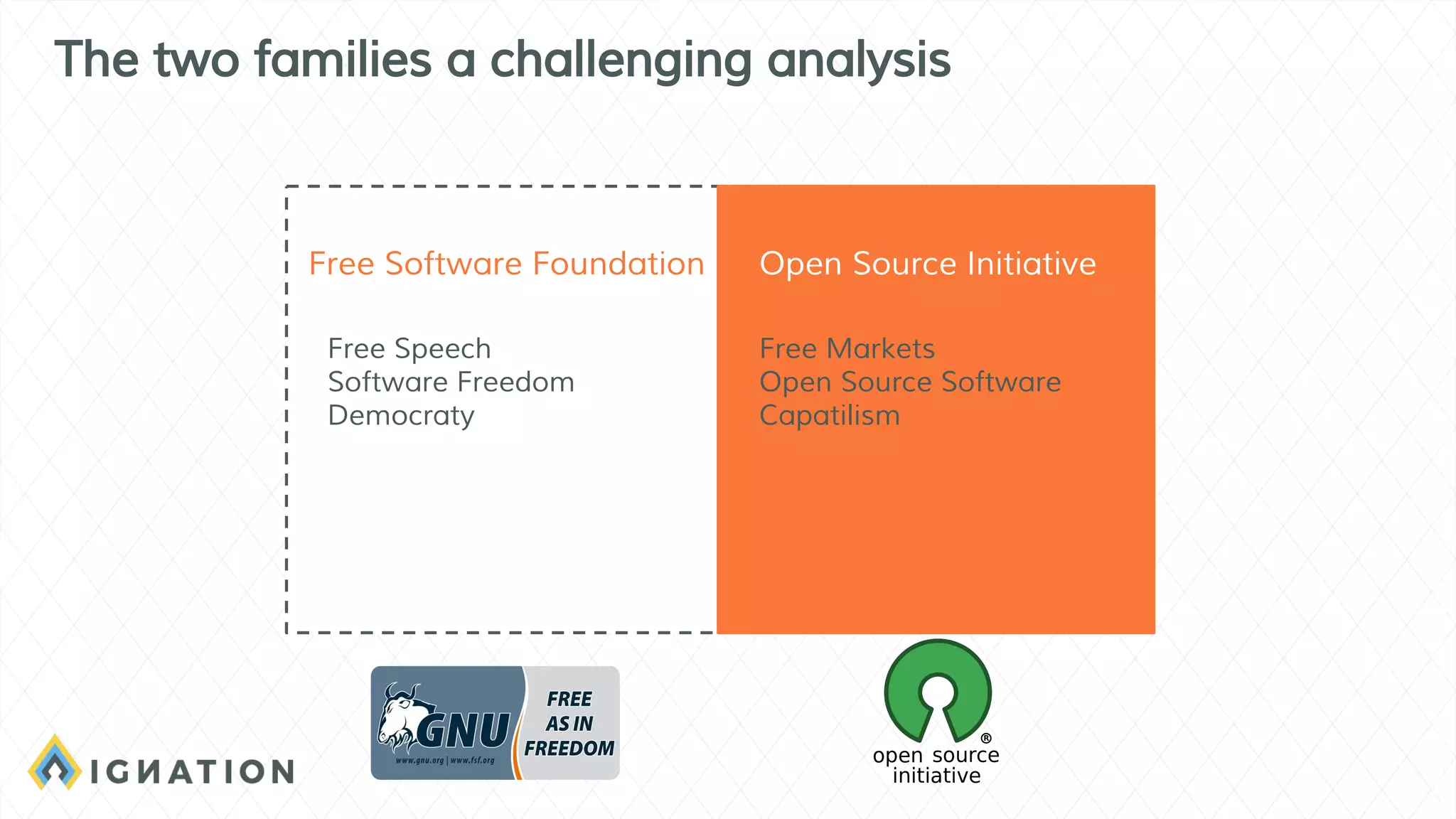
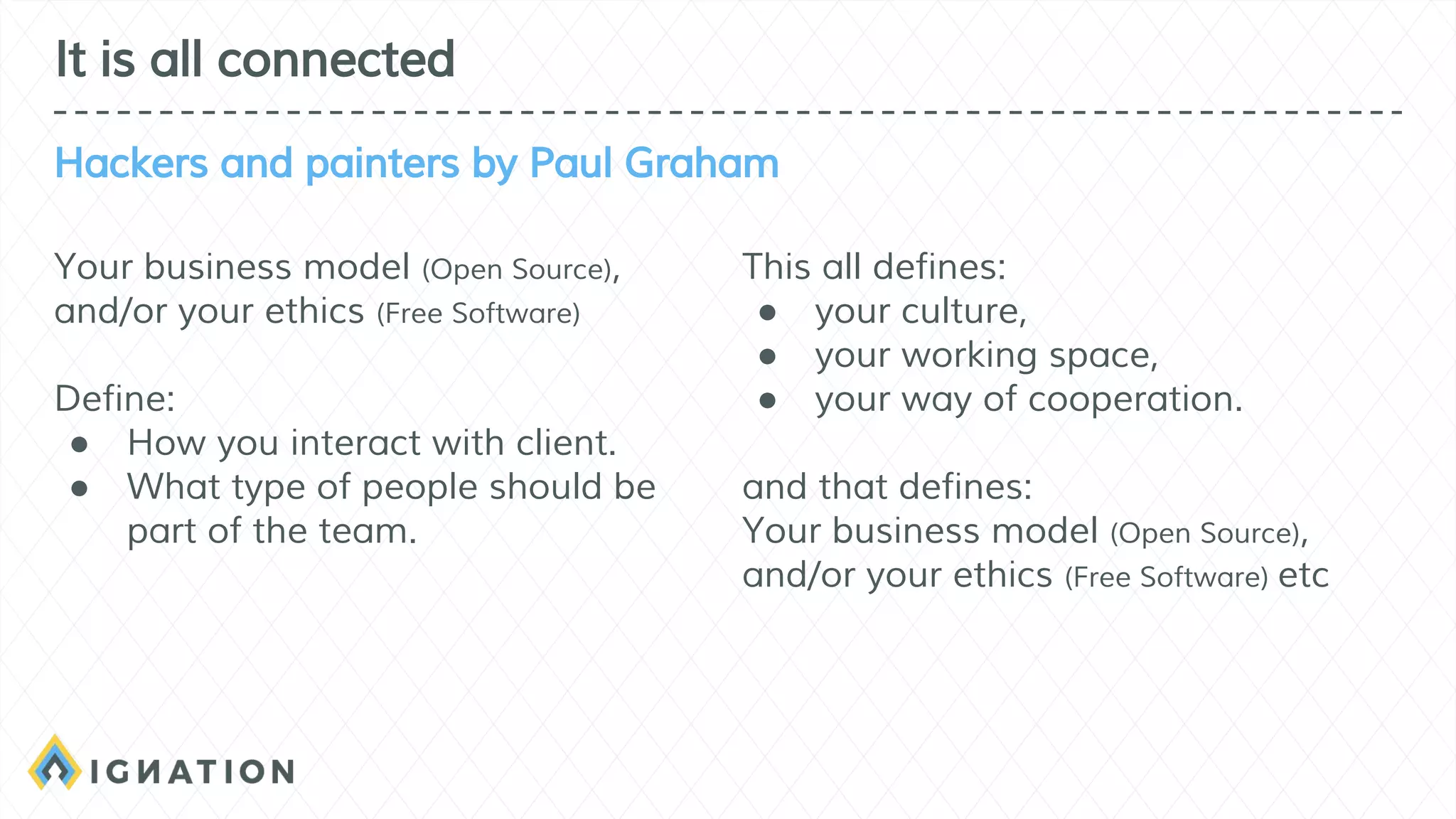
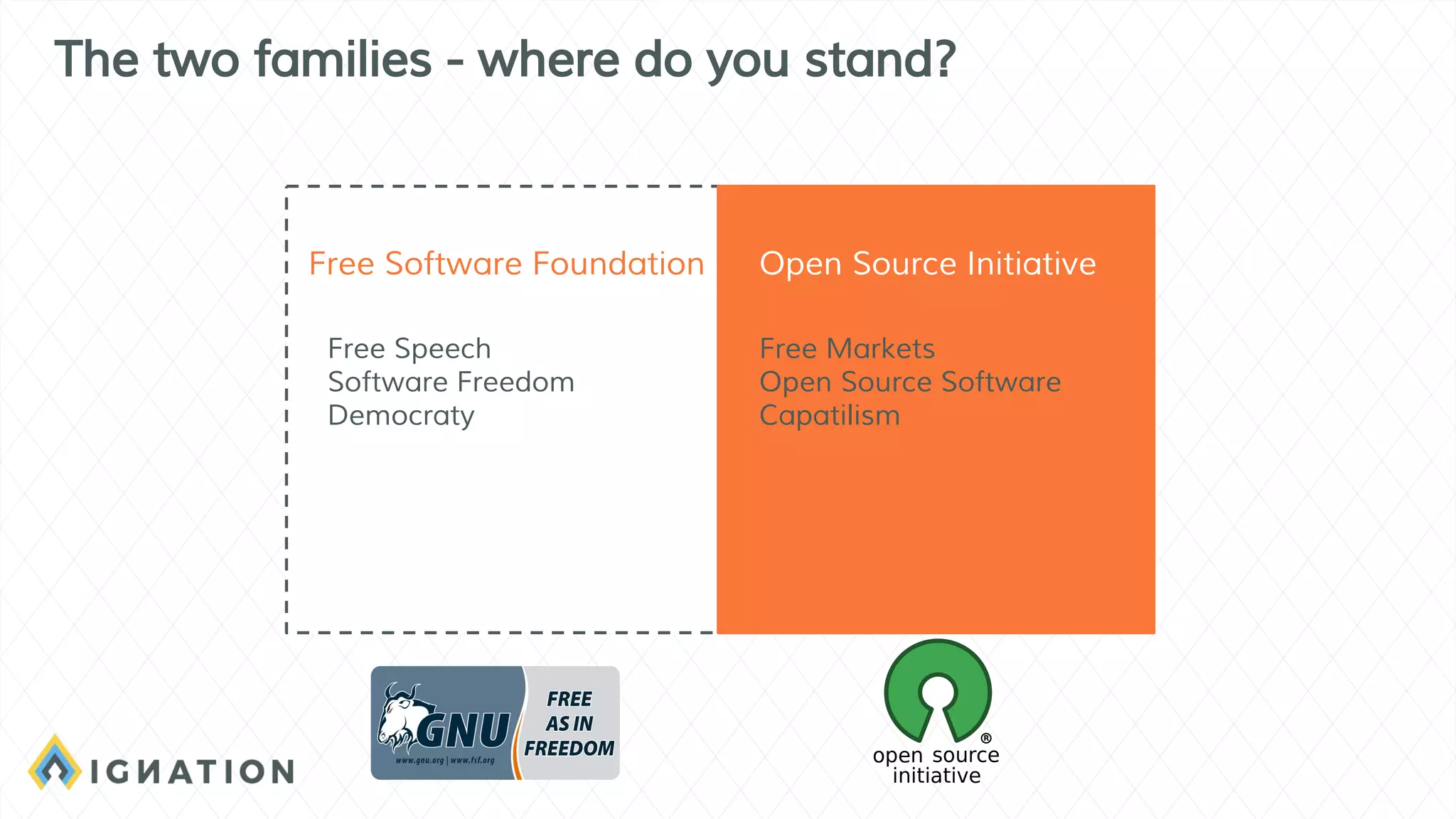
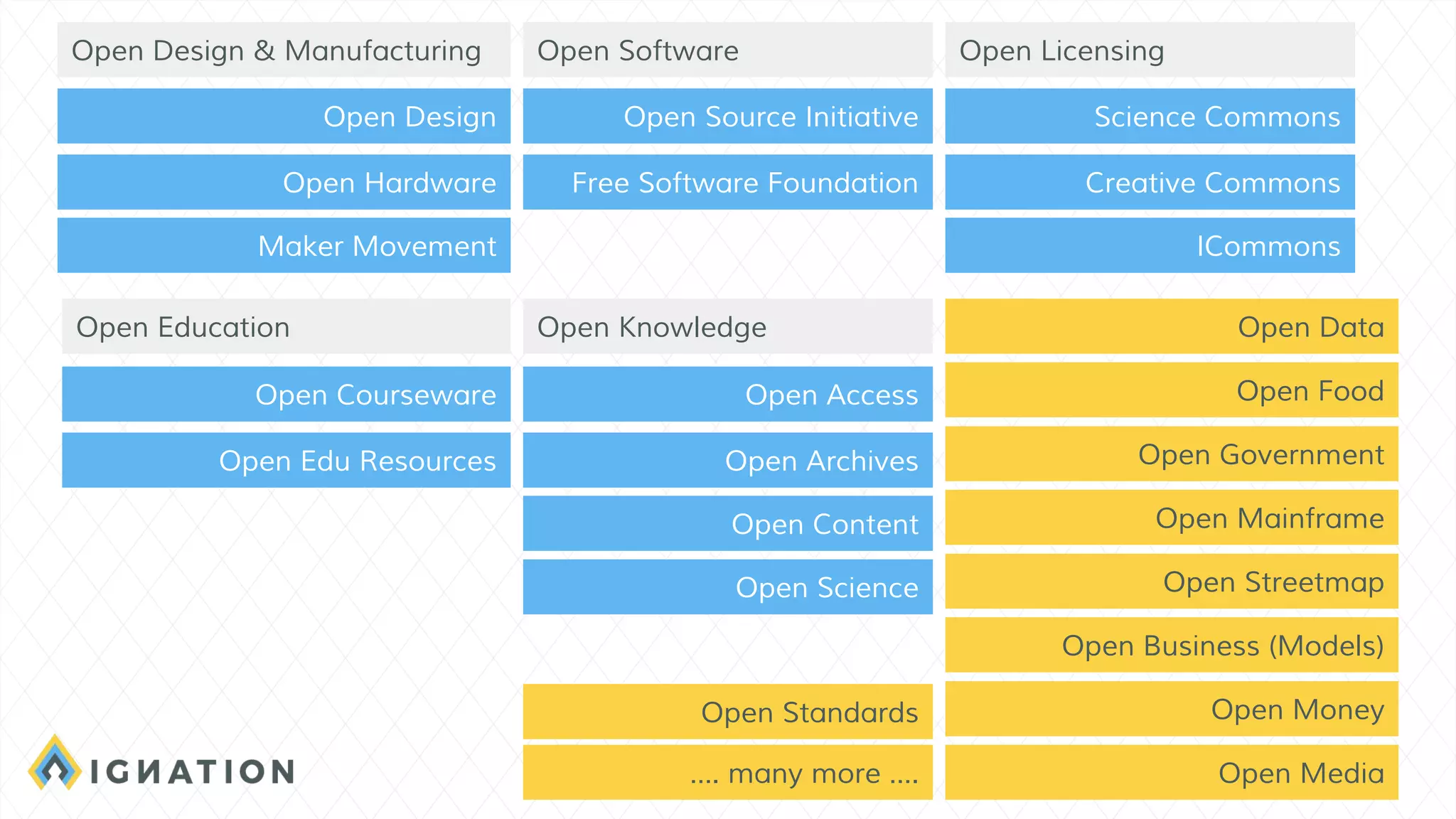
The document outlines the history and evolution of open source and free software, emphasizing key milestones from the 1960s to the present, including significant court cases and foundational movements like the Free Software Foundation and the Open Source Initiative. It discusses the philosophical differences between free software, which sees proprietary software as a social issue, and open source software, which focuses on practical business advantages. Additionally, it addresses the importance of community, business models, and ethical considerations in shaping software development and sharing practices.