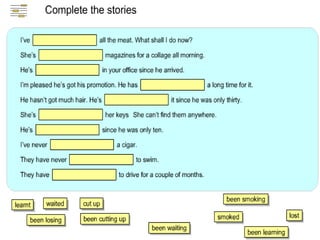
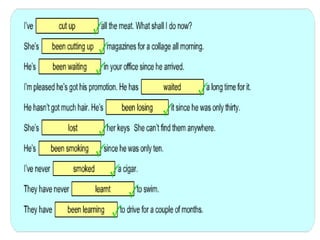
The document discusses the differences between the present perfect and present perfect continuous tenses. The present perfect is used for finished actions that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, while the present perfect continuous is used for unfinished or ongoing actions that began in the past and continue in the present. There are some exceptions where the tenses can be used interchangeably or where one emphasizes duration over the other.