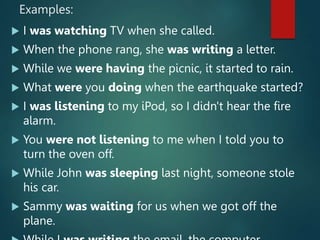
1) The document discusses the past continuous tense in English, which is used to describe actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past.
2) It provides examples of how to form the past continuous tense and common uses including interrupted actions, parallel actions, setting an atmosphere, and expressing repetition or irritation with words like "always."
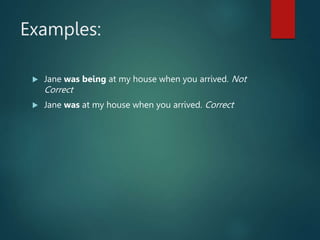
3) The summary also notes the differences between using "when" and "while" with the past continuous tense and limitations with non-continuous verbs.