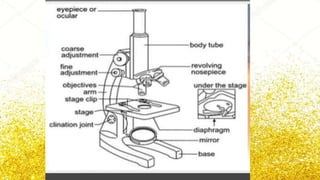
The document provides information about the major organs and systems in the human body like the liver, heart, kidneys, lungs and brain. It then discusses the parts and functions of a microscope, identifying components such as the eyepiece, body tube, stage, objectives, and how it is used to magnify specimens. The importance of the compound microscope is that it allows scientists to observe microorganisms, cells, and other small structures.