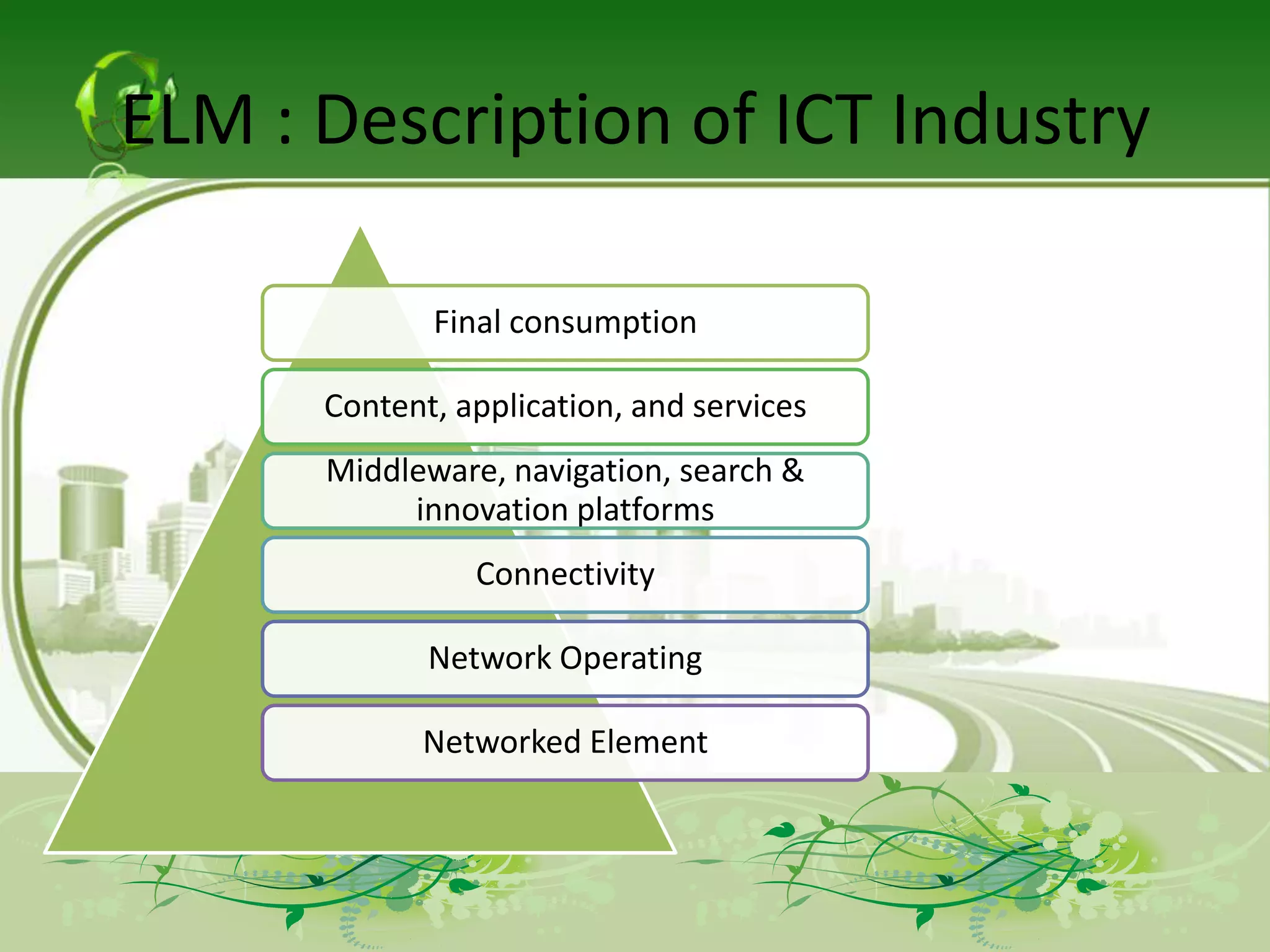
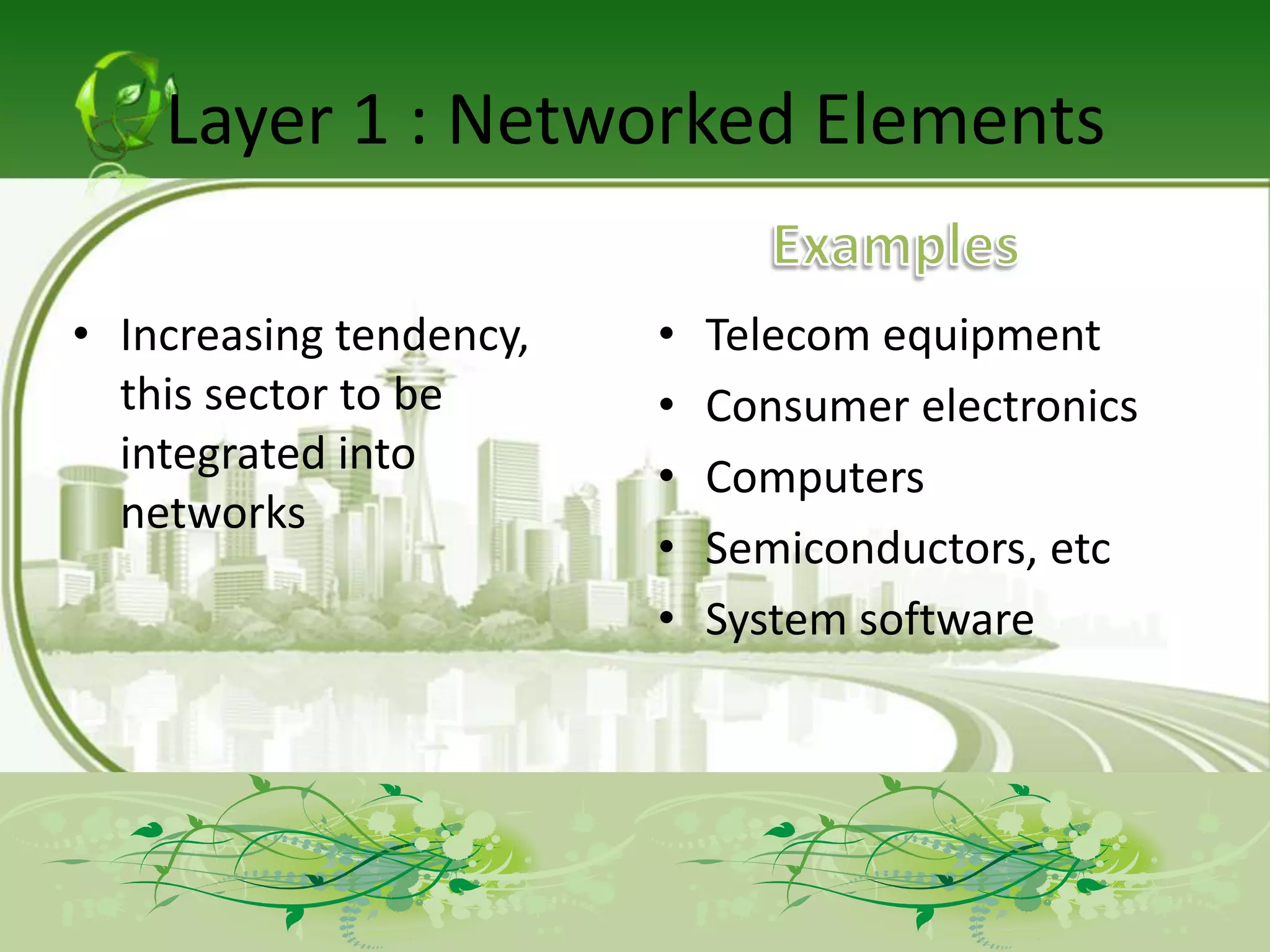
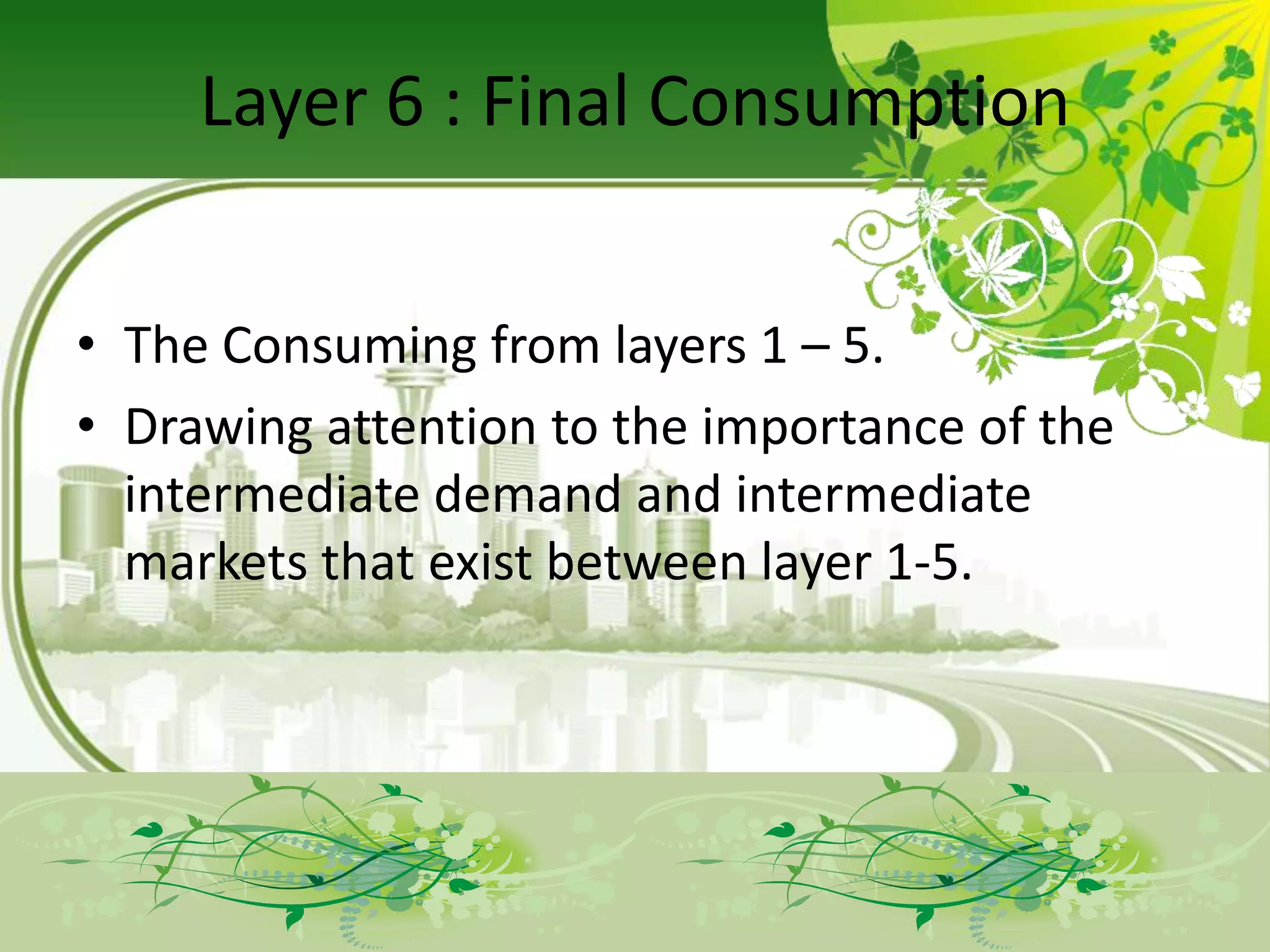
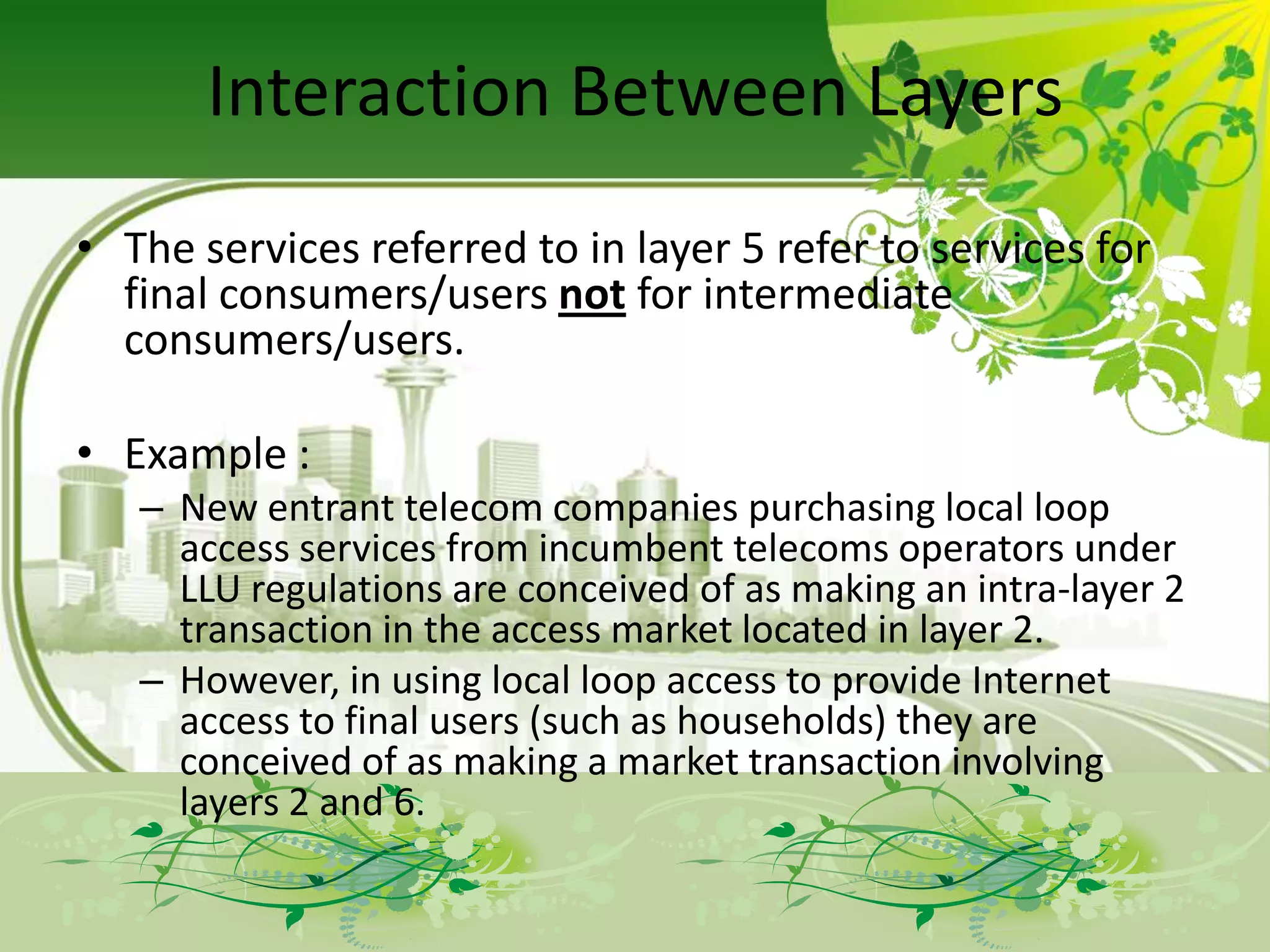
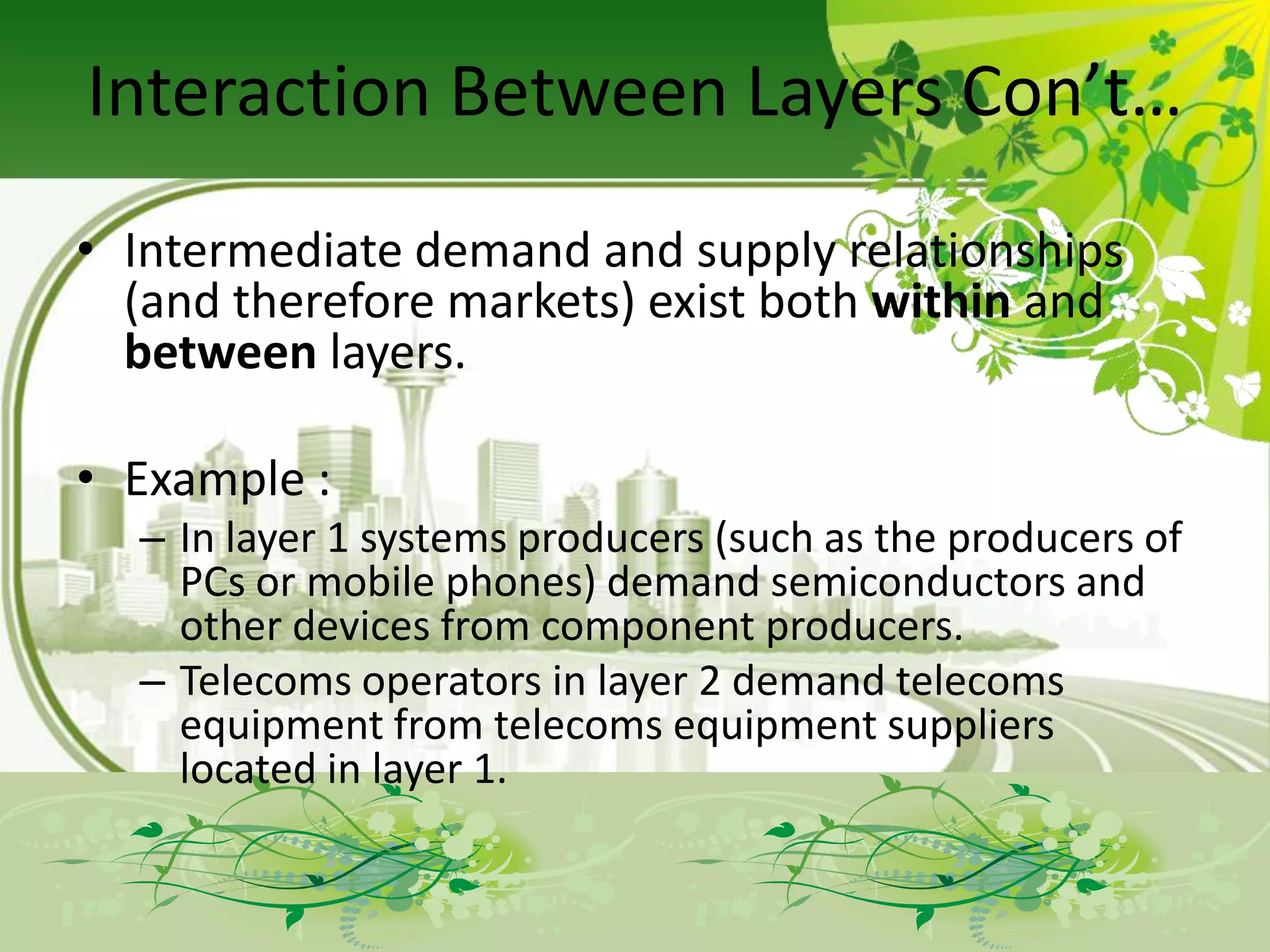
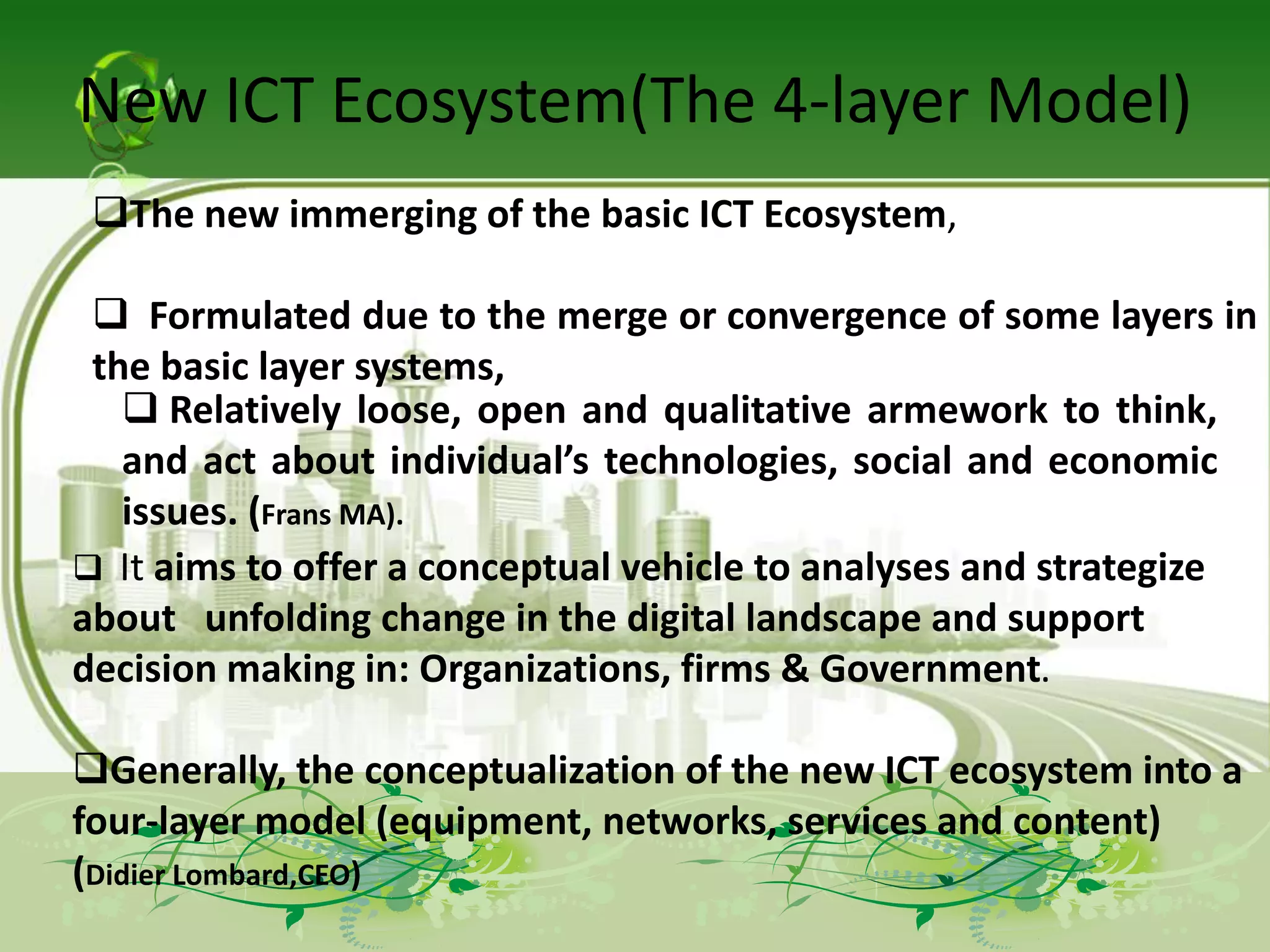
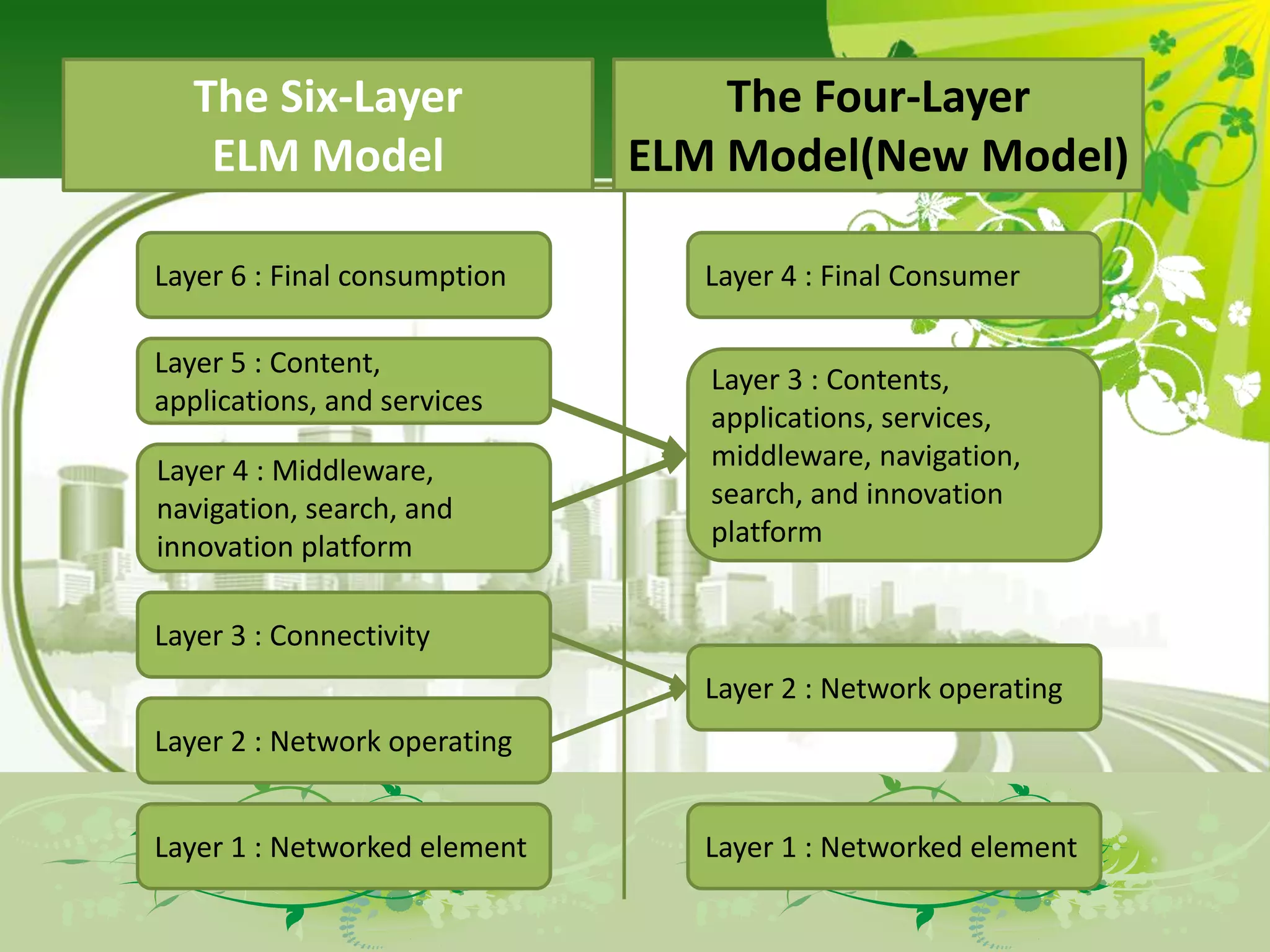
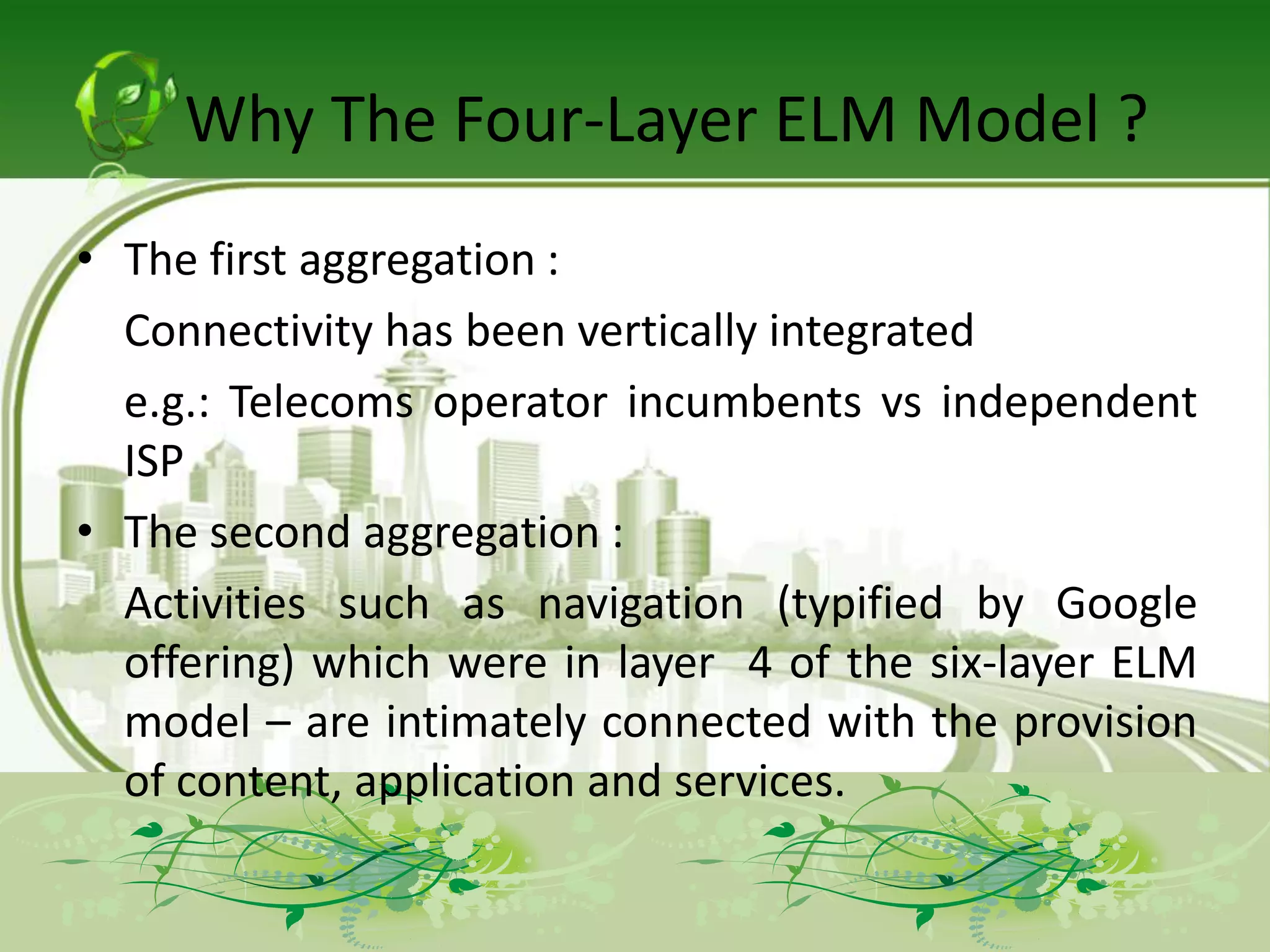
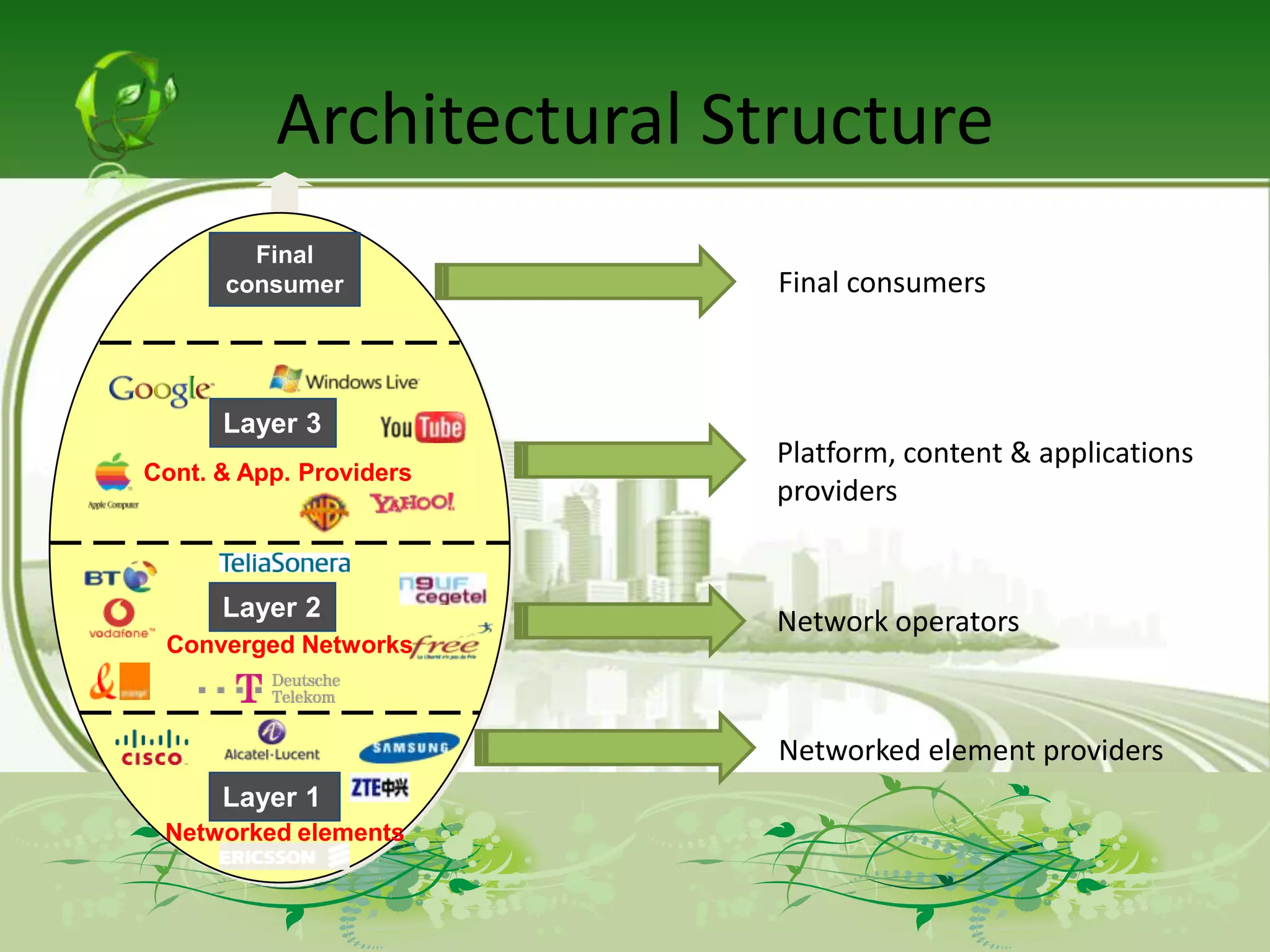
The document describes the evolution of models for the ICT ecosystem from a six-layer model to a new four-layer model. The six-layer model included layers for networked elements, network operating, connectivity, middleware/navigation/search, content/applications/services, and final consumption. The new four-layer model aggregated some of these layers due to convergence of technologies and activities. Specifically, it merged connectivity with network operating, and merged middleware/navigation/search with content/applications/services. This new four-layer model includes layers for networked elements, converged networks, content/applications/platforms, and final consumers.