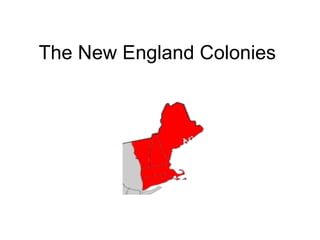
The New England colonies consisted of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island. The climate was colder than other regions due to its northern location, which prevented diseases but also caused severe winters that killed people. The geography was mostly hilly with rocky soil unsuitable for farming, so the economy depended on natural resources like fish, whales, trees, and furs. Shipbuilding, rum production from molasses, and the triangular slave trade were important economic activities. Towns focused on religion, especially Puritanism, and did not tolerate other faiths. Most residents lived in villages and worked small nearby farms or trades.