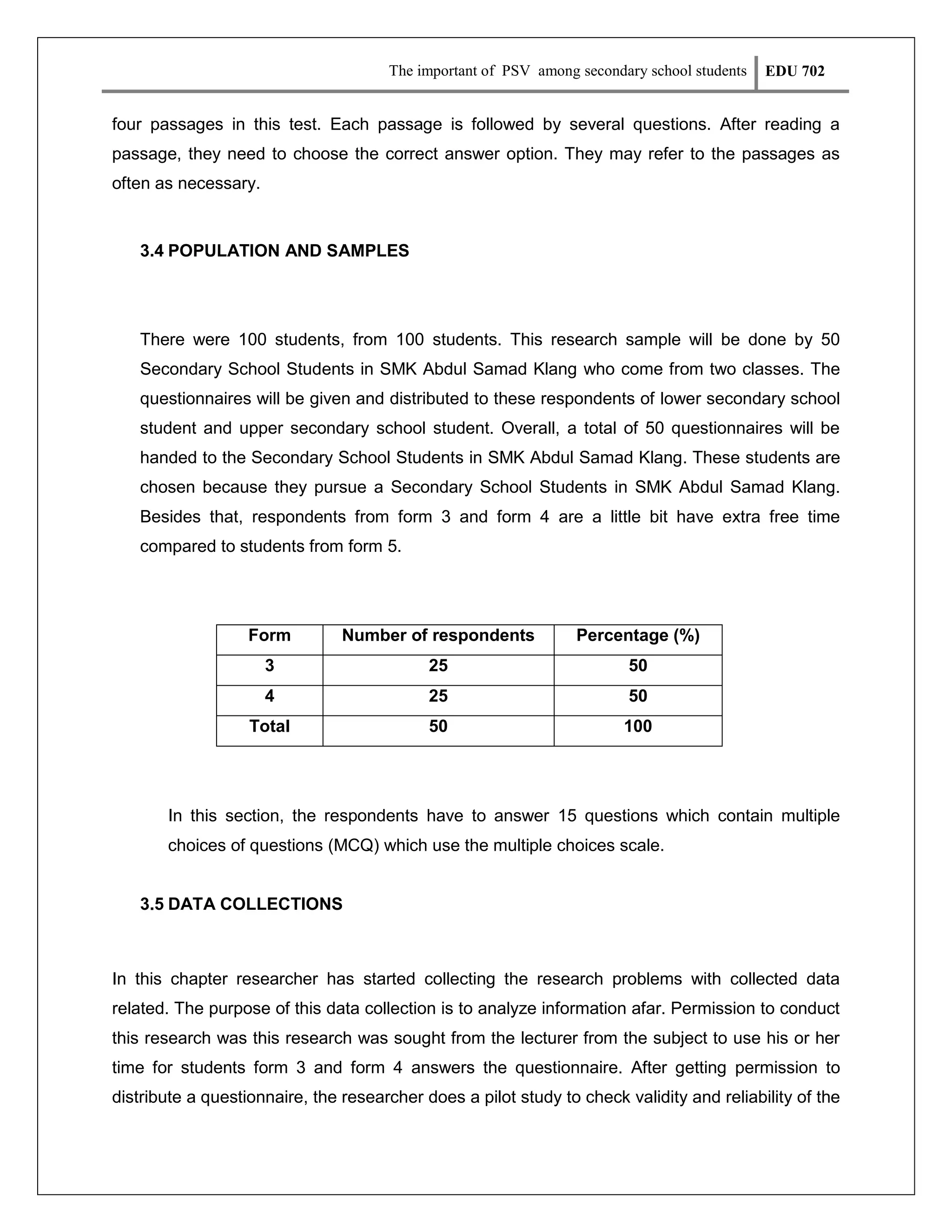
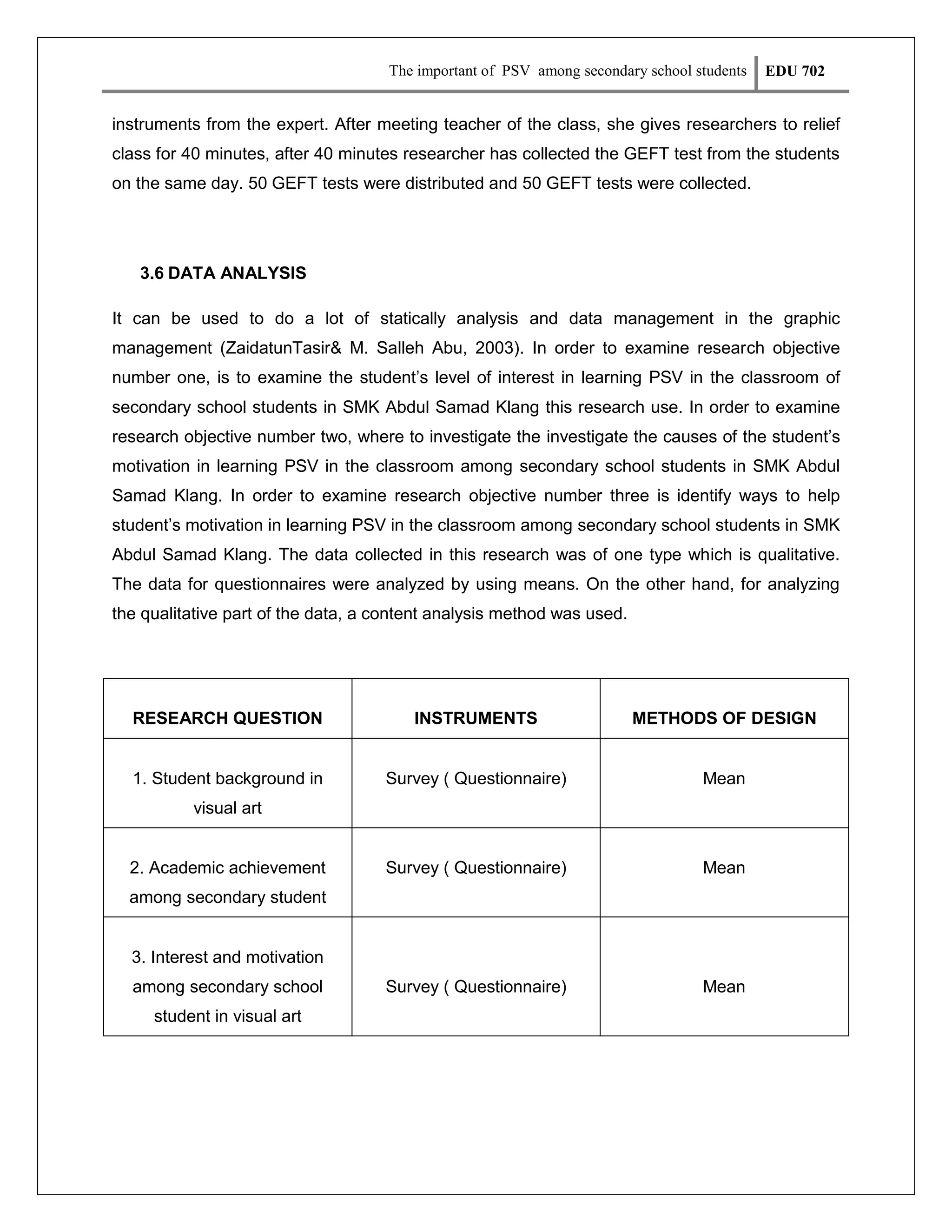
This document discusses a research proposal on examining the importance of visual art (PSV) among secondary school students in Malaysia. It aims to investigate student interest levels and motivation in learning PSV, and identify ways to help improve student motivation. The study is significant as it could enhance how PSV is taught and help standardize the subject. The literature review discusses previous studies on factors influencing student interest in PSV, such as individual differences, talent, and teaching methods. The study's objectives are to examine student interest levels and motivation in PSV, understand the causes of low motivation, and identify ways to increase motivation.