1. The document outlines principles and components for planning art and elementary classroom lessons that integrate art with other subjects like reading, science, and social studies.
2. It discusses identifying a "big idea", researching artworks and literature to inspire lesson ideas, and planning learning experiences where teachers and students work together on community-focused projects.
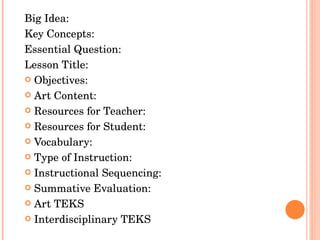
3. The sample lesson plan template includes sections for objectives, resources, vocabulary, instructional strategies with motivation, instruction, practice, and assessment.