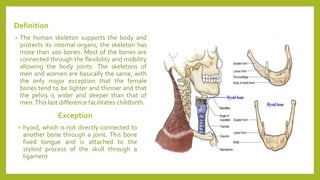
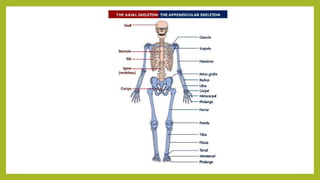
The human skeleton consists of over 200 bones that support the body, protect internal organs, and allow for movement. The axial skeleton contains 80 bones including the skull, spine, ribs, and sternum, while the appendicular skeleton has 128 bones that make up the limbs. Key differences between male and female skeletons include lighter and thinner bones in women, and a wider pelvis to facilitate childbirth. Careers that involve studying the human skeleton include forensic anthropology and traumatology, which examines bone injuries and fractures to understand impacts to structure and function.