The document summarizes key aspects of the French Revolution including:
1) Important figures like Napoleon Bonaparte, Louis XVI, and Robespierre.
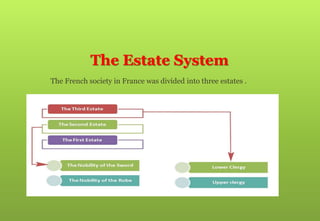
2) Discrimination in the estate system which caused resentment among the third estate who faced high taxes.
3) Events that sparked the revolution like the subsistence crisis and storming of the Bastille.
4) Changes like abolishing the monarchy and establishing a republic, and symbols of the revolution like the tricolor flag and Phrygian cap.