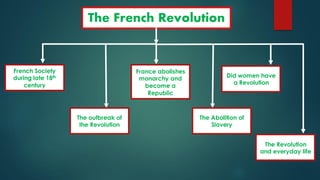
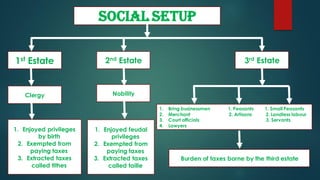
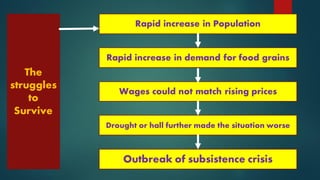
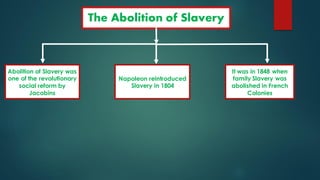
The French Revolution began in 1789 due to financial troubles from wars and an extravagant royal court that led the king to impose high taxes, mostly on the Third Estate. As economic conditions worsened and ideas of equality and democracy spread, the Third Estate revolted and formed the National Assembly. On July 14, 1789 angry mobs in Paris stormed the Bastille prison, starting the Revolution. France became a constitutional monarchy but growing unrest led to the establishment of the First French Republic in 1792 and the execution of the king and queen. A Reign of Terror followed under Robespierre until his own execution in 1794, after which the Directory ruled until Napoleon's rise to power.