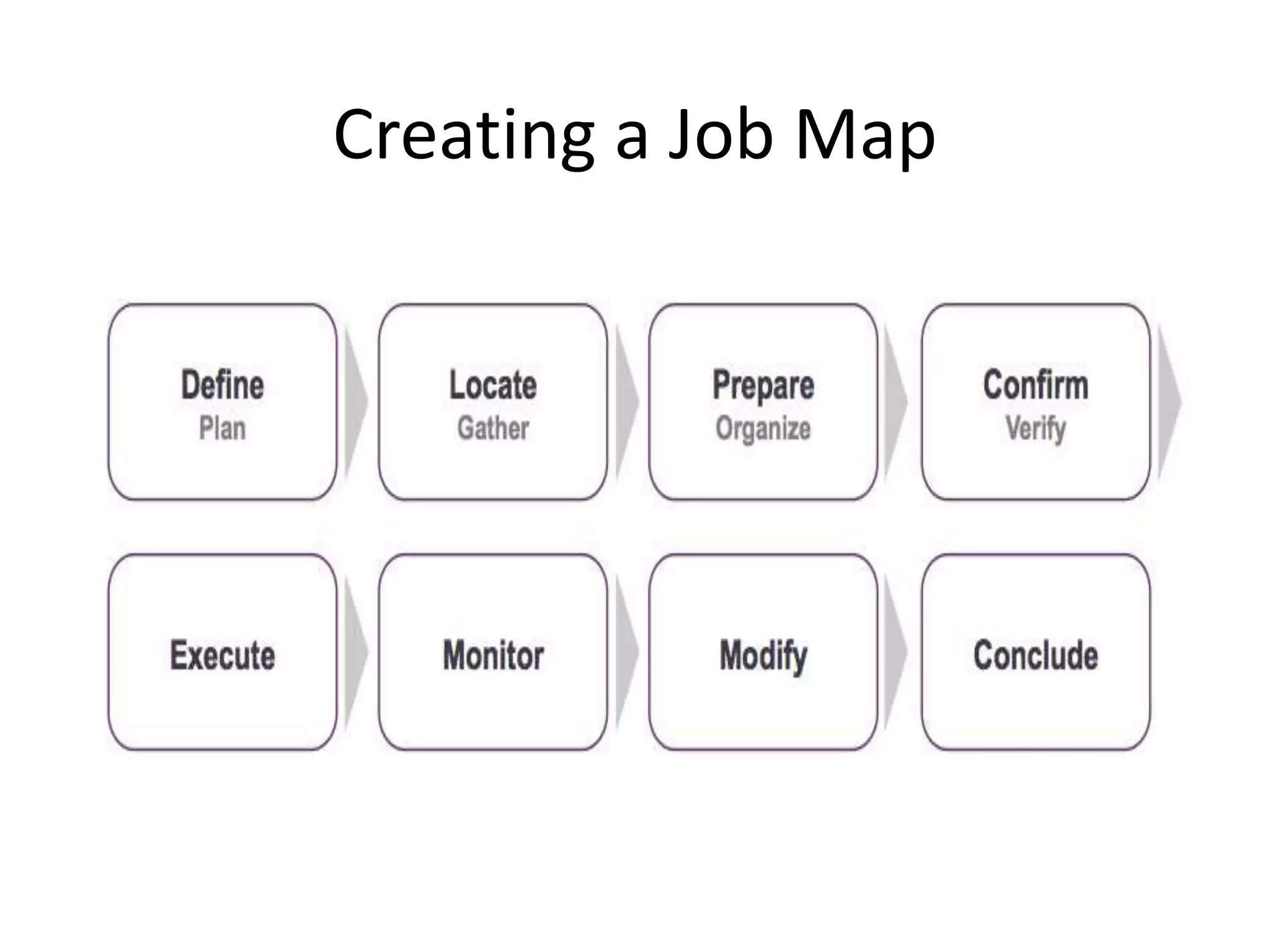
Job mapping involves breaking a job down into its constituent steps:
1) Define the objective and plan the approach
2) Locate the necessary inputs
3) Prepare the inputs and environment
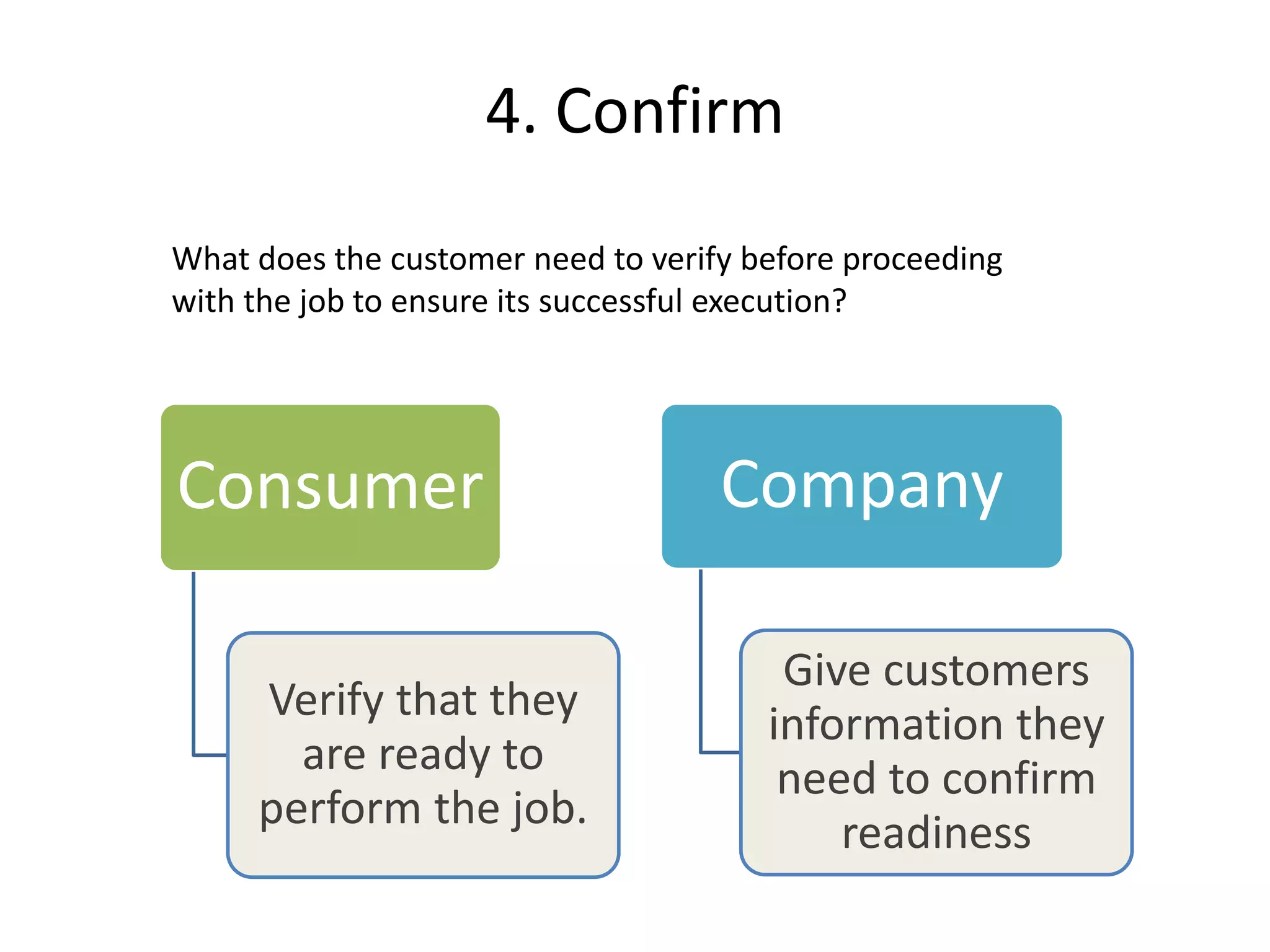
4) Confirm readiness to execute
5) Execute the job
6) Monitor the job's execution
7) Modify if needed to complete the job successfully
8) Conclude the job by finishing or preparing to repeat
Understanding the job from the customer's perspective allows companies to innovate by improving execution, eliminating steps, enabling new locations/times, or addressing overlooked steps.