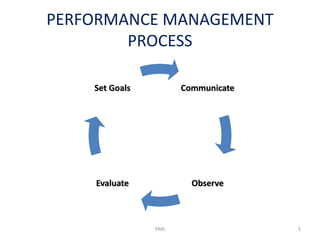
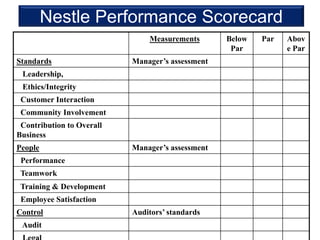
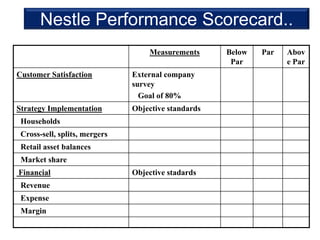
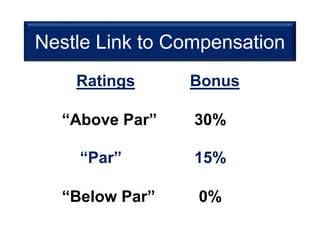
This document discusses performance management systems (PMS). It defines performance management as identifying, measuring, and evaluating employee performance to align it with organizational goals. A key part of PMS is continuous communication between managers and employees to set expectations, provide feedback, and evaluate results. The document contrasts performance management, which is an ongoing process to improve effectiveness, with performance appraisal, which is an annual formal review. It outlines why companies like Nestle consider PMS important for talent development, continuous learning, and building diverse high-performing teams. The document also discusses techniques Nestle uses in its PMS, including a balanced scorecard linked to compensation.