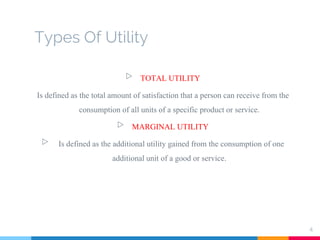
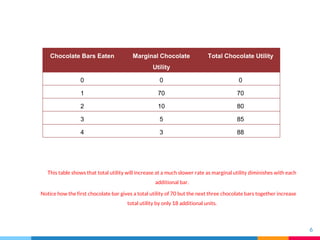
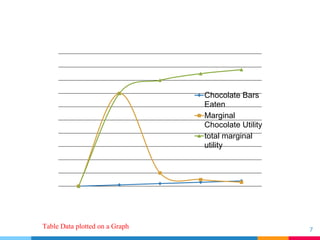
Utility refers to the total satisfaction received from consuming a good or service. Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit, while total utility is the satisfaction from all units consumed. Diminishing marginal utility means that each additional unit provides less satisfaction than the previous one, as shown by the example of chocolate bars. The first bar has a high marginal utility of 70, but each additional bar provides less, with the total utility increasing more slowly. This concept helps explain the downward sloping demand curve, as consumers are willing to pay more for additional units when marginal utility is higher at lower quantities consumed.