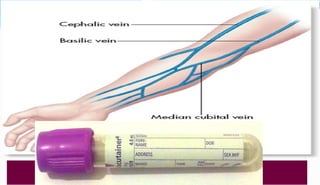
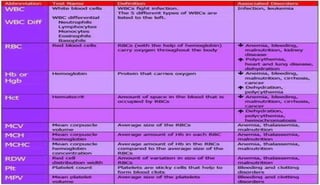
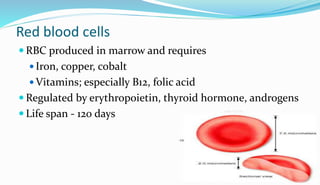
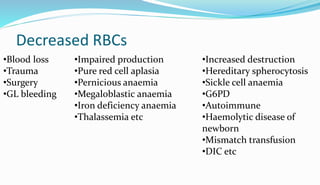
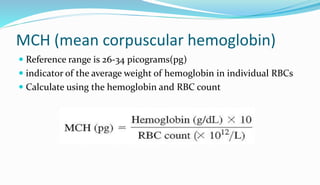
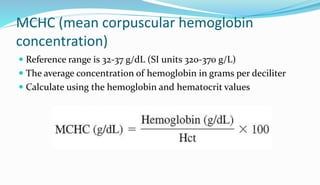
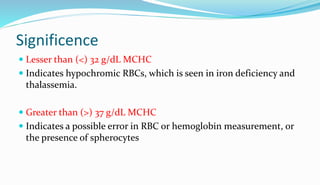
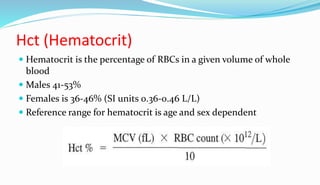
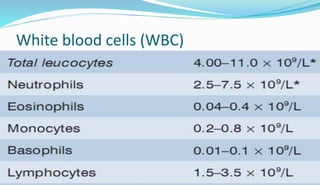
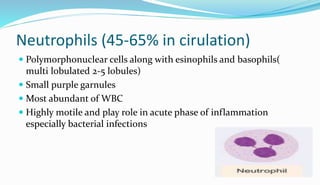
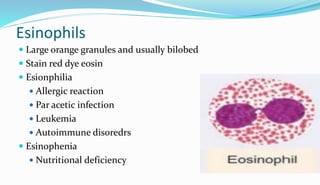
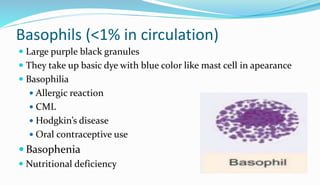
The document provides information about a complete blood count (CBC) test. It discusses the various cellular components of blood that are evaluated in a CBC like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. For each cell type, it describes their normal ranges, clinical significance of abnormal values, and what conditions they may indicate. The CBC provides important clues about a person's overall health by examining the number and types of circulating cells in their blood.