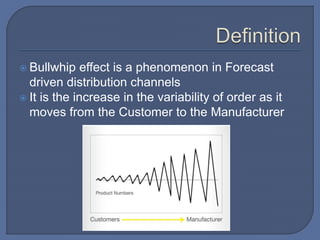
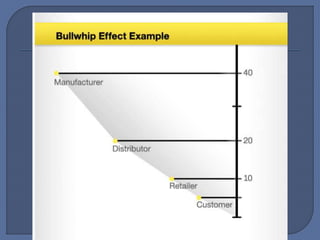
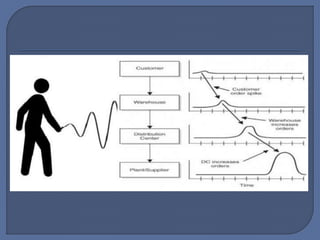
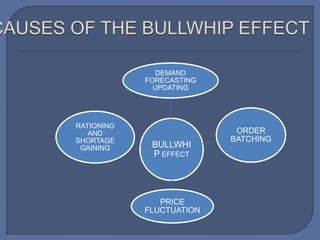
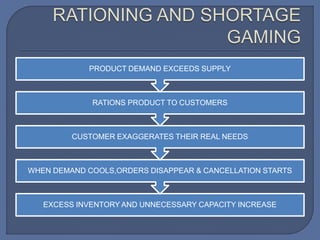
The document discusses the bullwhip effect, which is an increase in variability of orders as they move up the supply chain from customer to manufacturer. Some symptoms of the bullwhip effect include excessive inventory, poor forecasts, insufficient capacity, and long backlogs. The bullwhip effect can be caused by factors such as forecasting methods, order batching, price fluctuations, rationing during shortages, and gaining behavior. Strategies to mitigate the bullwhip effect include improved forecasting methods, visibility of downstream demand data through approaches like VMI/CRP, bypassing intermediaries, and reducing price discounting and order exaggeration.