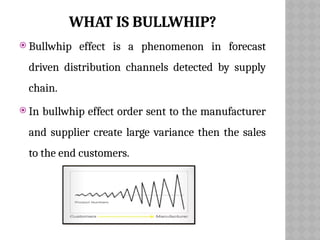
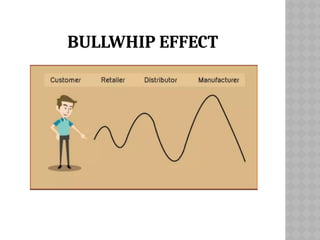
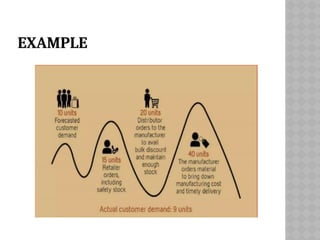
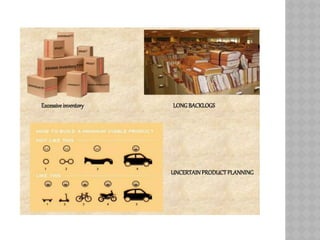
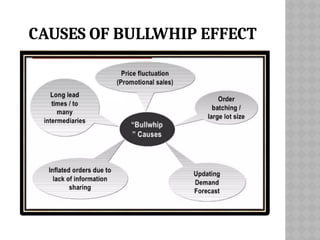
The bullwhip effect is a phenomenon in supply chain management where small changes in customer demand lead to large fluctuations in orders placed by retailers and manufacturers. This distortion is caused by factors such as disorganization, lack of communication, and order batching, resulting in excessive inventory and inaccurate product forecasts. To mitigate the bullwhip effect, real-time demand information and information sharing among supply chain partners are essential.