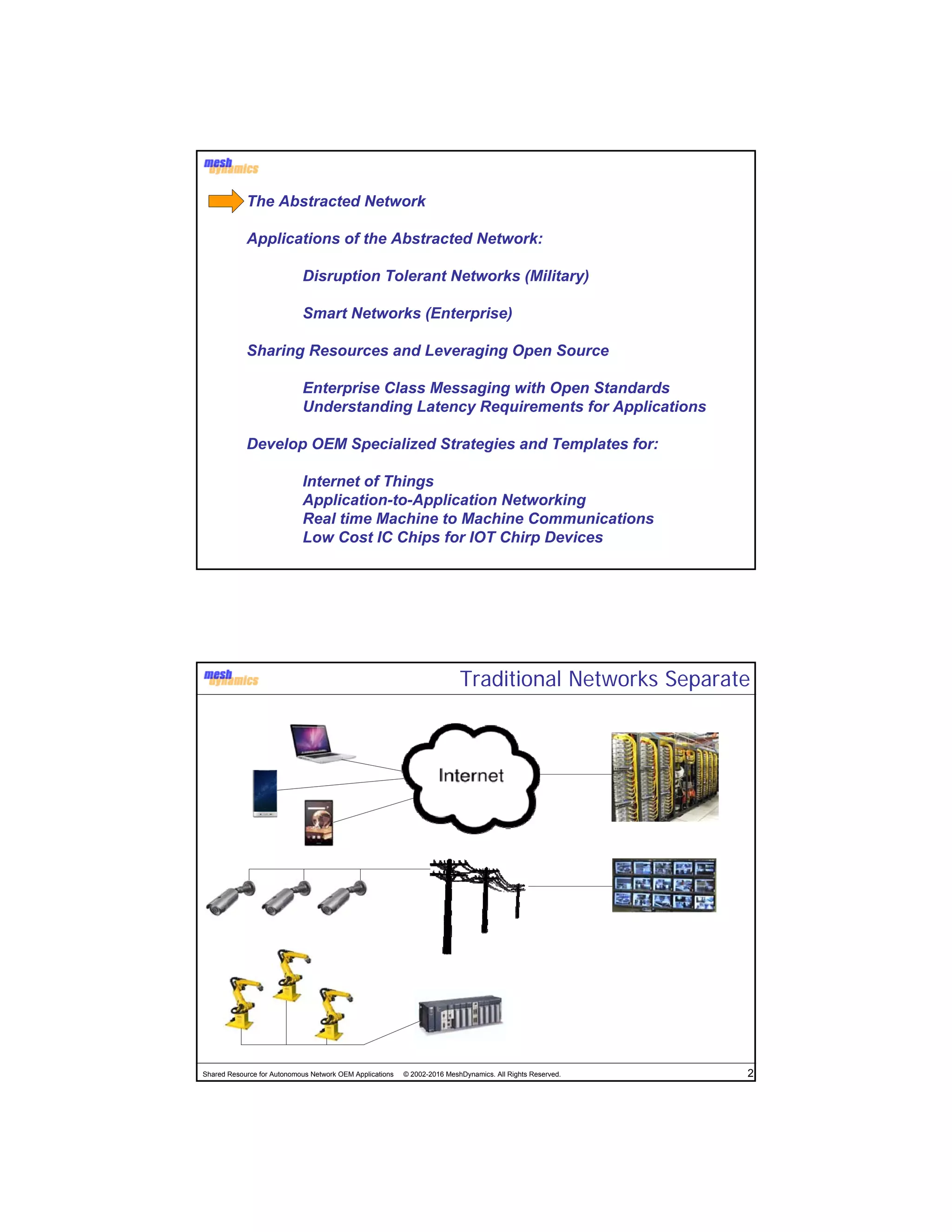
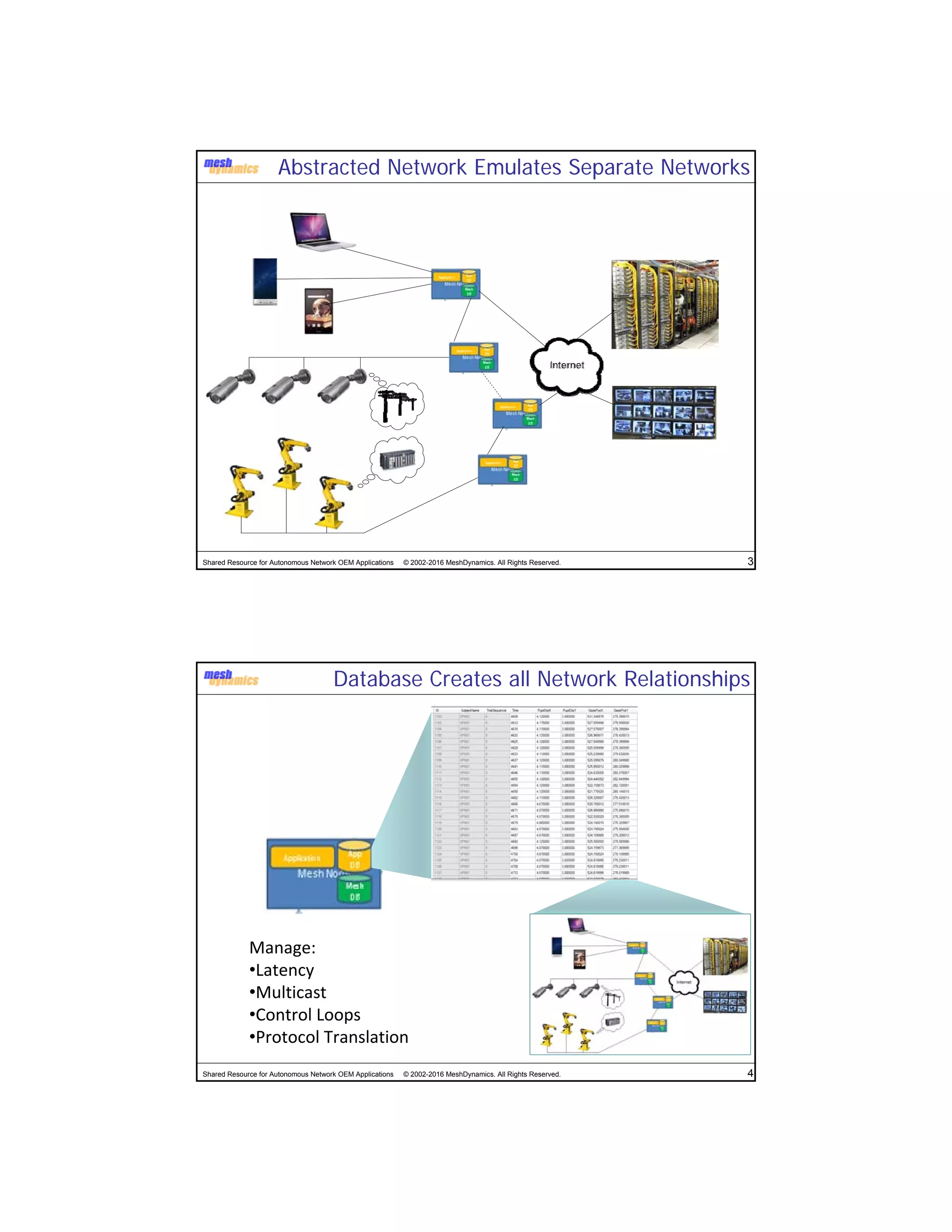
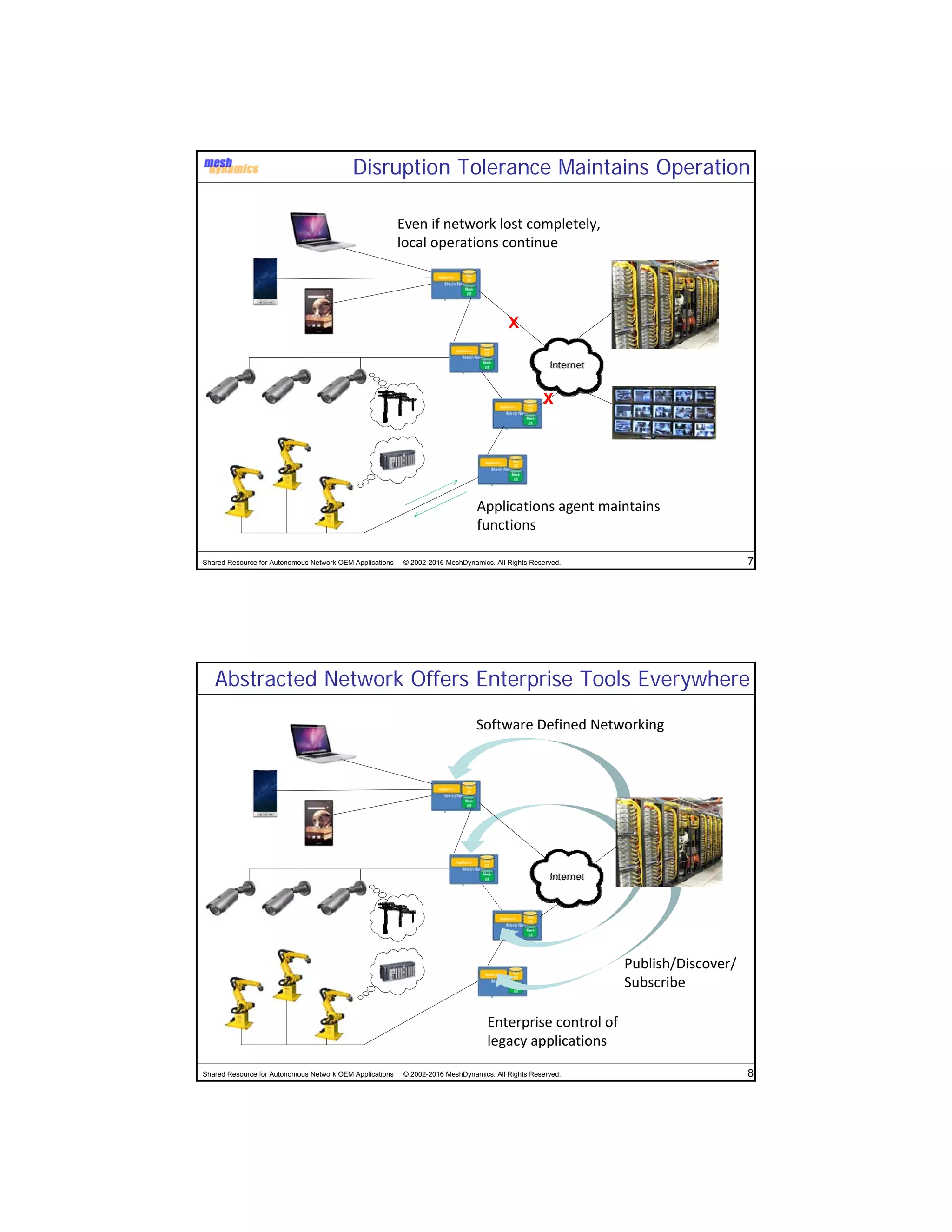
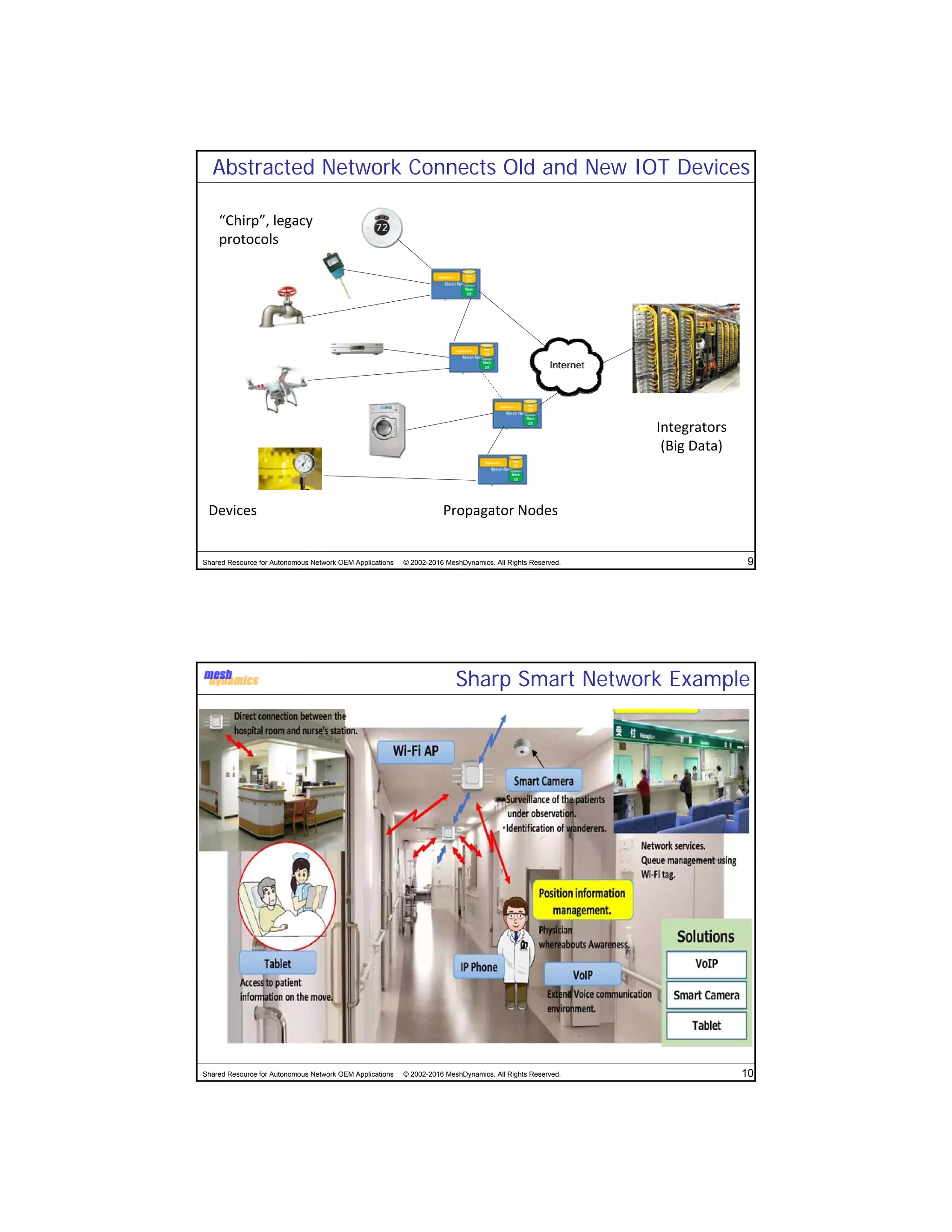
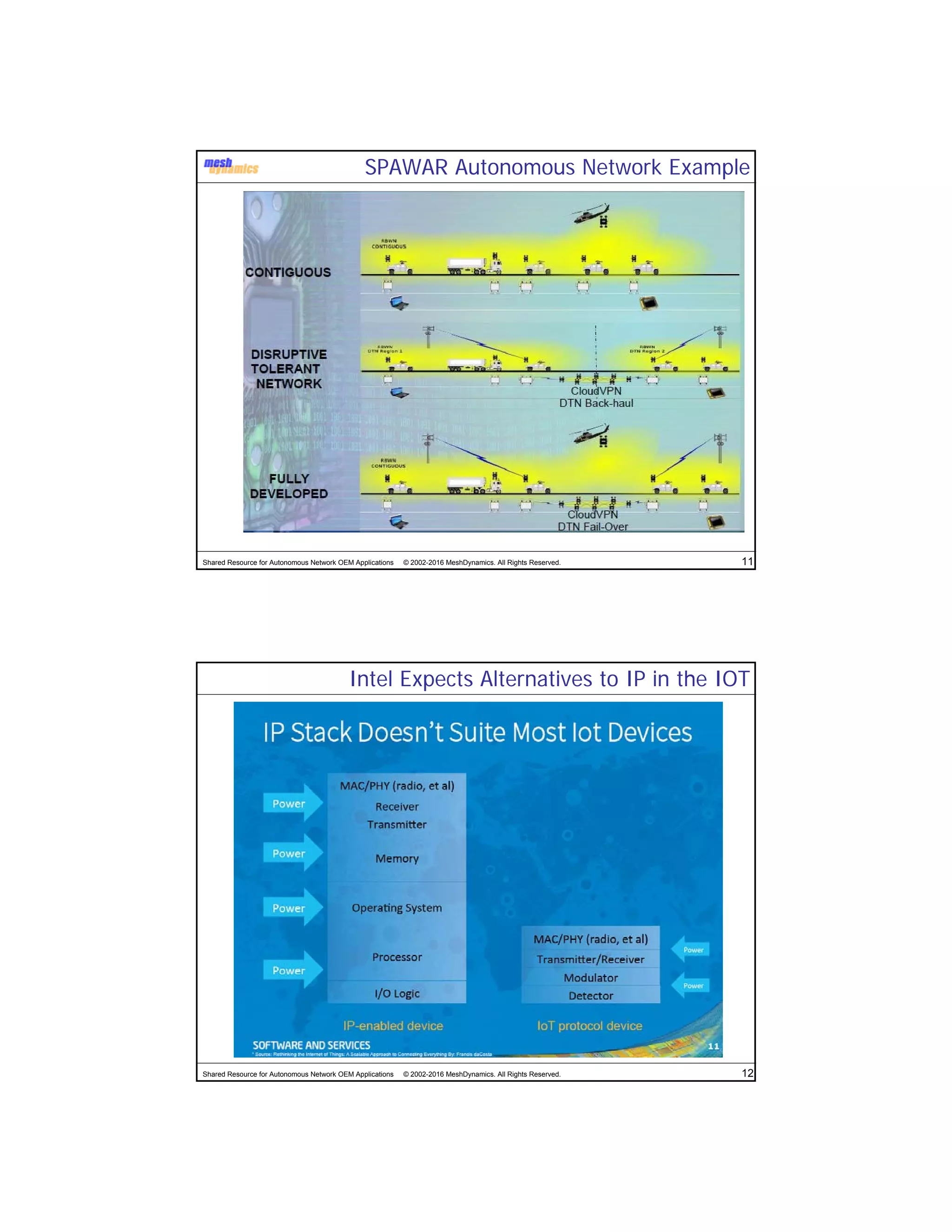
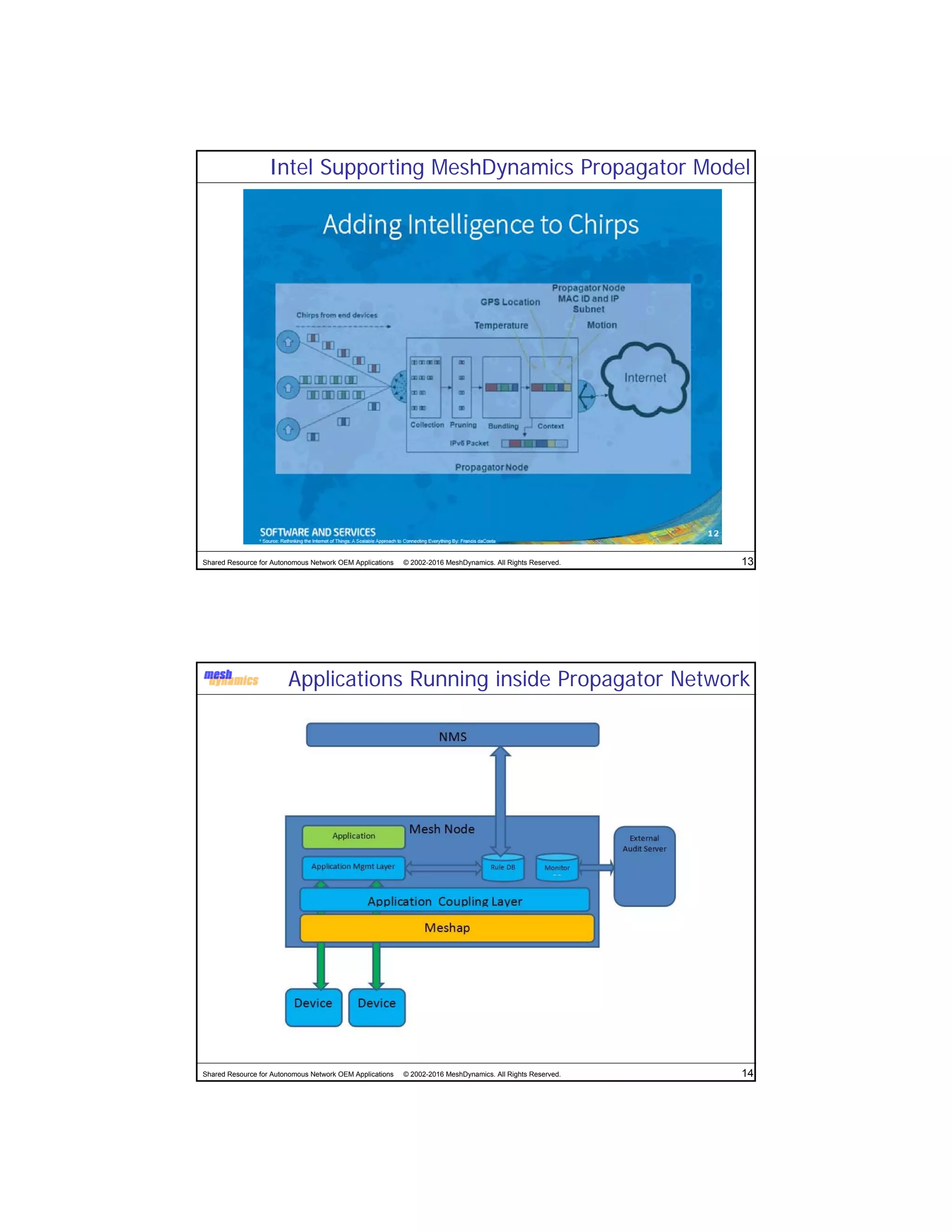
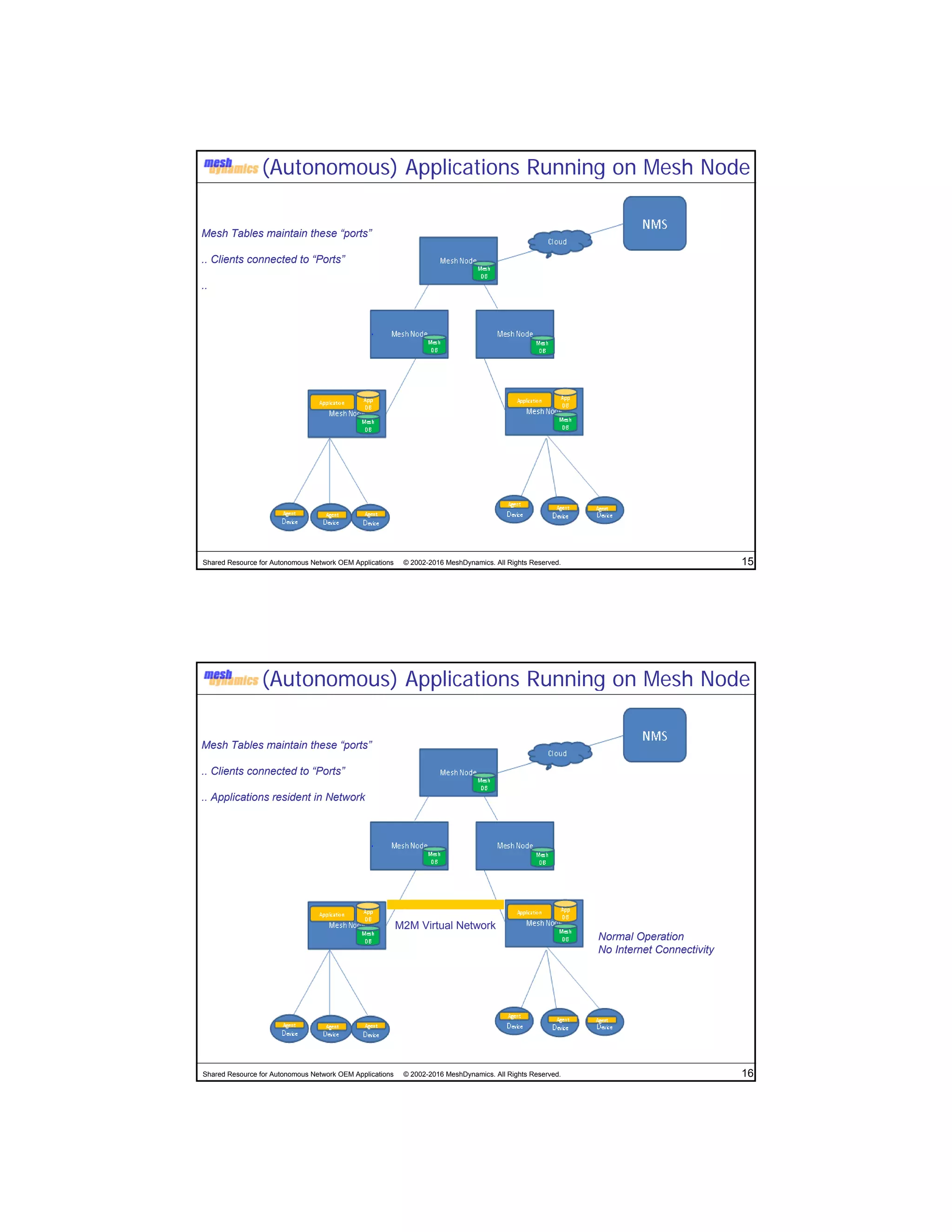
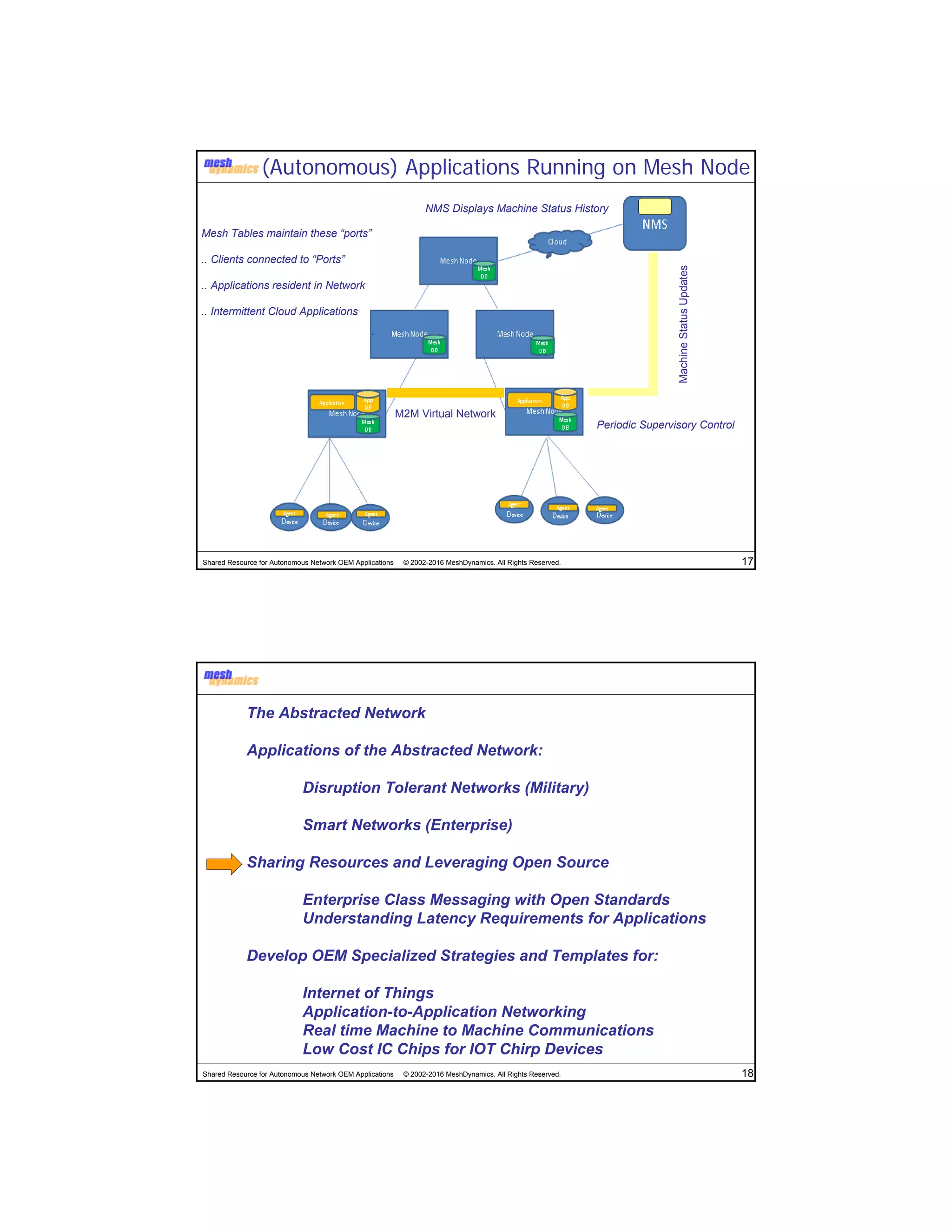
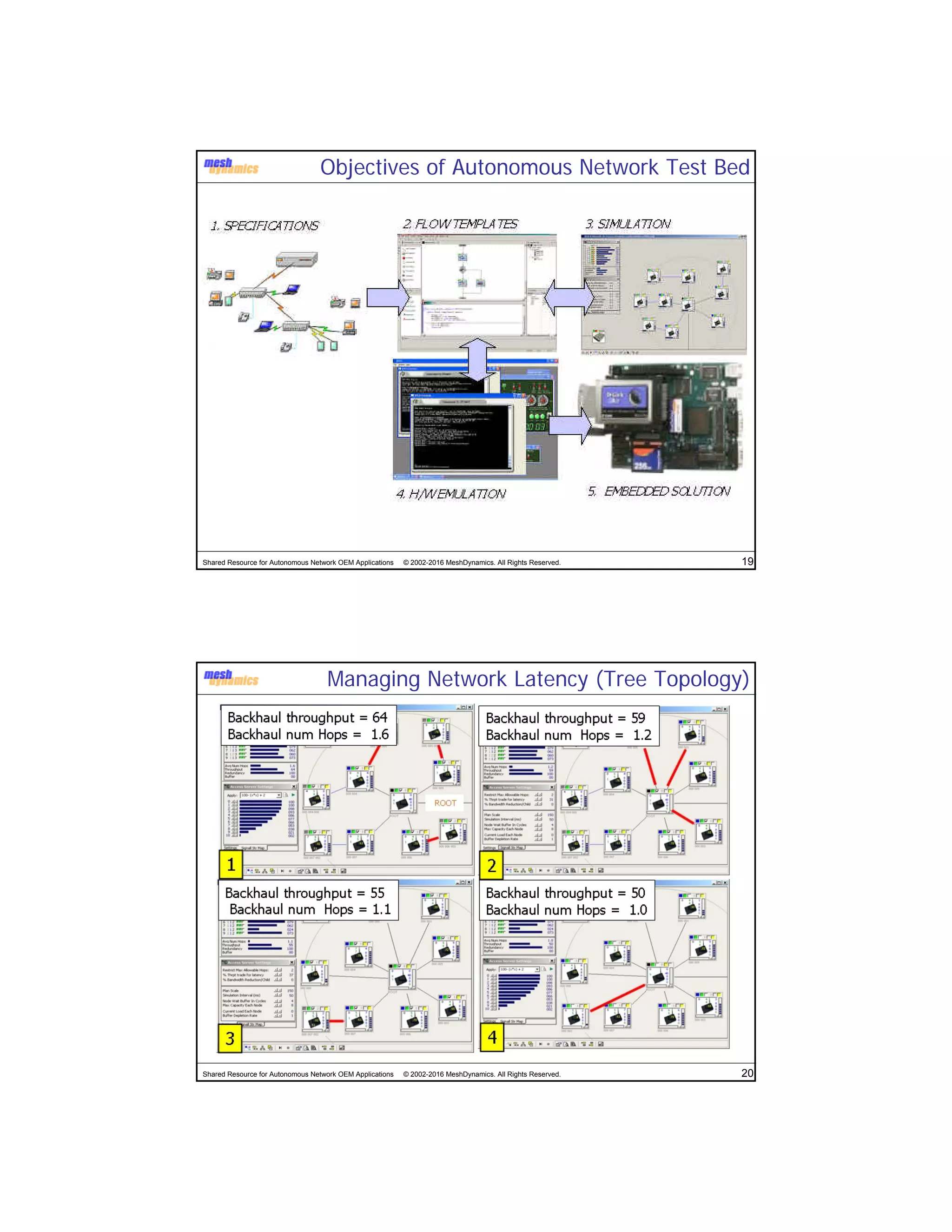
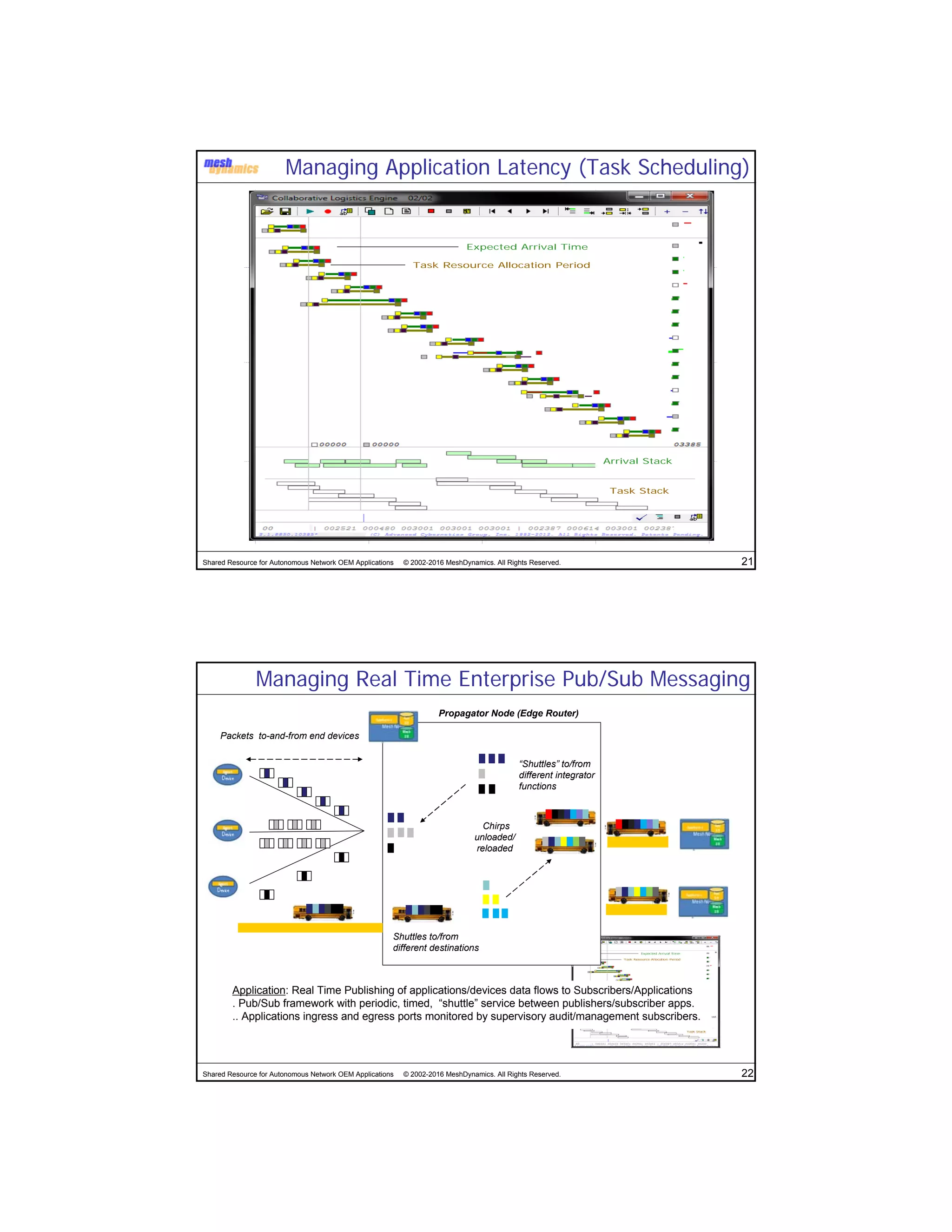
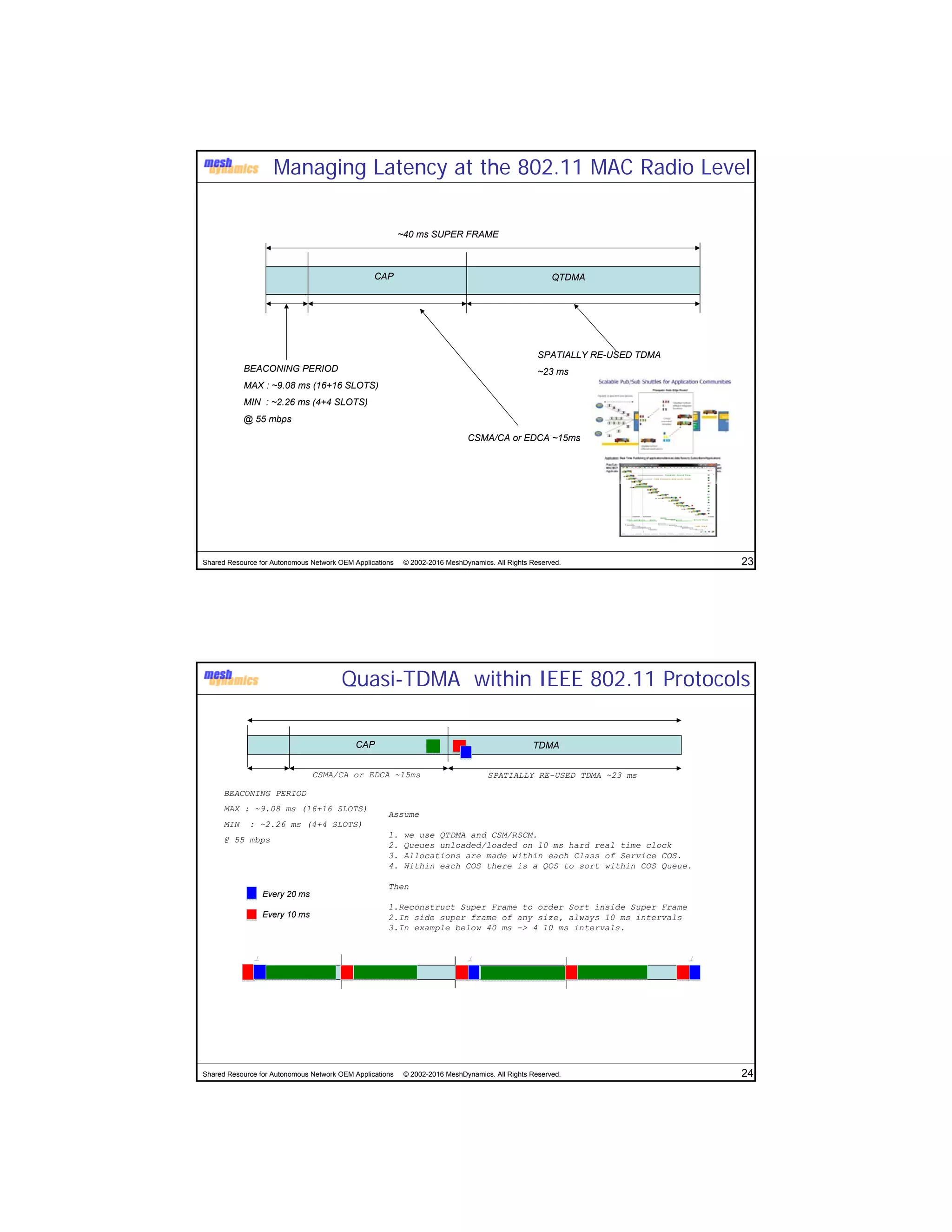
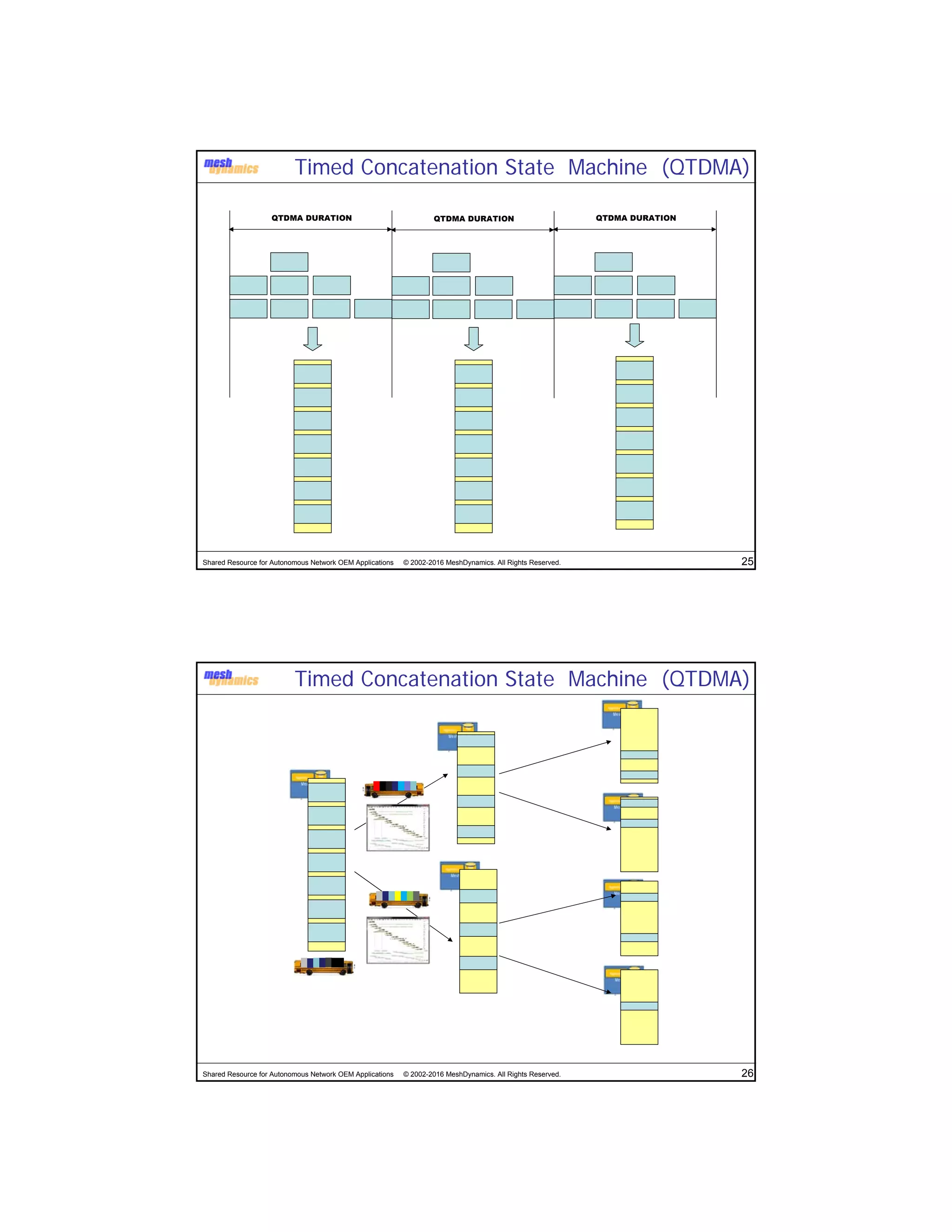
The document discusses the abstracted network, focusing on its applications in disruption-tolerant and smart networks, which utilize open-source messaging and cater to latency requirements. It emphasizes the development of specialized strategies for IoT connectivity and machine-to-machine communication, along with innovations in low-cost IC chips. Key concepts include maintaining network connections amid disruptions and integrating both legacy and modern IoT devices.