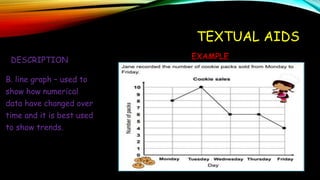
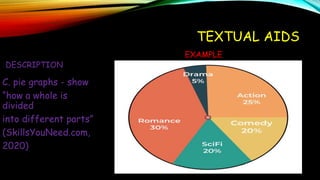
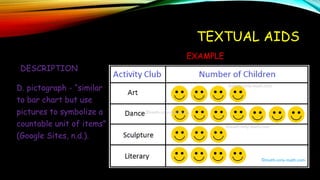
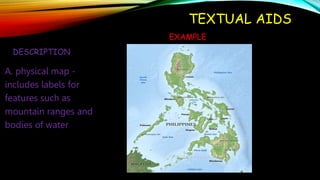
Textual aids refer to non-textual elements in a document that help readers understand and direct them to important content. This includes elements like titles, subtitles, illustrations, tables, graphs and charts. They serve two main functions - to draw attention to key ideas and provide supplemental information. Common textual aids are titles and subtitles that introduce topics, illustrations that facilitate understanding, tables that organize facts and figures, and graphs like bar graphs, line graphs and pie charts that visually represent relationships in data. Maps also act as textual aids by visually depicting physical or political features.