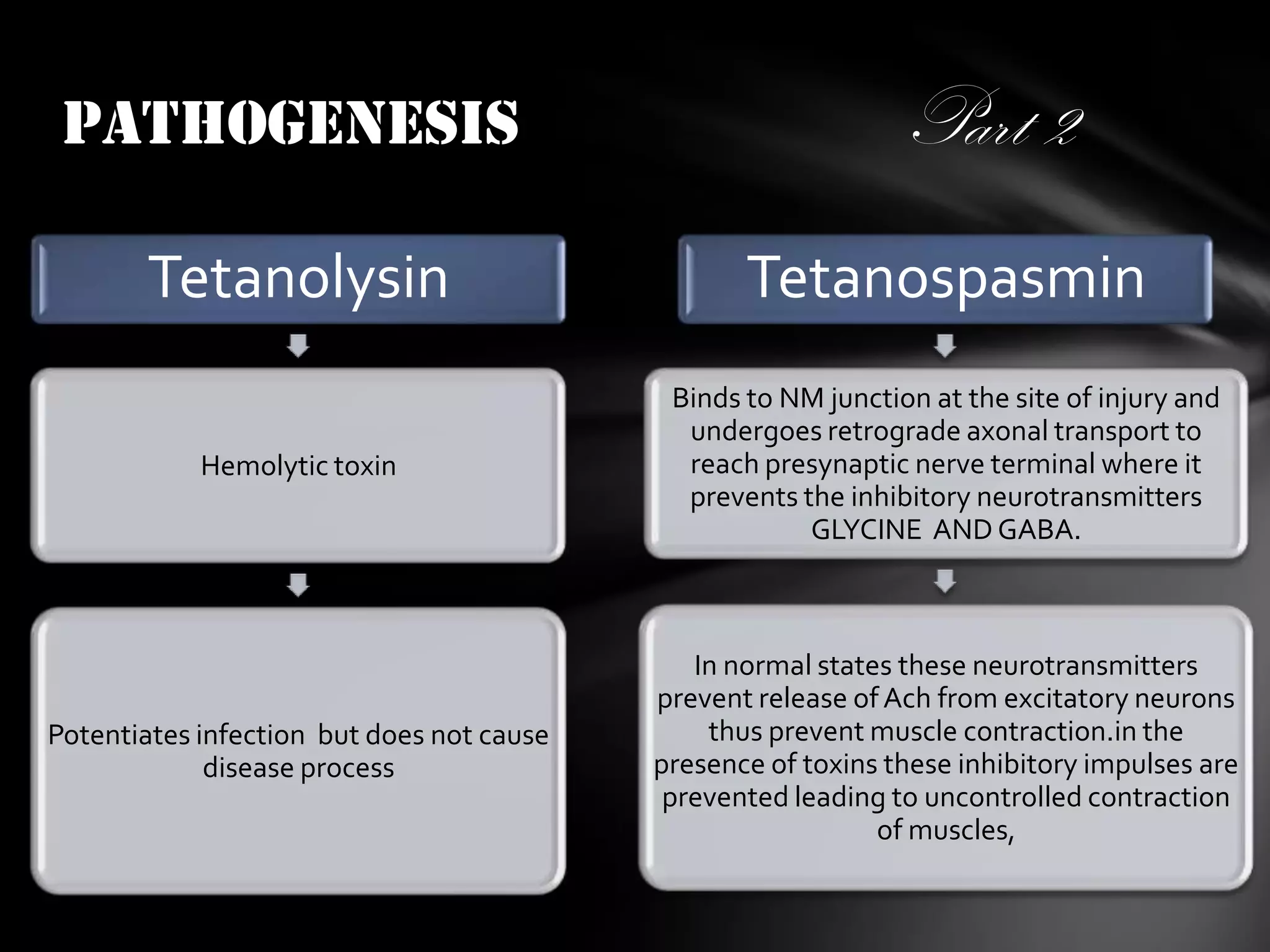
1. Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani, which produces a potent neurotoxin called tetanospasmin that prevents inhibitory neurotransmitters, causing uncontrolled muscle contractions.
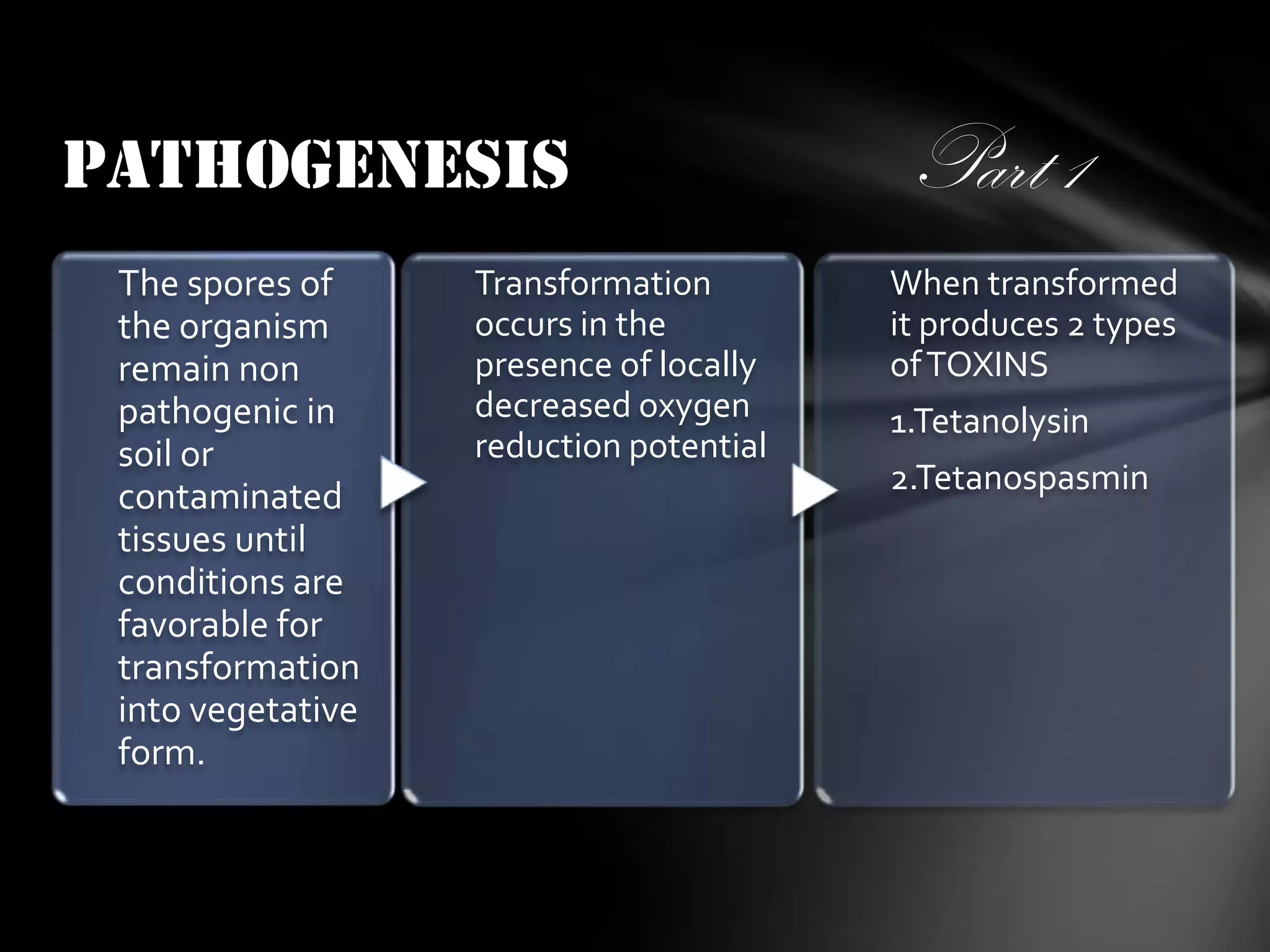
2. The spores can remain dormant in soil until transforming in an oxygen-poor environment, where the bacterium produces tetanolysin and tetanospasmin toxins. Tetanospasmin is transported to motor neurons and prevents inhibition, leading to tetanic spasms.
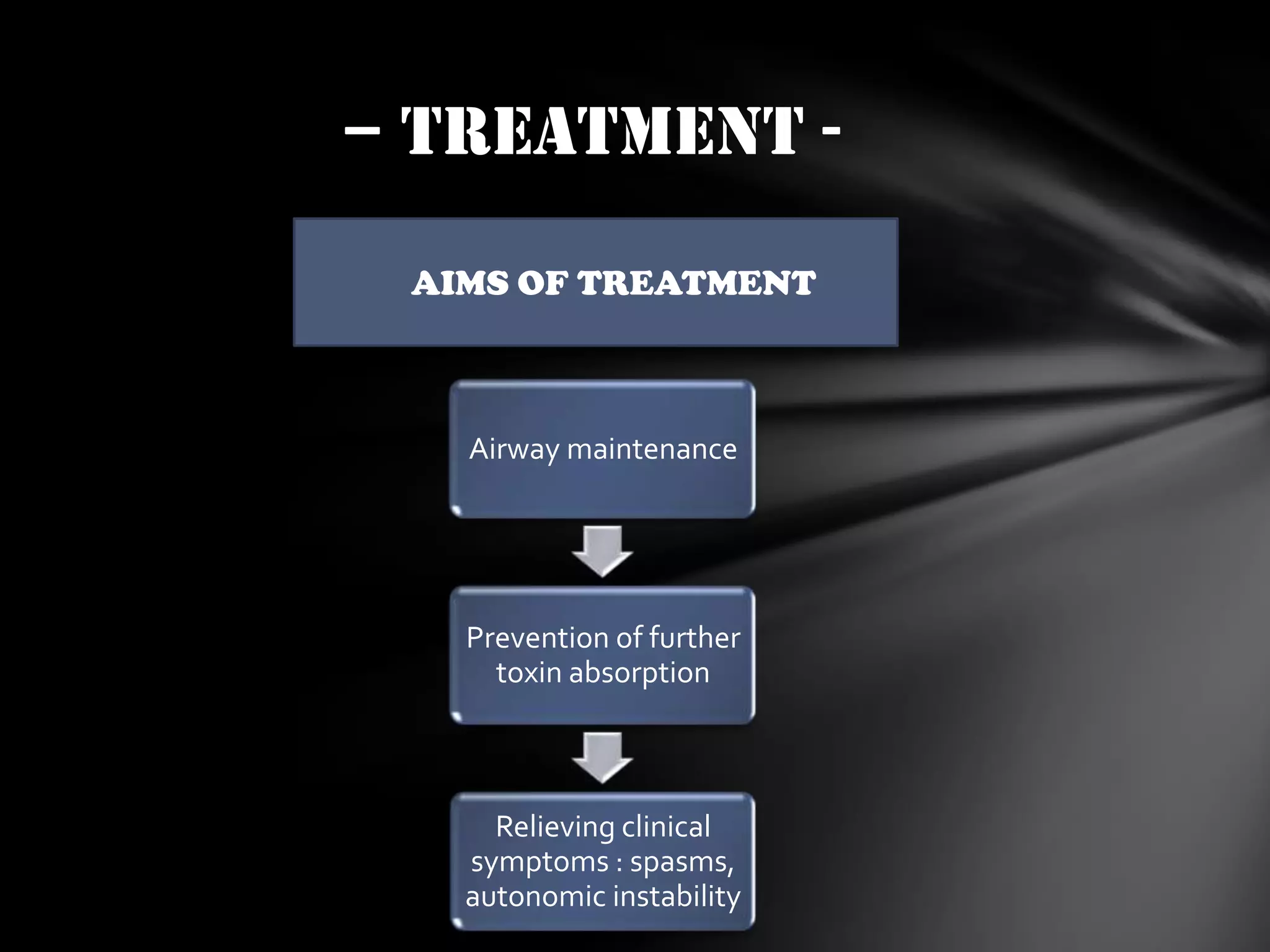
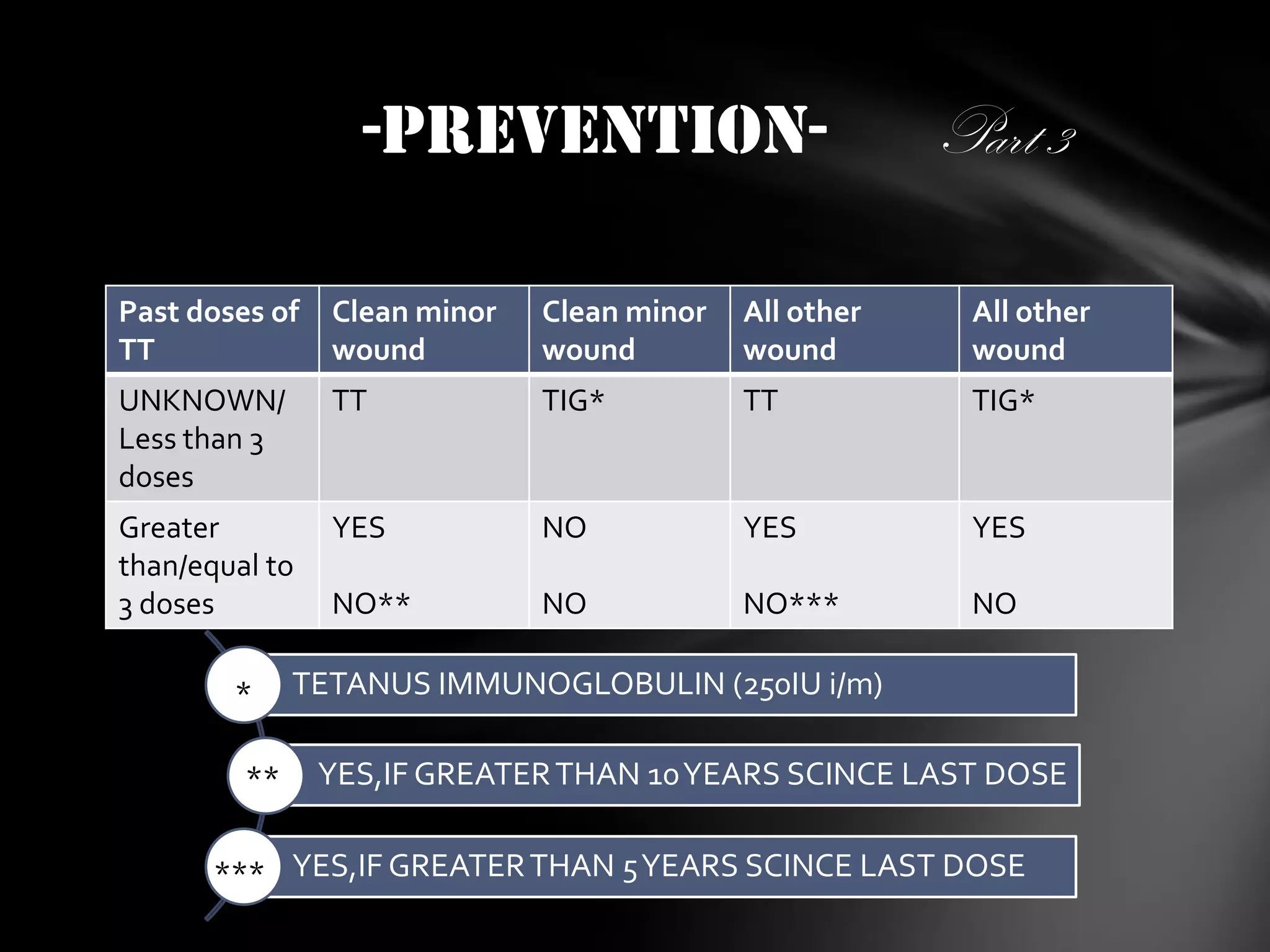
3. Treatment involves airway management, preventing further toxin absorption with antitoxin immunoglobulin, and relieving symptoms like spasms with benzodiazepines and antibiotics. Immunization with tetan