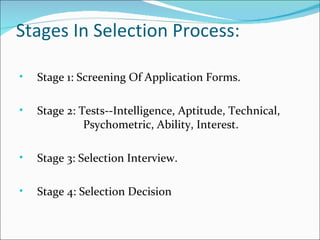
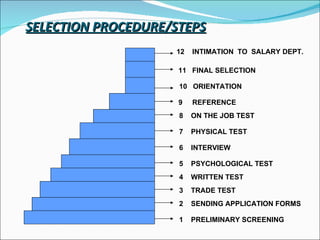
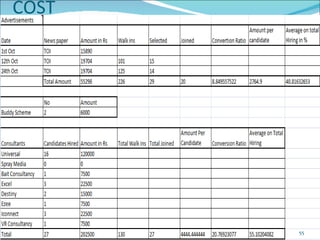
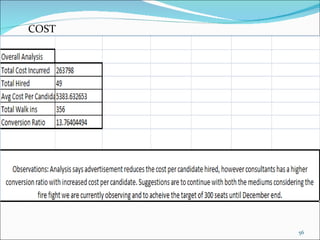
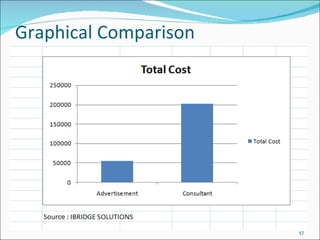
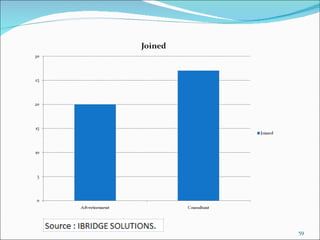
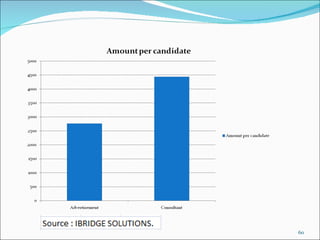
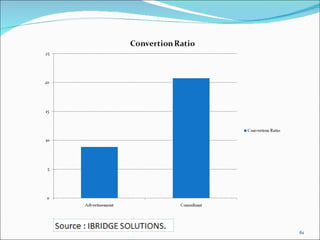
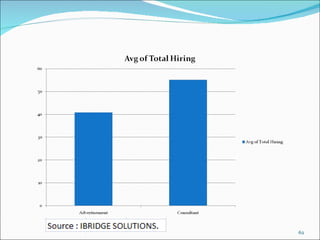
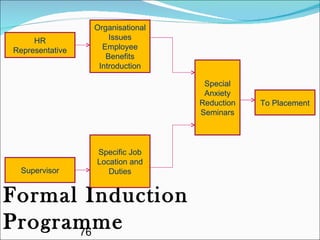
The document discusses recruitment, selection processes, methods, and psychological testing used in hiring. It defines recruitment as activities that provide applicants for open positions. Selection involves evaluating applicants' qualifications and characteristics for suitability. Common steps include interviews, tests, reference checks, and making a job offer. Psychological testing aims to objectively and validly assess personalities and competencies relevant to jobs. The document also discusses advertisements used in recruitment and the roles of recruitment consultants.











![Types Of Psychological Tests Psychological tests fall into several categories : Aptitude tests : It refers to potentiality that a person has to profit from certain kind of training. Achievement tests: It helps to measure the proficiency that a person has been able to achieve. Intelligence tests : It attempts to measure the intelligence—that is, basic ability to understand the world around you, assimilate its functioning, and apply this knowledge to enhance the quality of your life. Or, as Alfred Whitehead said about intelligence, “it enables the individual to profit by error without being slaughtered by it.”[ 1 ] Intelligence, therefore, is a measure of a potential, not a measure of what you’ve learned (as in an achievement test), and so it is supposed to be independent of culture. IQ=Mental Age/Actual Age*100 For example, a six year old child with a mental age of 6 would have an IQ of 100 (the “average” IQ score); a six year old child with a mental age of 9 would have an IQ of 150. Today, intelligence is measured according to individual deviation from standardized norms, with 100 being the average.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recruitment-selection-process-methods-and-steps-1207897252784197-9-120223234039-phpapp02/85/Recruitment-selection-process-methods-and-steps-1207897252784197-9-12-320.jpg)