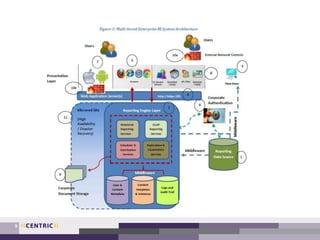
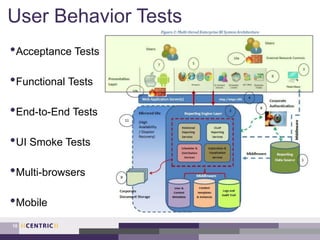
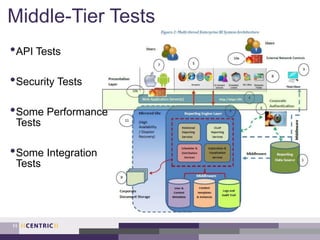
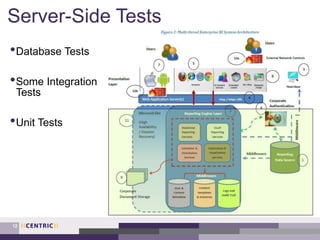
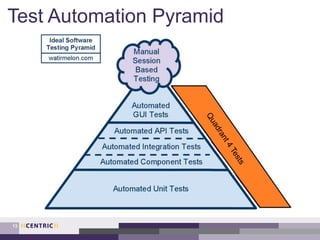
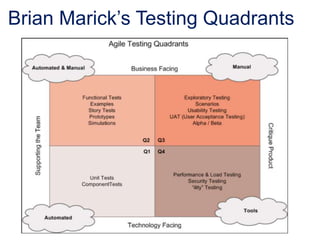
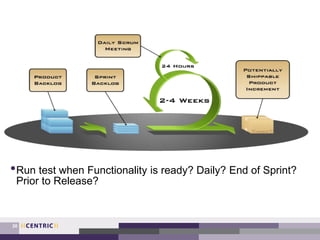
This document provides an overview of creating a testing strategy. It begins with explaining why a testing strategy is important, as testing accounts for a large portion of IT budgets. It then discusses the key questions a testing strategy should answer: what to test, where to test, when to test, how to test, and who will test.
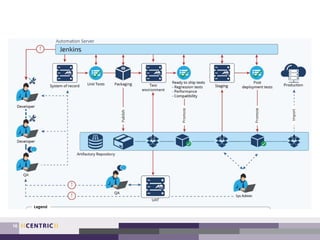
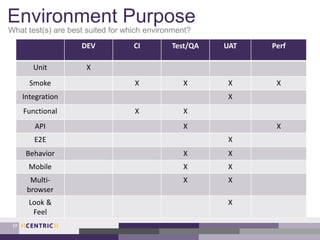
The document outlines a process for creating a testing strategy, including assessing the current state, defining a future vision, and creating a roadmap to get from the current to future state. It provides examples of what to include under each section of the strategy, such as system architecture under "what to test" and test environments under "where to test". Overall, the document provides guidance on developing a