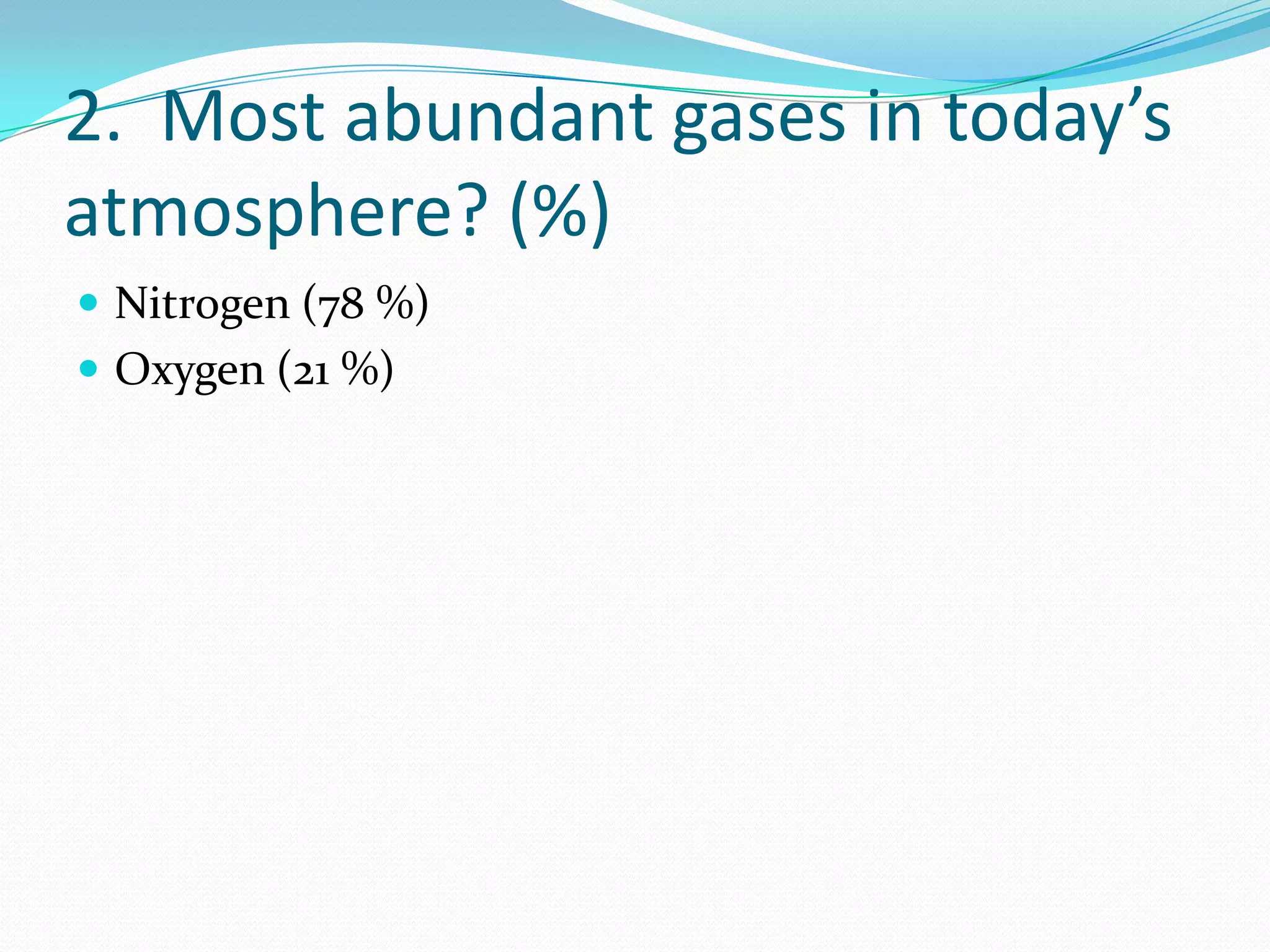
1. Water vapor is a cloud droplet. The most abundant gases in Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). The most abundant gas in the stratosphere is ozone.
2. The temperature in the stratosphere increases due to absorption of ultraviolet radiation by ozone. A "stormy and puffy" cloud is formally called a cumulonimbus cloud.
3. Solar energy reaches Earth by radiation in the form of visible light, which is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see.