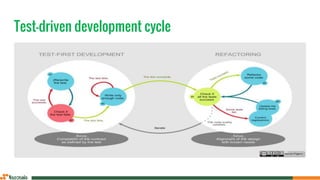
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development process involving the writing of an initial failing test case, creating the minimum code to pass it, and then refactoring the code. TDD encourages smaller, manageable units, with benefits including reduced debugging effort and self-documenting tests, while methodologies such as acceptance test-driven development (ATDD) and specification by example (SBE) enhance collaboration and understanding of requirements. Although TDD improves design and productivity, it may be inadequate for certain types of applications and can lead to a false sense of security if misapplied.