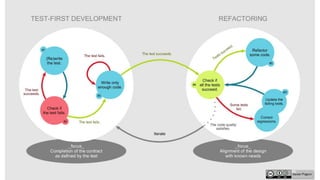
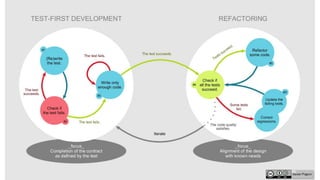
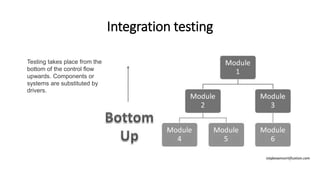
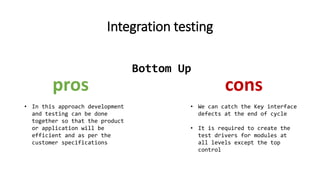
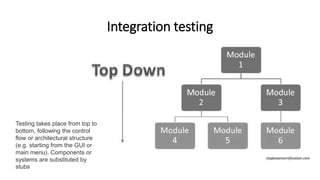
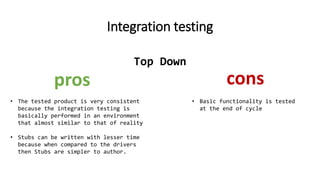
The document outlines an upcoming programming workshop that will cover various JetBrains IDEs like PyCharm, IntelliJ IDEA, and PhpStorm. It then discusses Test Driven Development (TDD), including what TDD is, the development cycle used in TDD, and benefits like encouraging simple designs and confidence. Different types of software tests are also listed like unit tests, integration tests, acceptance tests, and others. Specific testing techniques like unit testing, integration testing using bottom-up and top-down approaches, and acceptance testing are then explained at a high level. Finally, some important notes on testing like trusting tests and prioritizing maintainability are provided.