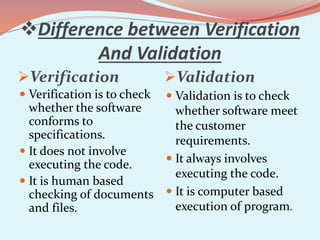
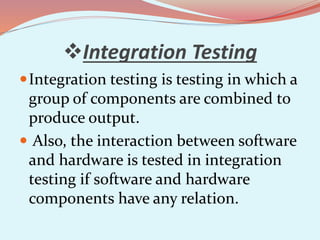
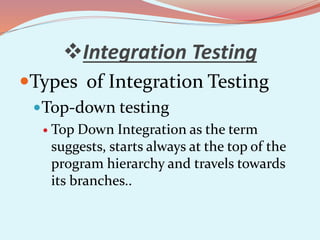
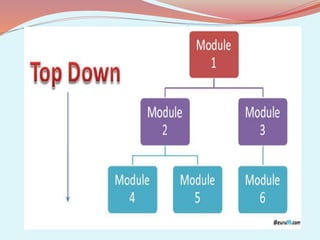
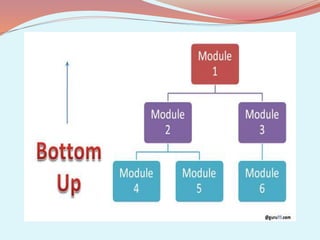
The document discusses software testing concepts like verification, validation, whitebox testing, and blackbox testing. Verification ensures the product satisfies specifications, while validation ensures it meets customer requirements. Whitebox testing uses internal knowledge to test code, while blackbox testing treats the system as a black box without internal knowledge. The document also covers different types of testing like unit, integration, and functional testing.