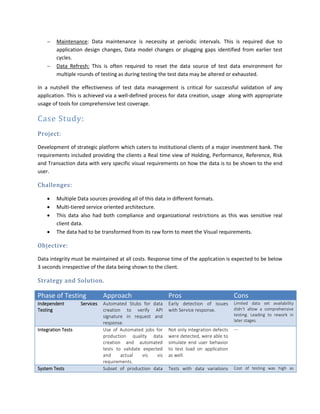
The document discusses the importance of test data management for effective continuous testing and integration in agile development, emphasizing the need for quality test data to detect defects early and optimize testing efforts. It outlines strategies for creating realistic test data, managing data requirements, and ensuring data integrity while complying with regulations. A case study highlights the challenges of integrating multiple data sources and the benefits of automated data creation in maintaining application performance and quality assurance.