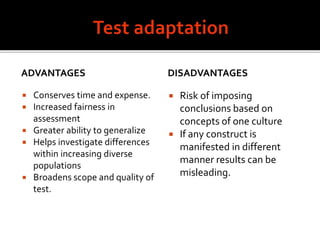
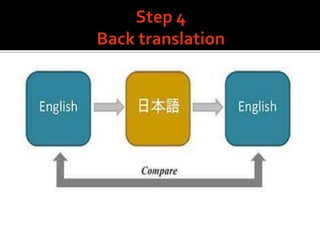
The document discusses the process of translating and adapting assessment instruments for cross-cultural studies, emphasizing the need for cultural and linguistic adjustments beyond literal translation. It outlines the advantages of adaptation, such as increased fairness and generalizability, along with disadvantages like potential misleading results due to cultural differences. The document also details the steps involved in the translation process, including expert evaluation and pilot studies to ensure the instrument's appropriateness and effectiveness in the new context.