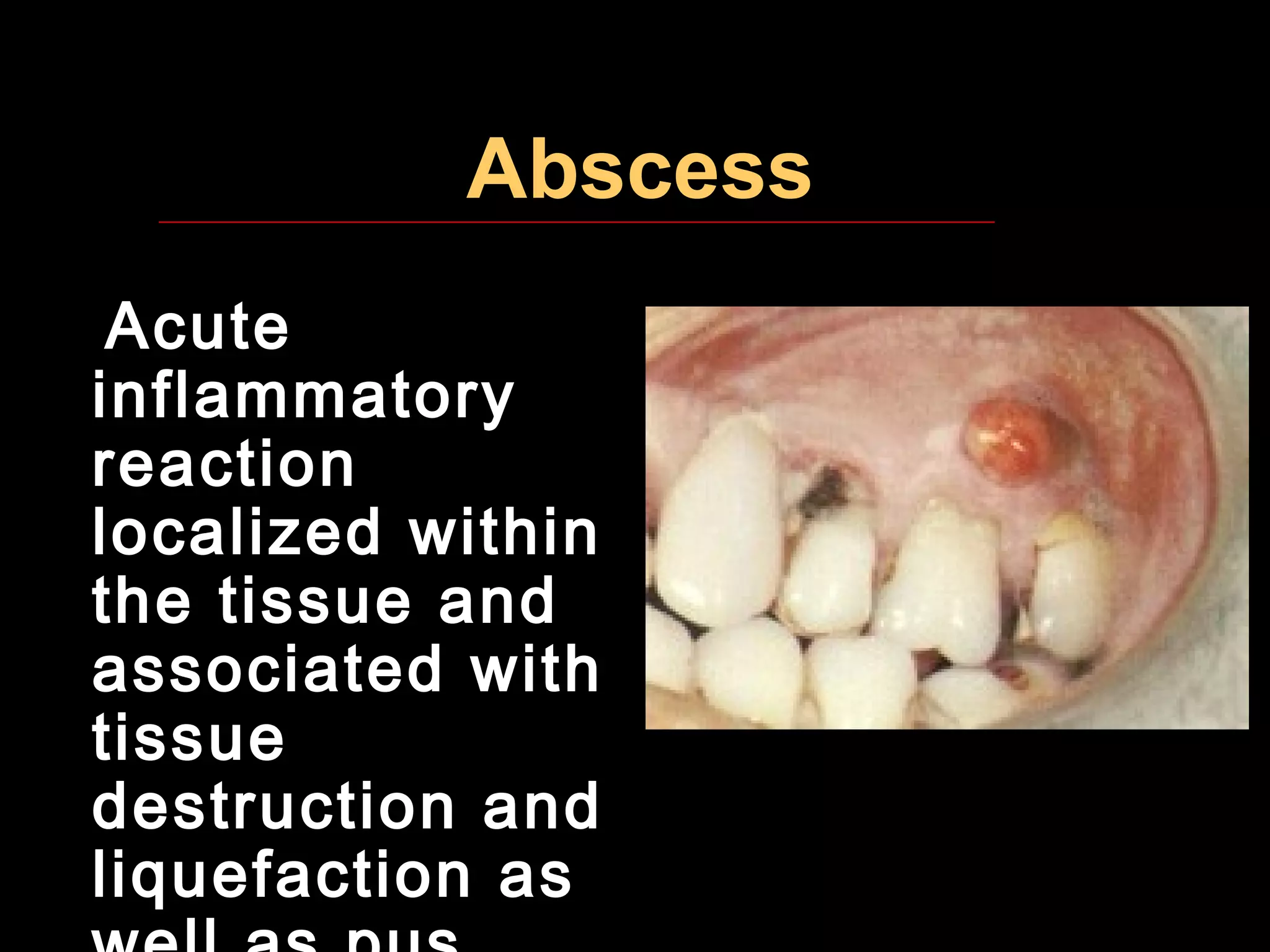
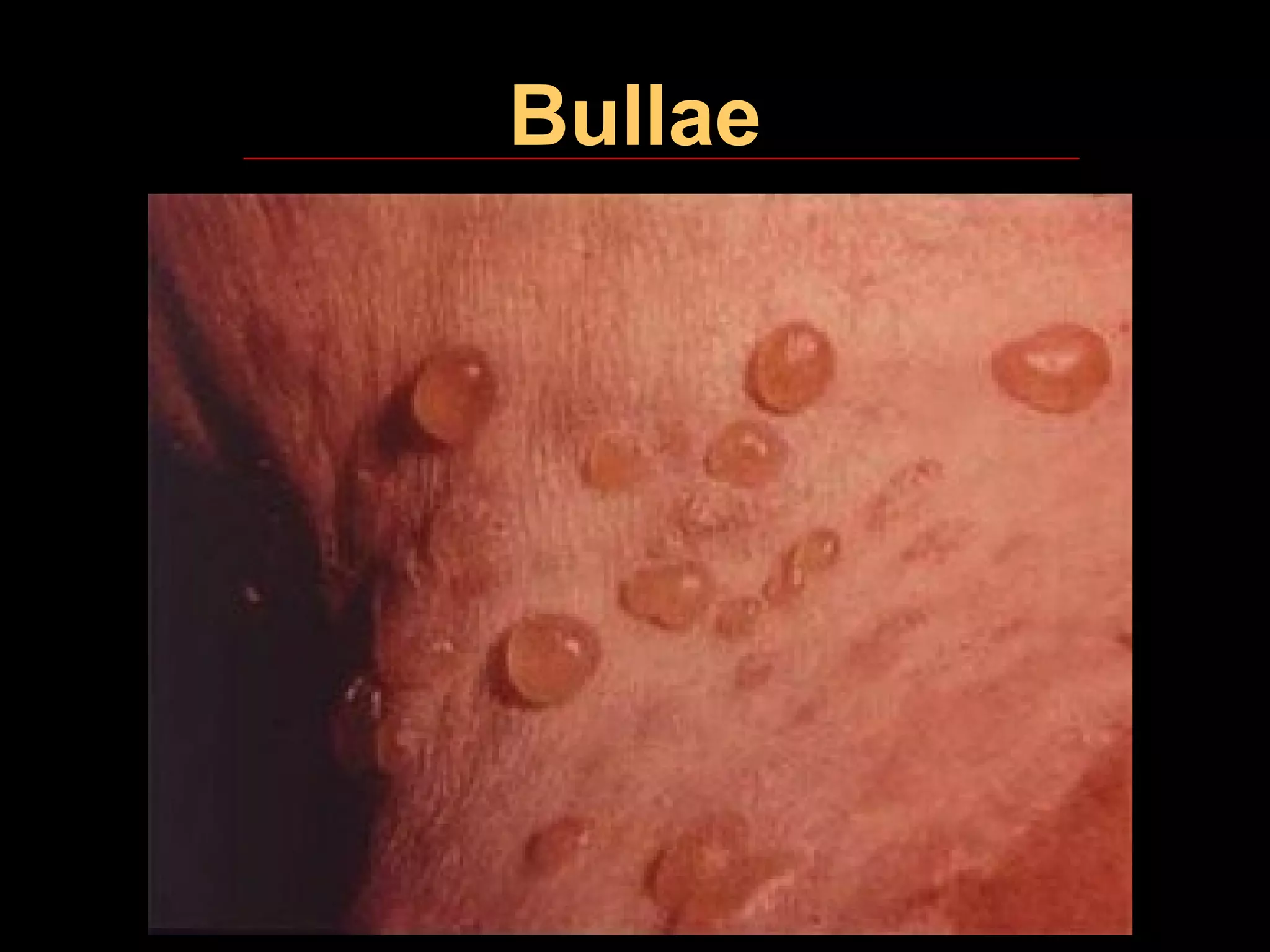
This document provides definitions and descriptions of key terminology used in oral pathology. It discusses general terms like provisional diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and final diagnosis. It also covers clinical examination terms involving inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation. Additionally, it defines histologic terms used to describe microscopic findings like hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, dysplasia and anaplasia. The document aims to provide standardized terminology for communication, documentation, description and classification in the field of oral pathology.